Monitoring Hunt groups
589
Programming Operations Guide
Monitoring Hunt groups
The Business Communications Manager system offers two ways to monitor hunt group activity.
You can use Silent Monitor (
“Setting up Silent Monitoring” on page 589
) to actively monitor
current calls or you can use the Hunt Metrics tables (
“Using Hunt group metrics” on page 591
) to
get an overview of how each hunt group is performing.
Setting up Silent Monitoring
To set up Silent Monitoring for your system:
1
Click on the keys beside
Services
,
Telephony Services
,
and
General Settings
.
2
Click on Silent Monitor.
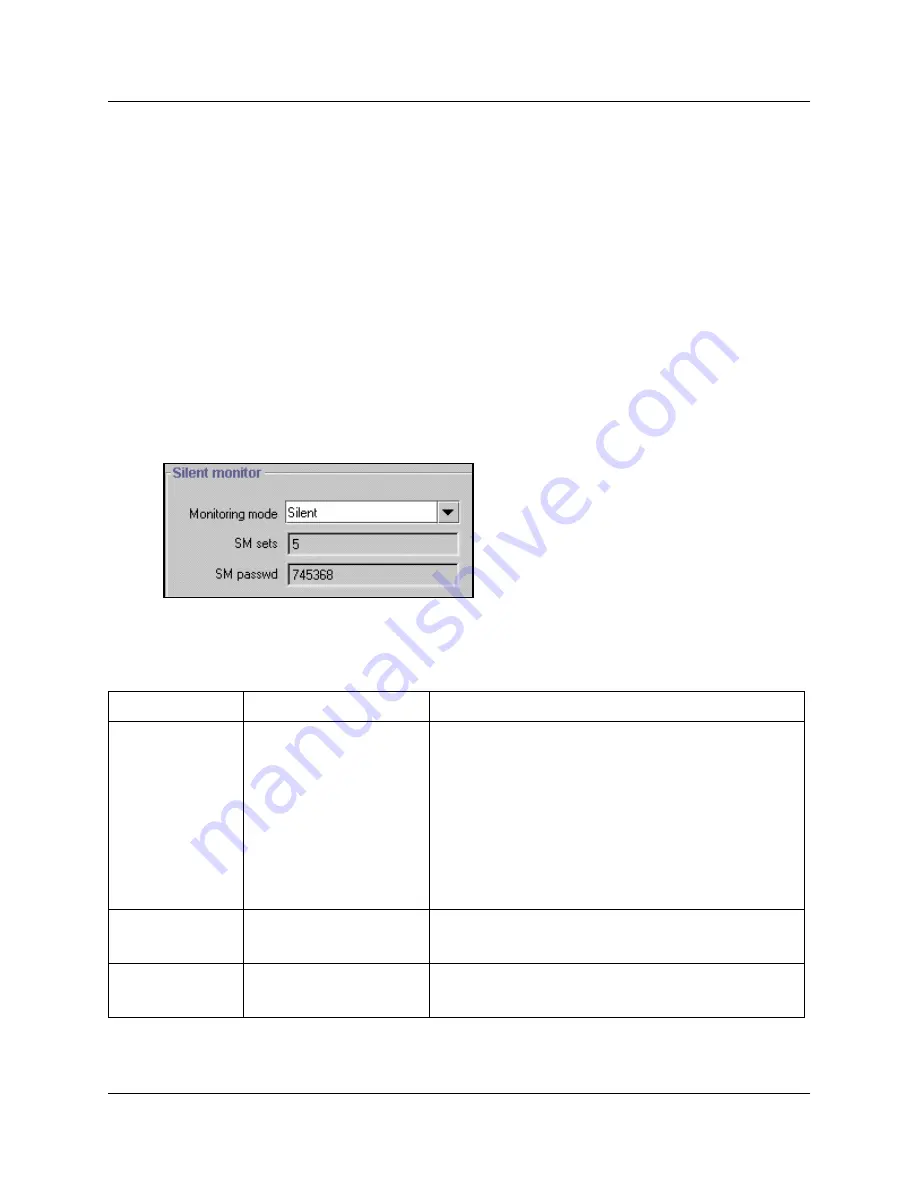
The Silent Monitor screen appears in the right frame.
Figure 206
Silent Monitoring system settings
3
The following table describes the settings that define how the silent monitor feature will work
on your system:
Table 135
Silent monitor system settings
Field
Values
Description
Monitoring mode
Silent
Non silent
Choose
Silent
if you want supervisors to be able to break into
a hunt group conversation without giving an indicator of their
presence.
Choose
Non silent
if you want the hunt group member and
the caller to hear a conference tone when a supervisor
breaks into a hunt group conversation.
Note:
Initial monitoring is muted at the supervisor set. If the
supervisor wants to speak within the conversation, a display
key on the two-line display becomes available, once the
connection is established.
The default changes based on country profile.
SM sets
1 to 30
Indicate the number of two-line telephones in your system
that you will allow to be used as supervisory telephones.
(Default: 5)
SM passwd
XXXXXX
A six-digit set that must be entered after the supervisor
presses
FEATURE
*550. To maintain system security,
change this password frequently. (Default: 745368 (SILENT))
Summary of Contents for BCM 3.7
Page 4: ...4 Software licensing N0008589 3 3...
Page 32: ...32 Contents N0008589 3 3 W 937 Index 939...
Page 46: ...46 Tables N0008589 3 3...
Page 64: ...64 How to get help N0008589 3 3...
Page 90: ...90 Manually activating Telnet N0008589 3 3...
Page 116: ...116 Delayed system restart N0008589 3 3...
Page 194: ...194 Configuring a data module N0008589 3 3...
Page 276: ...276 Setting line telco features N0008589 3 3...
Page 310: ...310 Using COS passwords N0008589 3 3...
Page 364: ...364 Enhanced 911 E911 configuration N0008589 3 3...
Page 380: ...380 Renumbering DNs N0008589 3 3...
Page 398: ...398 Saving wizard pages on your computer N0008589 3 3...
Page 458: ...458 Voice Mail settings N0008589 3 3...
Page 488: ...488 Setting system telco features N0008589 3 3...
Page 508: ...508 Other programming that affects public networking N0008589 3 3...
Page 522: ...522 PRI networking using Call by Call services N0008589 3 3...
Page 592: ...592 Monitoring Hunt groups N0008589 3 3...
Page 636: ...636 Configuring Double Density N0008589 3 3...
Page 640: ...640 Using the Network Update Wizard N0008589 3 3...
Page 666: ...666 Importing and Exporting DHCP data N0008589 3 3...
Page 722: ...722 Restarting the router N0008589 3 3...
Page 726: ...726 Important Web Cache considerations N0008589 3 3...
Page 748: ...748 Configuring an Interface with NAT N0008589 3 3...
Page 794: ...794 IPSec N0008589 3 3...
Page 818: ...818 Configuring the Policy Agent characteristics N0008589 3 3...
Page 832: ...832 Firewall rules for Business Communications Manager with Dialup interfaces N0008589 3 3...
Page 876: ...876 ISDN Programming N0008589 3 3...
Page 1004: ...1004 Index N0008589 3 3...






























