LEFT TOOL AREA AND HARDWARE CONTROL TOOLS
LSM 710 and LSM 780
Carl Zeiss
Processing Tab
Systems
130 M60-1-0025
e
02/2010
5.3.11
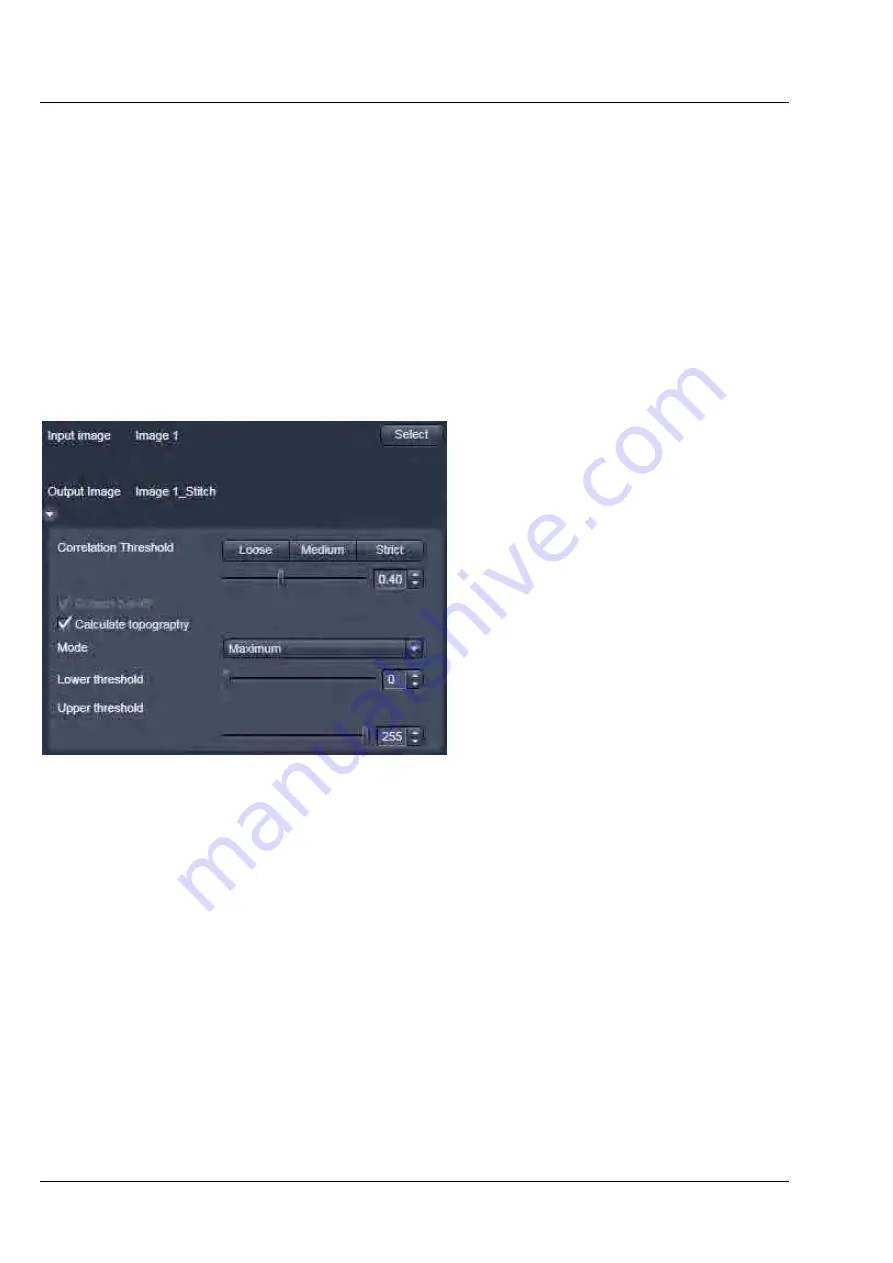
Stitch
With this function tiled images acquired with Versions of ZEN 2010 and the tiling function can be
stitched together in 2D and 3D.
Select a tiled image (or stack) with the select button.
The
correlation threshold
is defining the accuracy with which the algorithm detects similarities in the
adjacent image planes.
If a 3D tile scan image has been acquired (Tile Scan combined with Z-Stack) then additional functions for
the stitching procedure are available.
Ignore Z Correction
will in some cases reveal better results for the 3D stitch. Depending on the image
data the last step of the stitch algorithm, which makes a correction of the Z-Stacks in Z looking at the
overall image, can lead to unwanted shifts of the stacks in Z. This can be avoided when this option is
checked.
Calculate Topography
provides a
topographic image of the 3D stitched
image data. This calculation can be done
in several modes (see also section
Topography View
).
First / Last maximum
•
Select
First maximum
to calculate the
topography surface by using the first
maximum coming from the top. This
mode provides better result for
surfaces of semitransparent materials
with inclusions of higher reflectivity or
transparent multi-layers with
subsurface layers of higher signal
intensity.
•
Select
Last maximum
to calculate the
topography surface by using the last
maximum coming from the top.
First / Last threshold
•
Select
First threshold
to calculate the topography surface by using the first slice coming from the
top, where the intensity reaches the value defined by the lower intensity threshold.
•
Set the
Threshold
to define the lower and upper intensity thresholds used for calculation of the
topography surface. Use of this function is recommended to find the real surface in the case of images
with pronounced noise. All image pixels with intensity less or higher than the thresholds set are
ignored for the surface calculation.
Correct bleaching
applies a correction factor to the double-
exposed pixels. Crossfading is the only method available here and does an interpolation of the
brightness values over a number of pixels in X or Y direction. The
Correction Width
in pixels can be
adjusted.
Fig. 138
Stitch function






























