6. Translation Formats
6-40
UniSite-xpi User Manual
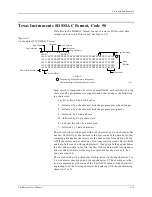
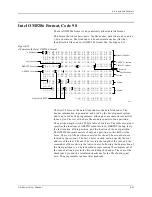
Fuse Information Fields
(L, K, F, C)
<fuse information> :: = [<default state>] <fuse list> {<fuse list>} [<fuse
checksum>]
<fuse list> : = ‘L’ <number> <delimiter> {<binary-digit> [<delimiter>]}
' * '
<fuse list> :: = ‘K’ <number> <delimiter> {<hex-digit> [<delimiter>]} ‘*’
<default state> :: = ‘F’ <binary-digit> ‘* ‘
<fuse checksum> :: = ‘C’ <hex-digit>:4 ‘* ‘
Each fuse of a device is assigned a decimal number and has two possible
states: zero, specifying a low-resistance link, or one, specifying a high
resistance link. The state of each fuse in the device is given by three fields:
the fuse list (L field or K field), the default state (F field), and the fuse
checksum (C field).
Fuse states are explicitly defined by either the L field or the K field. The
character L begins the L field and is followed by the decimal number of
the first fuse for which this field defines a state. The first fuse number is
followed by a list of binary values indicating the fuse states.
The information in the K field is the same as that of the L field except that
the information is represented by hex characters instead of binary values.
This allows more compact representation of the fusemap data. The
character K begins the K field and is followed by the decimal number of
the first fuse. The fuse data follow the fuse number and are represented
by hex characters. Each bit of each hex character represents the state of
one fuse, so each hex character represents four fuses. The most significant
bit of the first hex character following the fuse number corresponds to the
state of that fuse number. The next most significant bit corresponds to the
state of the next fuse number, etc. The least significant bit of the first hex
character corresponds to the state of the fuse at the location specified by
the fuse number plus three.
The K field supports download operations only. The K field is not part of
the JEDEC standard, but is supported by Data I/O for fast data transfer.
The L and K fields can be any length desired, and any number of L or K
fields can be specified. If the state of a fuse is specified more than once,
the last state specified replaces all previous ones for that fuse. The F field
defines the states of fuses that are not explicitly defined in the L or K
fields. If no F field is specified, all fuse states must be defined by L or K
fields.
Summary of Contents for UniSite-xpi
Page 2: ...981 0014 UniSite Programming System User Manual Also Covering Legacy UniSite Programmers ...
Page 72: ...2 Setup and Installation 2 42 UniSite xpi User Manual ...
Page 134: ...3 Getting Started 3 62 UniSite xpi User Manual ...
Page 238: ...5 Computer Remote Control 5 10 UniSite xpi User Manual ...
Page 296: ...6 Translation Formats 6 58 UniSite xpi User Manual ...
Page 402: ...Keep Current Subscription Service 6 Keep Current ...