guaranteed fail
lower
threshold
guaranteed pass
upper
threshold
guaranteed fail
1.375
4.875
22
78
f[MHz]
Clocks
149
SPNU563A – March 2018
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Architecture
2.4.6.1
Oscillator Monitor
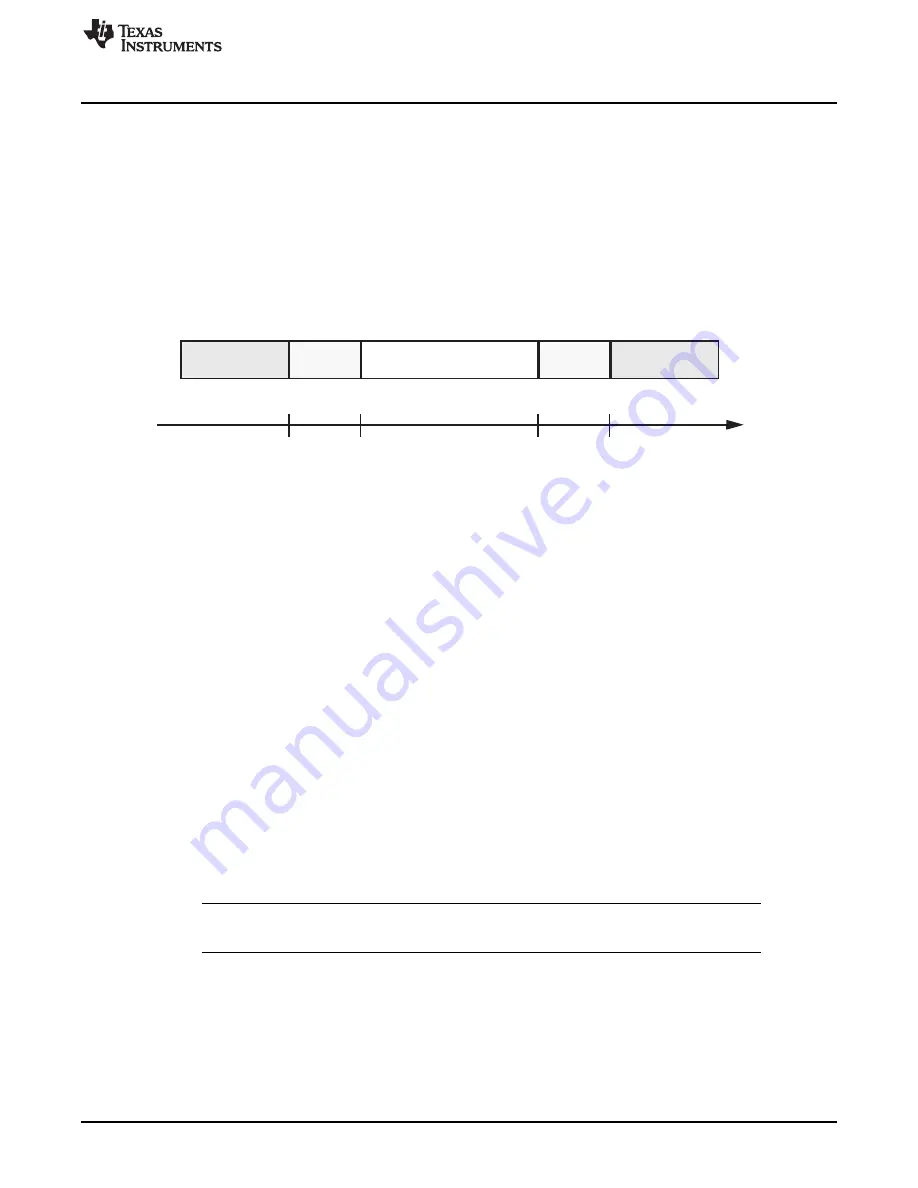
The oscillator clock frequency is monitored by a dedicated circuitry called CLKDET using the HF LPO as
the reference clock. The CLKDET flags an oscillator fail condition whenever the OSCIN frequency falls
outside of a range which is defined by the HF LPO frequency.
The valid OSCIN range is defined as a minimum of f
(HF LPO)
/ 4 to a maximum of f
(HF LPO)
× 4.
The untrimmed HF LPO frequency on this device can range from 5.5 MHz to 19.5 MHz. This results in a
valid OSCIN frequency range depicted in
The application can select the device response to an oscillator fail indication. Refer to
for more
details on the oscillator monitoring and the system response choices.
Figure 2-7. LPO and Clock Detection, Untrimmed HF LPO
2.4.6.2
PLL Slip Detector
Both the PLL macros implemented on the microcontrollers have an embedded slip detection circuit. A PLL
slip is detected by the slip detector under the following conditions:
1. Reference cycle slip, RFSLIP — the output clock is running
too fast
relative to the reference clock
2. Feedback cycle slip, FBSLIP — the output clock is running
too slow
relative to the reference clock
The device also includes optional filters that can be enabled before a slip indication from the PLL is
actually logged in the system module Global Status Register (GLBSTAT). Also, once a PLL slip condition
is logged in the system module global status register, the application can choose the device’s response to
the slip indication. Refer to
for more details on PLL slip and the system response choices.
2.4.6.3
External Clock Monitor
The microcontrollers support two terminals called ECLK1 and ECLK2 – External Clock, which are used to
output a slow frequency which is divided down from the device system clock frequency. An external circuit
can monitor the ECLK1 and/or ECLK2 frequency in order to check that the device is operating at the
correct frequency.
The frequency of the signal output on the ECLKx pin can be divided down by 1 to 65536 from the
peripheral clock (VCLK) frequency using the External Clock Prescaler Control Register (ECPCNTL) for
ECLK1 and ECPCNTL1 for ECLK2. The actual clock output on ECLK1 is enabled by setting the ECP CLK
FUN bit of the SYSPC1 control register. By default, the ECLK1 terminal is in GIO mode. ECLK2
functionality can be enabled by writing 5h to the ECP_KEY field of the ECPCNTL1 register.
NOTE:
ECLK2 is multiplexed with EMIF_CLK and ECLK2 is not a primary function after reset. User
will need to select ECLK2 to be brought out to the terminal using IOMM module.
2.4.6.4
Dual-Clock Comparators
The microcontrollers include two instances of the dual-clock comparator (DCC) module. This module
includes two down counters which independently count from two separate seed values at the rate of two
independent clock frequencies. One of the clock inputs is a reference clock input, selectable between the
main oscillator or the HF LPO in functional mode. The second clock input is selectable from among a set
of defined signals as described in
and
. This mechanism can be used to
use a known-good clock to measure the frequency of another clock.
















































