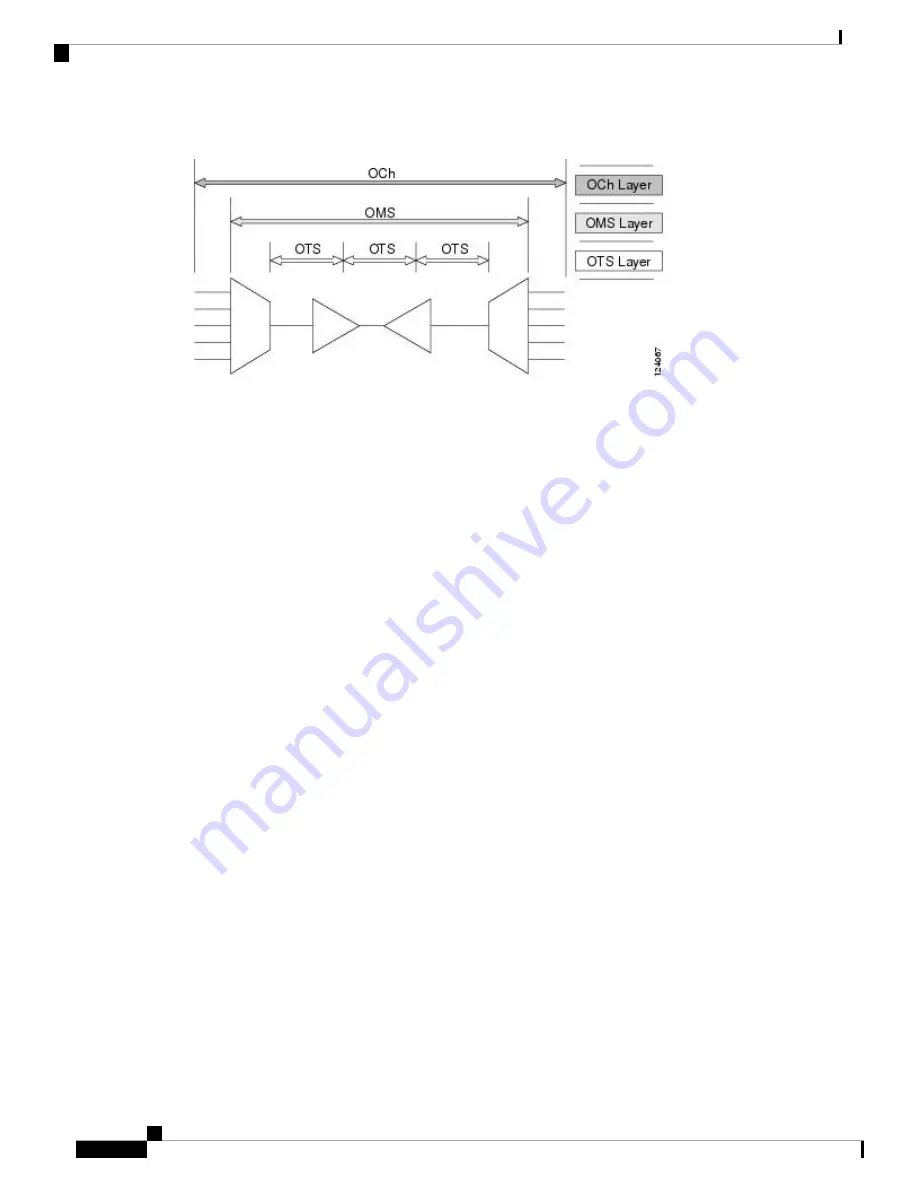
Figure 9: Optical Transport Network Layers
Optical Channel Layer
The optical channel (OCH) layer is the outermost part of the OTN and spans from client to client. The optical
channel is built as follows:
A client signal such as SONET, Gigabit Ethernet, IP, ATM, Fibre Channel, or enterprise system connection
(ESCON) is mapped to a client payload area and combined with an overhead to create the optical channel
payload unit (OPUk).
A second overhead is added to the OPUk unit to create the optical channel data unit (ODUk).
A third overhead including forward error correction (FEC) is added to the ODUk to create the optical channel
transport unit (OTUk).
A fourth overhead is added to the OTUk to create the entire OCH layer.
Optical Multiplex Section Layer
The optical multiplex section (OMS) of the OTN allows carriers to identify errors occurring within DWDM
network sections. The OMS layer consists of a payload and an overhead (OMS-OH). It supports the ability
to monitor multiplexed sections of the network, for example, the span between an optical multiplexer such as
the 32MUX-O card and an optical demultiplexer such as the 32DMX-O card.
Optical Transmission Section Layer
The optical transmission section (OTS) layer supports monitoring partial spans of a network multiplexed
sections. This layer consists of a payload and an overhead (OTS-OH). It is a transmission span between two
elements in an optical network, such as between:
• A multiplexer such as the 32MUX-O card and an amplifier such as the OPT-PRE card
• An amplifier and another amplifier, such as the OPT-BST card and the OPT-PRE card
• An amplifier such as the OPT-BST card and a demultiplexer such as the 32DMX card
Cisco NCS 2000 series Troubleshooting Guide, Release 11.0
28
General Troubleshooting
Optical Channel Layer
















































