Appendix - 123
MELSEC-Q
APPENDICES
FLS SIGNAL (forward limit signal)
This is the input signal that notifies the user
that the limit switch (b contact configuration,
normally ON) installed at the upper limit of the
positioning control enabled range has been
activated.
The positioning operation stops when the FLS
signal turns OFF (non-continuity).
G CODE
These are standardized (coded) 2-digit
numerical values (00 to 99) designating
various control functions of the NC module.
Also called G functions.
Example :
G01 Linear
interpolation
G02 Circular interpolation CW (clockwise)
G04 Dwell
G28 OPR
G50 Max. spindle speed setting
GAIN
The changing of the ratio between two values
having a proportional relation. Seen on a
graph, the changing of the incline of the
characteristics.
13
10
2
10
Raising
the gain
Output
Lowering
the gain
Input
For example, when 10 is output for an input of
10, the output can be changed to 12, 5, etc.,
by changing the gain.
GD
2
The inertia moment. The sum total of the mass
(dm) of each small area configuring an object
multiplied by the square of the distance (r) of
each of those areas from a given straight line.
The relation with I = r
2
dmGD
2
is given by 4gI,
with "g" being gravitational acceleration.
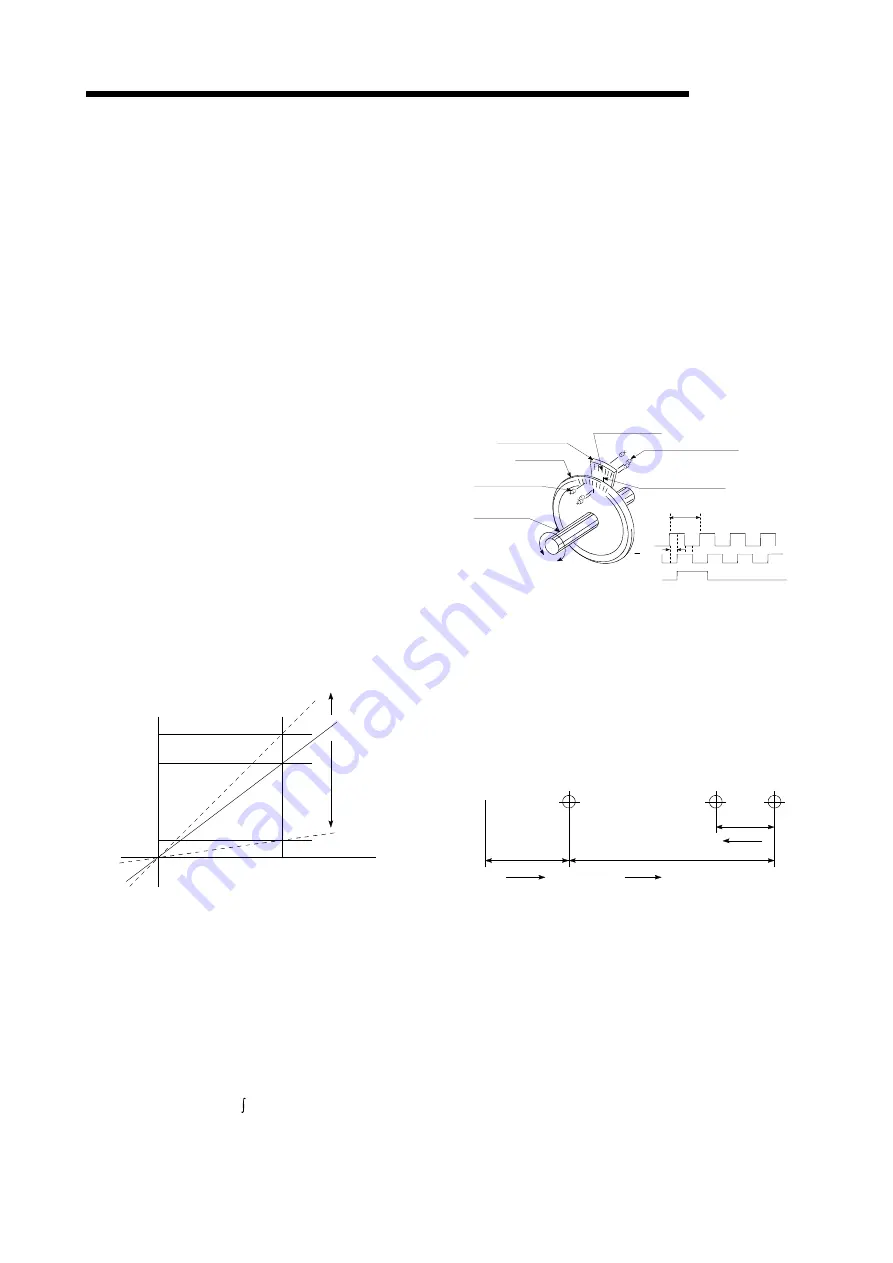
INCREMENTAL ENCODER
A device that simply outputs ON/OFF pulses
by the rotation of the axis. 1-phase types
output only A pulses, and do not indicate the
axis rotation direction. 2-phase types output
both A and B pulse trains, and can judge the
rotation direction. The direction is judged to be
forward if the B pulse train turns ON when A is
ON, and judged to be reverse if A turns ON
when B is ON. There is also another type of
incremental encoder with a zero signal. The
most commonly used incremental encoders
output between 100 and 10,000 pulses per
axis rotation. Refer to "ENCODER".
A
B
A
Z
B
1
4
A signal slit
B signal slit
Slit disk
Light-emitting diode
Phototransistor
Zero signal slit
Rotating axis
1 pitch
pitch
Zero signal
1 pulse per axis rotation
Output waveform 2-phase + OP output
INCREMENTAL SYSTEM
The current value is 0 in this system. Positions
are expressed by the designated direction and
distance of travel. Also called the relative
address system. This system is used in fixed-
feed, etc. Compare ABSOLUTE SYSTEM.
No.1
No.2
No.3
0
0
0
Stop
Left
Right
Right No. 2 is several millimeters
to the right of No. 1.
INERTIA
The property of an object, when not being
affected by external forces, where it tries to
maintain its current condition. The inertia
moment.
Summary of Contents for Melsec-Q QD75D1
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...A 20 MEMO ...
Page 24: ...MEMO ...
Page 41: ...1 17 MELSEC Q 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO ...
Page 48: ...1 24 MELSEC Q 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO ...
Page 60: ...2 12 MELSEC Q 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO ...
Page 137: ...5 33 MELSEC Q 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO ...
Page 232: ...5 128 MELSEC Q 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO ...
Page 252: ...6 20 MELSEC Q 6 SEQUENCE PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL ...
Page 253: ...6 21 MELSEC Q 6 SEQUENCE PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL ...
Page 278: ...6 46 MELSEC Q 6 SEQUENCE PROGRAM USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO ...
Page 292: ...MEMO ...
Page 436: ...9 120 MELSEC Q 9 MAJOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO ...
Page 464: ...10 28 MELSEC Q 10 HIGH LEVEL POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO ...
Page 638: ...14 24 MELSEC Q 14 DEDICATED INSTRUCTIONS MEMO ...
Page 647: ...15 9 MELSEC Q 15 TROUBLESHOOTING MEMO ...
Page 686: ...15 48 MELSEC Q 15 TROUBLESHOOTING MEMO ...
Page 839: ...Appendix 153 MELSEC Q APPENDICES 6 QD75D4N 90 23 27 4 12 98 4 46 Unit mm ...
Page 840: ...Appendix 154 MELSEC Q APPENDICES 7 QD75P1 QD75P2 QD75P4 27 4 23 98 90 4 46 unit mm ...
Page 841: ...Appendix 155 MELSEC Q APPENDICES 8 QD75D1 QD75D2 QD75D4 27 4 23 90 12 98 4 46 unit mm ...
Page 842: ...Appendix 156 MELSEC Q APPENDICES MEMO ...
Page 857: ......
Page 858: ......















































