146
4.5.10
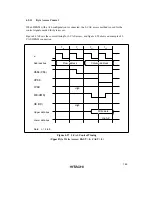
Wait Control
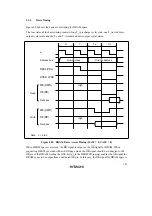
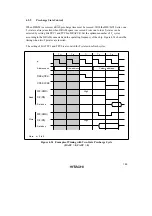
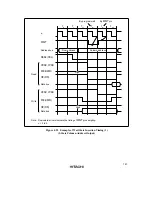
There are two ways of inserting wait states in a DRAM access cycle: (1) program wait insertion
and (2) pin wait insertion using the
WAIT
pin.
Wait states are inserted to extend the
CAS
assertion period in a read access to DRAM space, and
to extend the write data setup time relative to the falling edge of
CAS
in a write access.
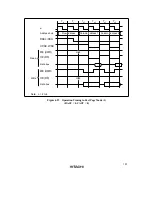
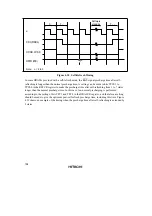
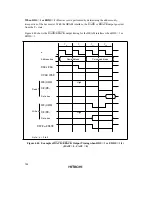
Program Wait Insertion: When the bit in ASTCR corresponding to an area designated as DRAM
space is set to 1, from 0 to 7 wait states can be inserted automatically between the T
c1
state and T
c2
state, according to the settings in registers WTCRA and WTCRB.
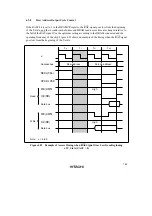
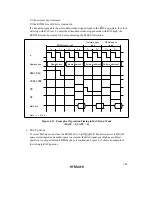
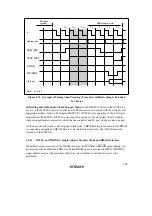
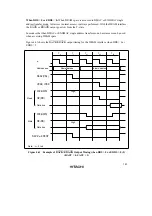
Pin Wait Insertion: When the WAITE bit in the BCR register is set to 1 and the ASTCR bit is set
to 1, wait input by means of the
WAIT
pin is enabled. When DRAM space is accessed in this
state, a program wait (T
w
) is first inserted. If the
WAIT
pin is low at the falling edge of ø in the
last T
c1
or T
w
state, another T
w
state is inserted. If the
WAIT
pin is held low, T
w
states are inserted
until it goes high.
Figures 4.25 and 4.26 show examples of wait state insertion timing in the case of 2-state and 3-
state column address output cycles.
Summary of Contents for H8S/2670
Page 5: ......
Page 9: ......
Page 199: ...182 ...
Page 361: ...344 ...
Page 393: ...376 ...
Page 647: ...630 ...