Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM002E-EN-P - February 2018
77
Connector Data and Feature Descriptions
Chapter 4
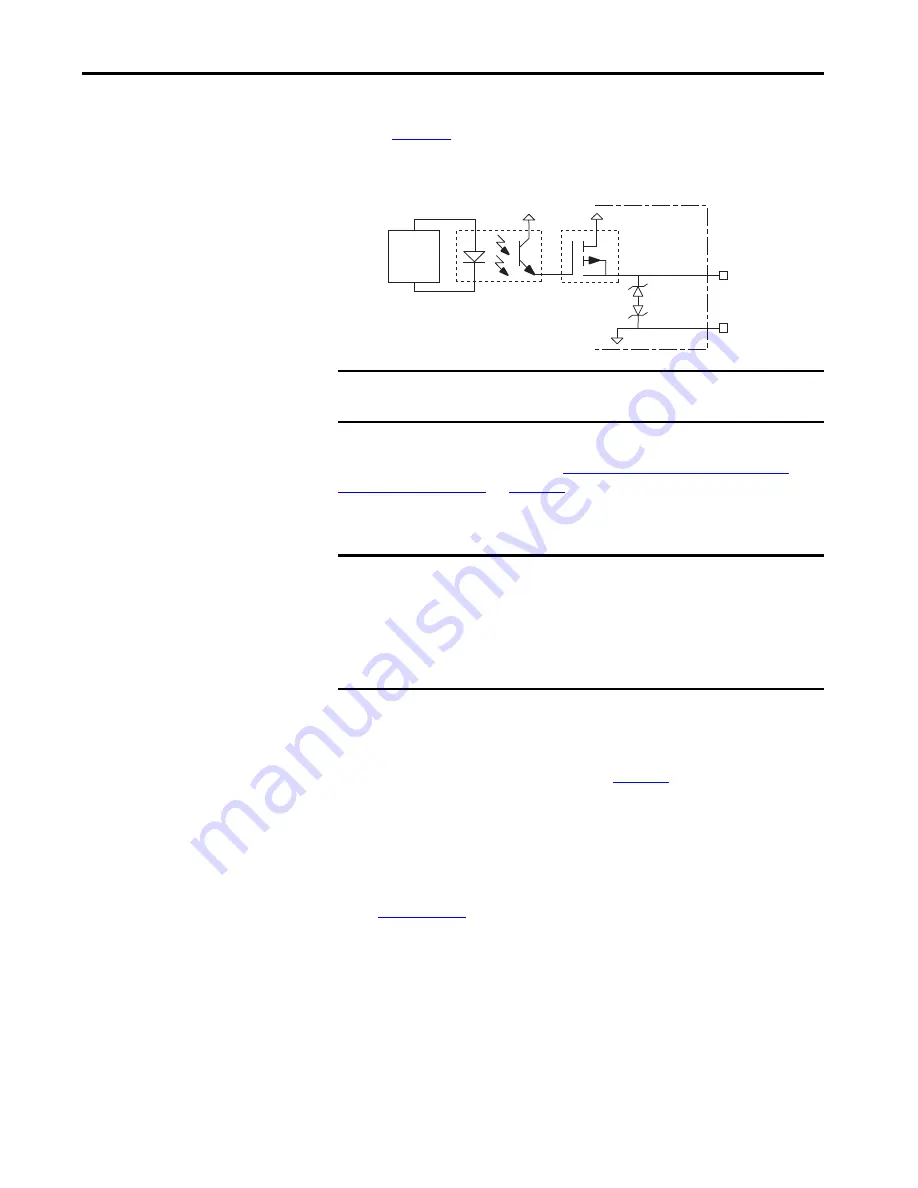
Two connections (BC-1 and BC-2) are required for the motor brake output
(refer to
). Connections are rated for 2.0 A @ +24V (dual-axis
inverters) and 5.0 A @ +24V (single-axis inverters).
Figure 44 - Motor Brake Circuit
Control of the solid-state relay to release the motor brake is configurable in the
Logix Designer application (refer to
Configure SPM Motor Closed-loop
). An active signal releases the motor
brake. Turn-on and turn-off delays are specified by the
MechanicalBrakeEngageDelay and MechanicalBrakeReleaseDelay settings.
These steps provide one method you can use to control a brake.
1. Wire the mechanical brake according to the appropriate interconnect
diagram in Appendix A beginning on
2. Enter the MechanicalBrakeEngageDelay and Mechanical
BrakeReleaseDelay times in the Logix Designer application.
Refer to Axis Properties>Parameter List. The delay times must be from
the appropriate motor family brake specifications table in the Kinetix
Rotary Motion Specifications Technical Data, publication
3. Use the drive stop-action default setting (Current Decel & Disable).
Refer to Axis Properties>Actions>Stop Action in the Logix Designer
application.
4. Use the motion instruction Motion Axis Stop (MAS) to decelerate the
servo motor to 0 rpm.
5. Use the motion instruction Motion Servo Off (MSF) to engage the
brake and disable drive.
MBRK+ (BC-1)
MBRK– (BC-2)
24V PWR
24V COM
INT PWR
Kinetix 5700
Servo Drive
Control
Board
Inductive
Energy
Clamp
IMPORTANT
Motor holding-brake switching frequency must not exceed 10 cycles/
min.
IMPORTANT
Holding brakes that are available on Allen-Bradley® rotary motors are
designed to hold a motor shaft at 0 rpm for up to the rated brake-
holding torque, not to stop the rotation of the motor shaft, or be used as
a safety device.
You must command the servo drive to 0 rpm and engage the brake only
after verifying that the motor shaft is at 0 rpm.






























