Image Optimization 5-89
5.13.5 Contrast Imaging QA
CAUTION:
Contrast Imaging QA images are provided for reference only, not for
confirming a diagnosis.
Contrast Imaging QA adopts time-intensity analysis to obtain perfusion quantification information of
velocity flow. This is usually performed on both suspected tissue and normal tissue to get specific
information of the suspected tissue.
1. Perform image scanning, freeze the image and select a range of images for analysis; or select a
desired cine loop from the stored images.
NOTE: in case of inaccurancy of the data, do not adjust the depth and the pan-zoom when saving
the cine.
2. Tap [Contrast QA] on the touch screen page to activate the function.
3. Mark out the interested part (ROI).
If necessary, perform curve fitting on the time-intensity curve.
4. Analyze the parameters of the curve, or perform B measurement.
5. Save the curved image, export the data and do parameter analysis.
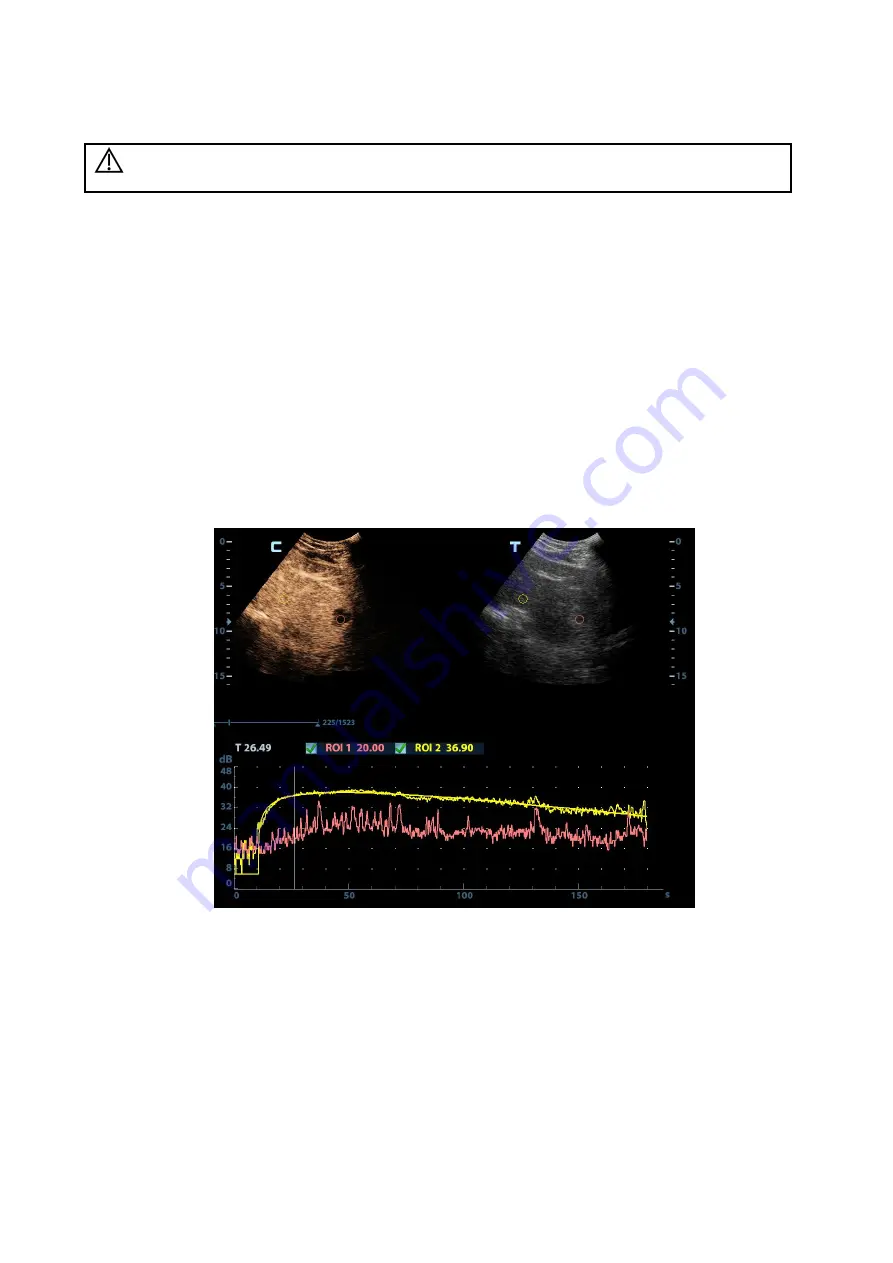
5.13.5.1 Contrast QA Screen
(For reference only)
1---Contrast cineloop window
Sample area: indicates sampling position of the analysis curve. The sample area is color-coded, 8
(maximum) sample areas can be indicated.
2---B Cineloop window
Sample areas are linked in the contrast cineloop window and B cineloop window.
3---Time-intensity curve
Y axis represents the intensity (unit: dB), while X axis represents the time (unit: s).
Frame marker: a white line that is perpendicular to the X axis, can be moved horizontally left to
right (right to left) by rolling the trackball.
1
2
3






























