E70 Series Instruction Manual
6.6 Absolute Position Setting Screen
I - 399
(Note 7) Automatic initialization cannot be started in the following cases. The operation message "Can't start" will appear
if starting is attempted.
- When "#0 Absolute posn set" is not set.
- When the "#2 Zero-P" setting is inappropriate.
- When "#2055 pushf" is not set.
- When "Z71 Abs encoder failure 0005" has occurred.
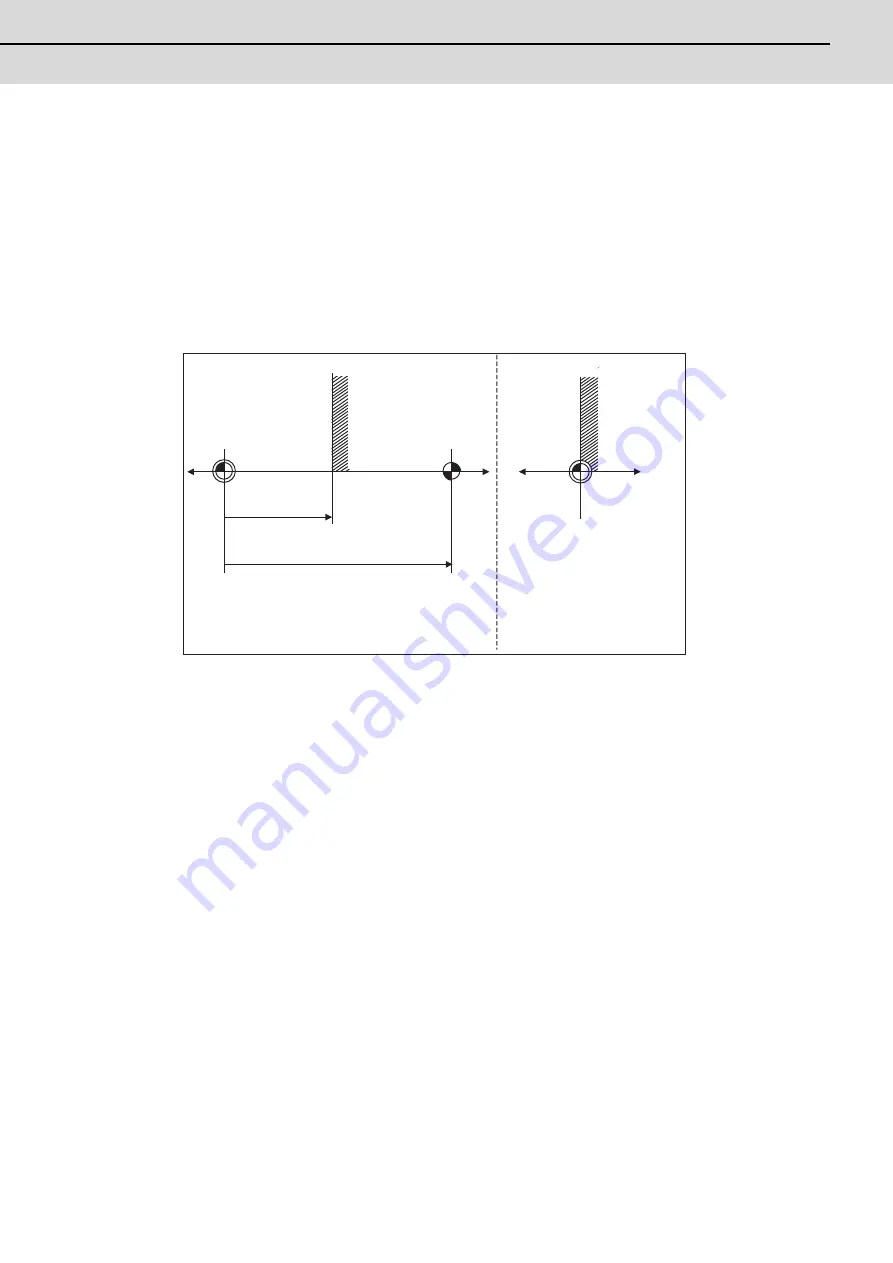
In the above cases, if the "#2 Zero-P" setting is inappropriate, this means that the relation of "#2 Zero-P" and
"#2037 G53ofs" is inappropriate. That is, if "#2 Zero-P" is smaller than the "#2037 G53ofs", the machine end
stopper will be located between the basic machine coordinate system zero point and reference position; this
disables automatic initialization. (Refer to the following left figure.)
If "#2 Zero-P " is set to "0", the machine end stopper direction is unpredictable; this also disables automatic
initialization. (Refer to the following right figure.)
Machine end stopper
(Mechanical basic
position)
Machine end
stopper
(Mechanical
basic position)
Looking from the basic machine coordinate system zero point,
the reference position is located far beyond the machine end
stopper, thus the reference position return cannot be carried out.
#2037 "G53ofs"
Basic machine coordinate
system zero point
Basic machine coordinate
system zero point
"#2 Zero-P"
Reference position
If the "#2 Zero-P" setting is "0", the
basic machine coordinate system
zero point is located on the machine
end stopper.
The direction of axis movement is
thus unpredictable.
Summary of Contents for E70 Series
Page 1: ......
Page 3: ......
Page 9: ......
Page 11: ......
Page 13: ......
Page 15: ......
Page 24: ...I SCREEN OPERATIONS ...
Page 25: ......
Page 26: ...I 1 1 Operating the Setting and Display Unit ...
Page 57: ...1 Operating the Setting and Display Unit MITSUBISHI CNC I 32 ...
Page 58: ...I 33 2 Monitor Screens ...
Page 139: ...2 Monitor Screens MITSUBISHI CNC I 114 ...
Page 140: ...I 115 3 Setup Screens ...
Page 232: ...I 207 4 Edit Screens ...
Page 314: ...I 289 5 Diagnosis Screens ...
Page 355: ...5 Diagnosis Screens MITSUBISHI CNC I 330 ...
Page 356: ...I 331 6 Maintenance Screens ...
Page 436: ...II MACHINE OPERATIONS ...
Page 437: ......
Page 439: ...MITSUBISHI CNC II 2 ...
Page 440: ...II 3 1 Operation State ...
Page 444: ...II 7 2 Indicator Lamps ...
Page 446: ...II 9 3 Reset Switch and Emergency Stop Button ...
Page 448: ...II 11 4 Operation Mode ...
Page 456: ...II 19 5 Operation Panel Switches in Operation Mode ...
Page 460: ...II 23 6 Operation Panel Switch Functions ...
Page 495: ...6 Operation Panel Switch Functions MITSUBISHI CNC II 58 ...
Page 496: ...II 59 7 Other Functions ...
Page 509: ...7 Other Functions MITSUBISHI CNC II 72 ...
Page 510: ...III MAINTENANCE ...
Page 511: ......
Page 512: ...III 1 1 Daily Maintenance and Periodic Inspection and Maintenance ...
Page 515: ...1 Daily Maintenance and Periodic Inspection and Maintenance MITSUBISHI CNC III 4 ...
Page 516: ...III 5 2 Hardware Replacement Methods ...
Page 531: ...2 Hardware Replacement Methods MITSUBISHI CNC III 20 ...
Page 532: ...IV APPENDIXES ...
Page 533: ......
Page 534: ...IV 1 Appendix 1 List of Function Codes ...
Page 536: ...IV 3 Appendix 2 Table of Command Value Ranges ...
Page 543: ...Appendix 2 Table of Command Value Ranges MITSUBISHI CNC IV 10 ...
Page 544: ...IV 11 Appendix 3 Circular Cutting Radius Error ...
Page 546: ...IV 13 Appendix 4 Registering Editing the Fixed Cycle Program ...
Page 561: ...Appendix 4 Registering Editing the Fixed Cycle Program MITSUBISHI CNC IV 28 ...
Page 562: ...IV 29 Appendix 5 RS 232C I O Device Parameter Setting Examples ...
Page 564: ...IV 31 Appendix 6 Explanation of Alarms ...
Page 678: ...IV 145 Appendix 7 Operation Messages ...
Page 699: ...Appendix 7 Operation Messages MITSUBISHI CNC IV 166 ...
Page 700: ...IV 167 Appendix 8 User Parameters ...
Page 777: ...Appendix 8 User Parameters MITSUBISHI CNC IV 244 ...
Page 782: ......















































