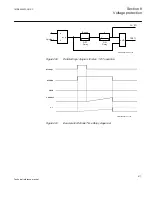
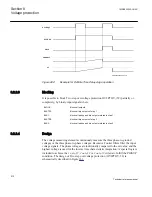
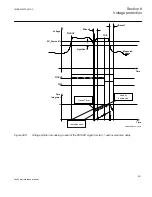
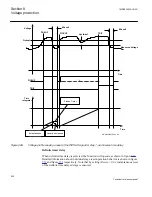
8.2.2.2
Time delay
The time delay for the two steps can be either definite time delay (DT) or inverse time
delay (TOV). For the inverse time delay four different modes are available:
•
inverse curve A
•
inverse curve B
•
inverse curve C
•
customer programmable inverse curve
The type A curve is described as:
t
TD
V
Vpickup
Vpickup
=
−
>
>
EQUATION1625 V2 EN
(Equation 125)
The type B curve is described as:
t
TD
V
Vpickup
Vpickup
=
⋅
⋅
−
>
>
−
−
480
32
0 5
0 035
.
.
ANSIEQUATION2287 V2 EN
(Equation 126)
The type C curve is described as:
t
TD
V
Vpickup
Vpickup
=
⋅
⋅
−
>
>
−
+
480
32
0 5
0 035
.
.
ANSIEQUATION2288 V2 EN
(Equation 127)
The customer programmable curve can be created as:
P
TD A
t
D
V Vpickup
B
C
Vpickup
×
=
+
-
×
-
æ
ö
ç
÷
è
ø
EQUATION1616 V1 EN
(Equation 128)
When the denominator in the expression is equal to zero the time delay will be infinity.
There will be an undesired discontinuity. Therefore, a tuning parameter
CrvSatn
is set
to compensate for this phenomenon. In the voltage interval Vpickup down to Vpickup
· (1.0 –
CrvSatn
/100) the used voltage will be: Vpickup · (1.0 –
CrvSatn
/100). If the
programmable curve is used this parameter must be calculated so that:
1MRK505222-UUS C
Section 8
Voltage protection
507
Technical reference manual
Summary of Contents for Relion 670 series
Page 1: ...Relion 670 series Line differential protection RED670 ANSI Technical reference manual...
Page 2: ......
Page 40: ...34...
Page 50: ...44...
Page 60: ...54...
Page 126: ...120...
Page 384: ...378...
Page 496: ...490...
Page 556: ...550...
Page 602: ...596...
Page 620: ...614...
Page 794: ...788...
Page 864: ...858...
Page 988: ...982...
Page 998: ...992...
Page 1084: ...1078...
Page 1164: ...1158...
Page 1168: ...1162...
Page 1220: ...1214...
Page 1230: ...1224...
Page 1231: ...1225...