4-260
Chapter 4 OPERATION
4
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
Chapter 4 OPERATION
4-261
12. "SYSTEM" mode
5. Condition for area check output
Selects the condition that allows the area check output to turn on, from either when the robot is
within a specified area or when outside it.
n
NOTE
• Any point on the boundary of the specified area is determined to be within the
area.
• If the area check cannot be performed correctly due to return-to-origin
incomplete, operation other than "MANUAL" or "AUTO" mode, or a memory error,
then the area check output will turn off regardless of the criterion setting.If the
specified port is the same as the port used by the program, then the area check
output has priority.
• The default setting is "IN" (output is on within specified area).
1
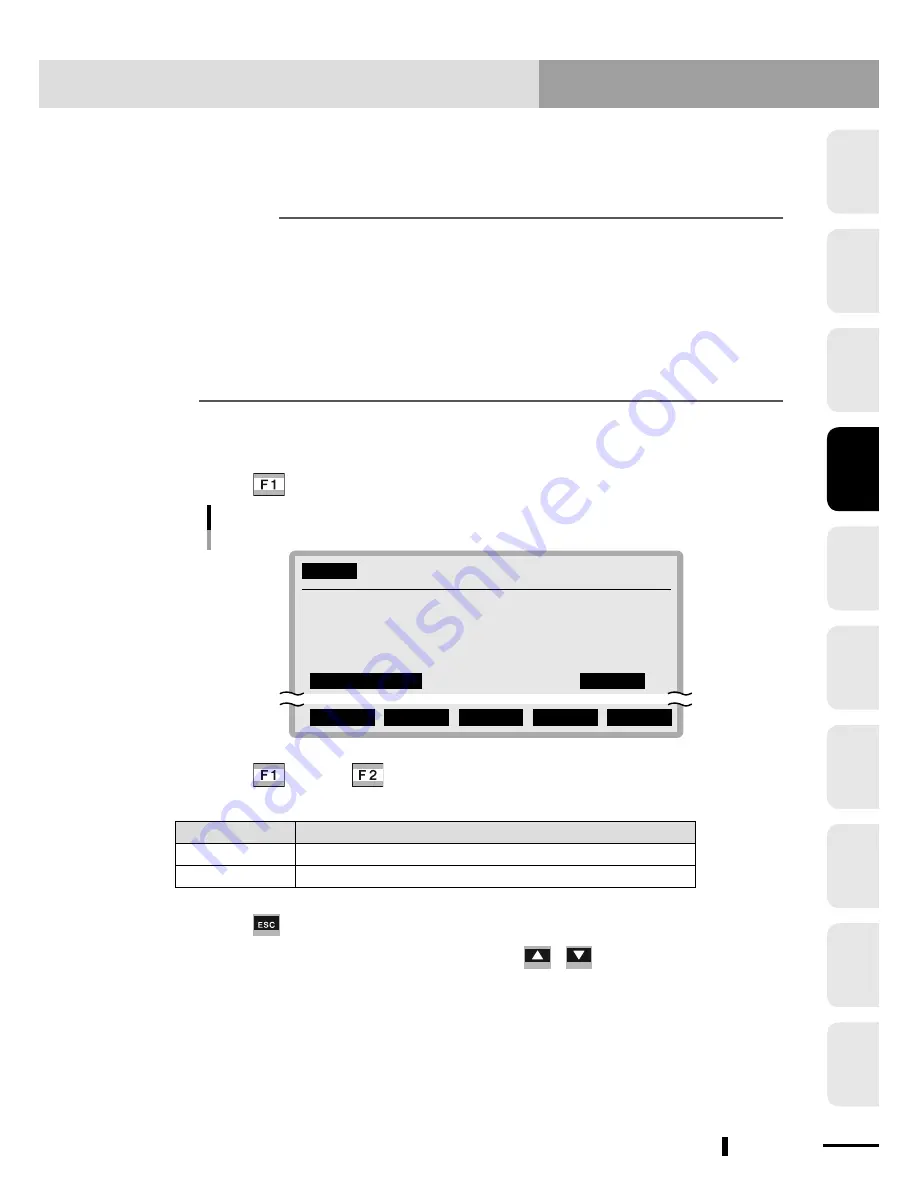
Select "5. Condition" in "SYSTEM>OPTION>POS.OUT>SELECT" mode.
2
Press
(EDIT).
SYSTEM
>OPTION>POS.OUT>SELECT V10.01
1.Output of area1 MAIN
2.Output port1(DO & SO) 20
3.Compare Point number11 P1
4.Compare Point number12 P2
5.Condition IN
IN OUT
Criterion selection for area check output
3
Press
(IN) or
(OUT) to select the criterion for area check
output.
Setting
Meaning
IN
Turns on when the robot enters a specified area.
OUT
Turns on when the robot goes out of a specified area.
4
Press
to quit the editing.
To continue setting other items, use the cursor (
/
) keys to select them.
Summary of Contents for RCX240
Page 1: ...RCX240 EUR6127206 E107 Ver 2 06 Userʼs Manual YAMAHA 4 AXIS ROBOT CONTROLLER ...
Page 2: ......
Page 18: ......
Page 34: ......
Page 78: ......
Page 402: ......
Page 448: ...5 46 Chapter 5 TWO ROBOT SETTING MEMO ...
Page 450: ......
Page 480: ...6 30 Chapter 6 PARALLEL I O INTERFACE MEMO ...
Page 482: ......
Page 494: ......
Page 506: ......
Page 512: ......
Page 522: ......
Page 611: ...INDEX ...
Page 612: ......
Page 617: ......
Page 619: ......






























