CHAPTER 17 INTERRUPT/EXCEPTION PROCESSING FUNCTION
User’s Manual U16896EJ2V0UD
544
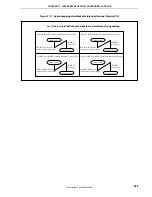
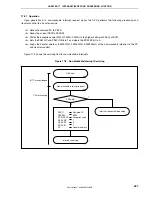
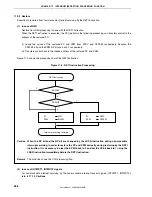
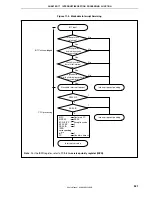
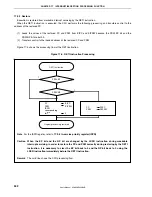
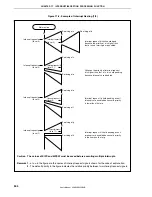
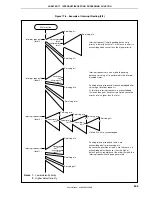
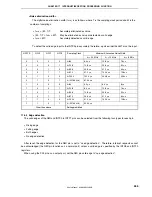
Figure 17-6. Example of Interrupt Nesting (1/2)
Main routine
EI
EI
Interrupt request a
(level 3)
Servicing of a
Servicing of b
Interrupt request b
(level 2)
Servicing of c
Interrupt request c
(level 3)
Interrupt request d
(level 2)
Servicing of d
Servicing of e
EI
Interrupt request e
(level 2)
Interrupt request f
(level 3)
Servicing of f
EI
Servicing of g
Interrupt request g
(level 1)
Interrupt request h
(level 1)
Servicing of h
Interrupt request h is held pending even if
interrupts are enabled because its priority
is the same as that of g.
Interrupt request f is held pending even if
interrupts are enabled because its priority
is lower than that of e.
Interrupt request b is acknowledged
because the priority of b is higher than
that of a and interrupts are enabled.
Although the priority of interrupt request
d is higher than that of c, d is held pending
because interrupts are disabled.
Caution The values of EIPC and EIPSW must be saved before executing multiple interrupts.
Remarks 1.
a to u in the figure are the names of interrupt request signals shown for the sake of explanation.
2.
The default priority in the figure indicates the relative priority between two interrupt request signals.