123
Program description:
Mixers
The programming procedure in detail
If you have not already done so, switch to the approp-
riate fl ight phase, e. g. “normal”, which will appear on
the screen.
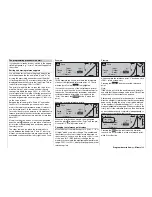
Setting and erasing reference points
You will fi nd a vertical line in the graph, and you can
shift this between the two end-points “L” and “H” by
moving the associated transmitter control (throttle /
collective pitch stick). The current stick position is also
displayed in numerical form in the “Input” line. This va-
lue will lie in the range -100% to +100%.
The point at which this line crosses the curve is ter-
med the “Output”, and it can be varied at the refe-
rence points within the range -125% to +125%. This
control signal affects only the collective pitch servos.
In the example above the stick is at -60% control tra-
vel and also generates an output signal of -60%, sin-
ce the curve is linear.
Between the two end-points “L” and “H” and the de-
fault Point 1 in the centre you can now set a maxi-
mum of four additional reference points. However, if
you fi rst erase point 1 in the centre of the transmit-
ter control travel, you can enter up to six additional re-
ference points, but please note that the distance bet-
ween adjacent reference points must be no less than
about 25%.
Now move the stick, and as soon as the highlighted
question mark
?
appears, you can place a reference
point at the corresponding stick position by pressing
the rotary control.
The order in which you place the (maximum) six
points between the end-points “L” and “H” is not sig-
nifi cant, as the reference points are automatically re-
numbered continuously from left to right in any case.
Example:
»Normal «
4
5
+90%
+90%
+100%
Point
Pitch
Input
Curve
off
Output
Note:
In this example the stick is located in the immediate
vicinity of the right-hand reference point “H”. That is
why the “point” value “
+100%
” is highlighted.
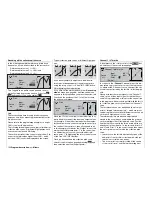
If you wish to erase one of the set reference points 1
to max. 6, move the stick close to the reference point
in question. The reference point number and the as-
sociated reference point value now appear in the
“Point” line; press the
CLEAR
button to erase that
point.
Example – erasing reference point 4:
»Normal «
4
5
+30%
+30%
+30%
4
Point
Pitch
Input
Curve
off
Output
When the point has been erased, the highlighted
question mark
?
re-appears after “Point”, and the pre-
vious point “5” now becomes point “4”.
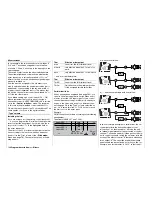
Changing the reference point values
Move the stick to the reference point “L (low), 1 ... 6 or
H (high)” which you wish to change. The number and
the current curve value of this point are displayed on
the screen. You can now use the rotary control or one
of the “free” INC / DEC buttons to change the mo-
mentary curve value in the highlighted fi eld within the
range -125% to +125%, without affecting the adjacent
reference points.
Example:
0%
+100%
+100%
»Normal «
Pitch
Input
Curve
off
Point
Output
As an example the reference point “2” has been set to
+100% in this screen-shot.
Pressing the
CLEAR
button erases the reference
point.
Note:
If the stick is not set to the exact reference point, ple-
ase note that the percentage value in the “Output” line
always refers to the current stick position.
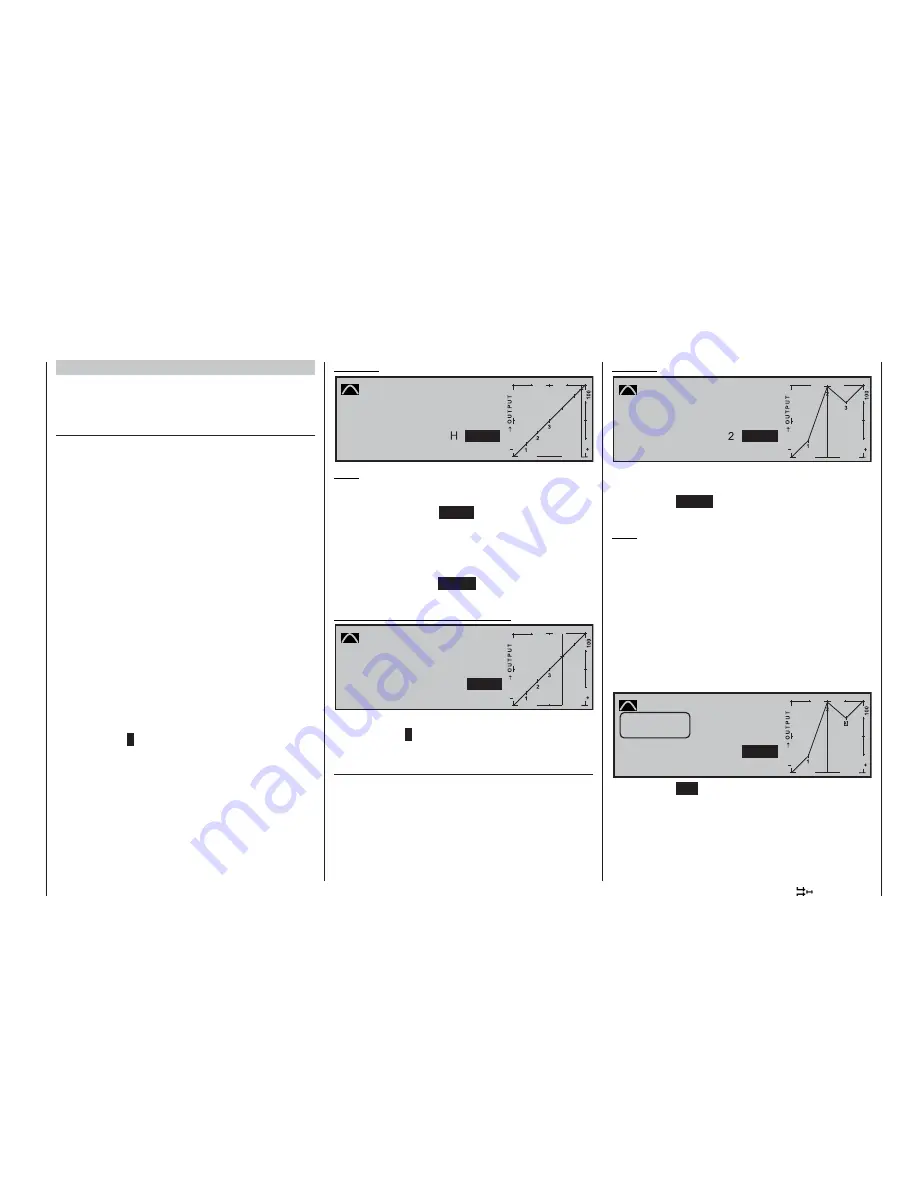
Alternatively you can skip in the upward or downward
direction straight to reference points that have already
been set, by turning the rotary control when pressed
in; the number of the addressed point 1 … max. 6 is
always highlighted in the graph. When you release the
rotary control, the reference point can then be altered
as described previously, completely independently of
the position of the transmitter control.
Kurve
0%
+100%
+55%
3
»Normal «
Pitch
Input
Curve
off
Point
Output
Trim point
Quit = ESC
Pressing the
ESC
button concludes this trim point
function. It is not possible to erase a reference point
while it is still active.
Summary of Contents for mx-24s
Page 1: ...1...
Page 19: ...19 For your notes...
Page 35: ...35 For your notes...
Page 41: ...41 41 For your notes...
Page 57: ...57 For your notes...
Page 63: ...63 63 For your notes...
Page 69: ...69 69 For your notes...
Page 85: ...85 85 For your notes...
Page 99: ...99 For your notes...
Page 143: ...143 For your notes...
Page 191: ...191 For your notes...
Page 212: ...212 212 For your notes...
Page 213: ...213 213 For your notes...
Page 214: ...214 For your notes...
Page 216: ...216...