IDT SMBus Interfaces
PES32NT24xG2 User Manual
12 - 9
January 30, 2013
Notes
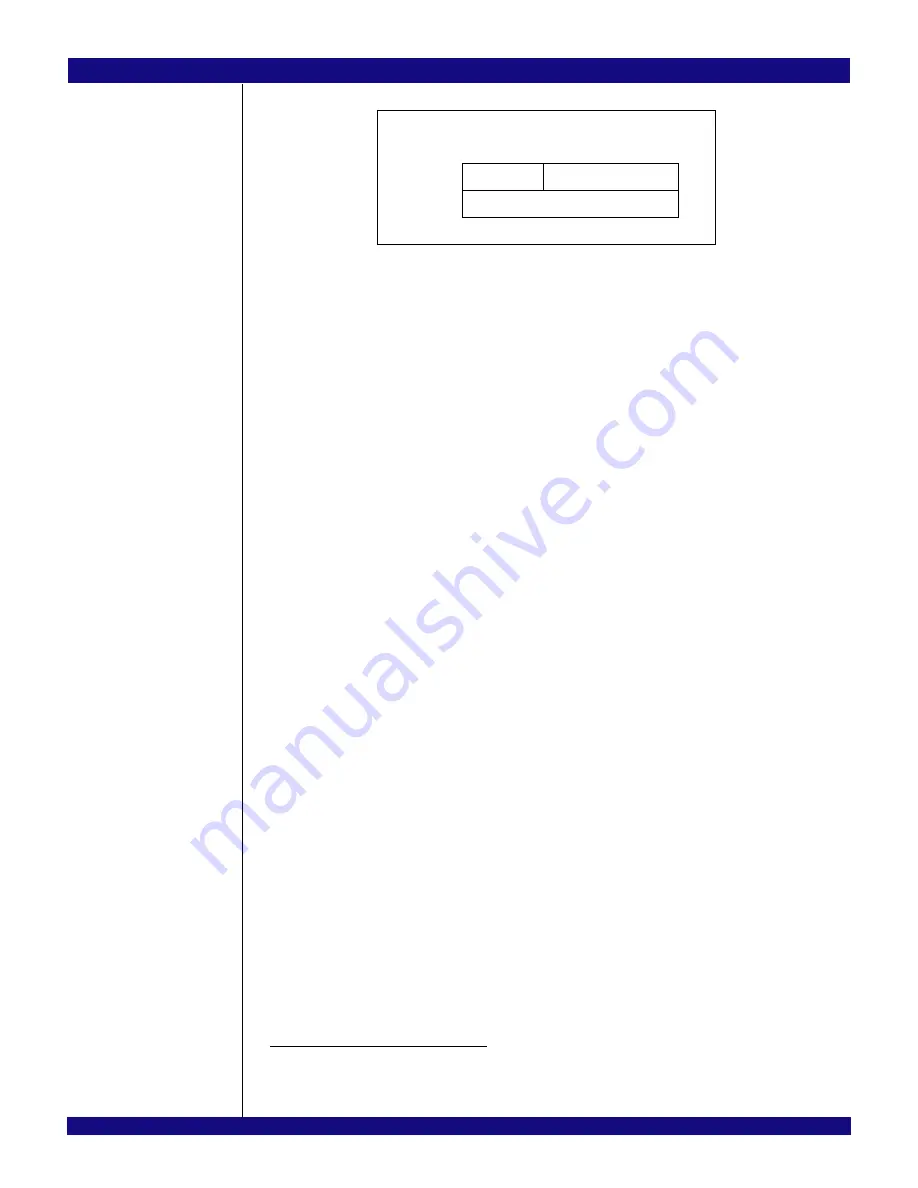
Figure 12.8 Configuration Done Sequence Format
The checksum in the configuration done sequence enables the integrity of the serial EEPROM initializa-
tion to be verified. The checksum is computed in the following manner. An 8-bit counter is initialized to zero
and the 8-bit sum is computed over the configuration bytes stored in the serial EEPROM, including the
entire contents of the configuration done sequence, with the checksum field initialized to zero.
1
The 1’s
complement of this sum is placed in the checksum field.
Configuration jump blocks processed while reading serial EEPROM are included in the checksum calcu-
lation, whether the jump is taken or ignored. For example, in the EEPROM layout shown in Figure 12.6, the
checksum in the configuration done block of Configuration A would include the two jump blocks at the
beginning of the EEPROM (i.e., to reach Configuration A, these jump blocks are processed even though the
jumps are not taken). In this same figure, the checksum in the configuration done block of Configuration B
would include also include the two jump blocks at the beginning of the EEPROM. Finally the configuration
done block of Configuration C would include the jump 0 block but not the jump 1 block, as only the former is
processed before the jump occurs.
The checksum is verified in the following manner. An 8-bit counter is cleared and the 8-bit sum is
computed over the bytes read from the serial EEPROM, including the entire contents of the configuration
done sequence.
2
The correct result should always be 0xFF (i.e., all ones). Checksum checking may be
disabled by setting the Ignore Checksum Errors (ICHECKSUM) bit in the SMBus Control (SMBUSCTL)
register.
A summary of possible errors during serial EEPROM initialization and specific action taken when
detected is summarized in Table 12.3.
–
The detection of any error causes the EEPROM Error Detected (EED) bit to be set in the SMBus
Status (SMBUSSTS) register, the loading of the serial EEPROM to be aborted and the RSTHALT
bit to be set in the SWCTL register. This allows debugging of the error condition via the slave
SMBus interface but prevents normal system operation with a potentially incorrectly initialized
device. Specific error information is recorded in the SMBUSSTS register. In addition, the first 3
bytes of the last configuration block processed normally by the master SMBus interface is
recorded in the SMBus Configuration Block Header Log (SMBUSCBHL) register.
–
The contents of the SMBUSCBHL register can be read to determine if an error exists in the last
configuration block that was successfully processed by the master SMBus interface. For example,
if a Jump configuration block has an invalid jump address (i.e., a target address at which no valid
configuration block is found), the SMBUSCBHL register would log the first 3 bytes of the jump
configuration block, thereby capturing the incorrect jump address.
Note that when loading of the serial EEPROM is aborted due to an error, EEPROM configuration blocks
loaded prior to the block on which the error is detected are executed normally. The configuration block on
which the error is detected may be fully executed, partially executed, or not executed depending on the type
of error found.
Once serial EEPROM initialization completes or when it is aborted, the EEPROM Done (EEPROM-
DONE) bit is set in the SMBUSSTS register.
1.
This includes the byte containing the TYPE field.
2.
This includes the checksum byte as well as the byte that contains the type and reserved field.
Bit
0
Bit
1
Bit
2
Bit
3
Bit
4
Bit
5
Bit
6
Bit
7
Byte 1
CHECKSUM[7:0]
Reserved
CFG TYPE
0x7
Byte 0
(must be zero)
Summary of Contents for PCI Express 89HPES32NT24xG2
Page 20: ...IDT Table of Contents PES32NT24xG2 User Manual x January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 24: ...IDT List of Tables PES32NT24xG2 User Manual xiv January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 28: ...IDT List of Figures PES32NT24xG2 User Manual xviii January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 56: ...IDT PES32NT24xG2 Device Overview PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 1 20 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 100: ...IDT Switch Core PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 4 22 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 128: ...IDT Failover PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 6 4 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 148: ...IDT Link Operation PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 7 20 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 164: ...IDT SerDes PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 8 16 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 170: ...IDT Power Management PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 9 6 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 196: ...IDT Transparent Switch Operation PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 10 26 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 244: ...IDT SMBus Interfaces PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 12 40 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 247: ...IDT General Purpose I O PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 13 3 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 248: ...IDT General Purpose I O PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 13 4 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 330: ...IDT Switch Events PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 16 6 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 342: ...IDT Multicast PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 17 12 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 344: ...IDT Temperature Sensor PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 18 2 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 384: ...IDT Register Organization PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 19 40 January 30 2013...
Page 492: ...IDT Proprietary Port Specific Registers PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 21 44 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 588: ...IDT NT Endpoint Registers PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 22 96 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 710: ...IDT JTAG Boundary Scan PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 25 12 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 743: ...IDT Usage Models PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 26 33 January 30 2013 Notes...
Page 744: ...IDT Usage Models PES32NT24xG2 User Manual 26 34 January 30 2013 Notes...






























