This example describes how to configure IP source guard with 802.1X user authentication
on a data VLAN, with a voice VLAN on the same interface:
•
Requirements on page 2889
•
Overview and Topology on page 2889
•
Configuration on page 2890
•
Verification on page 2892
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
•
One EX Series switch
•
Junos OS Release 9.2 or later for EX Series switches
•
A DHCP server to provide IP addresses to network devices on the switch
•
A RADIUS server to provide 802.1X authentication
Before you configure IP source guard for the data VLANs, be sure you have:
•
Connected the DHCP server to the switch.
•
Connected the RADIUS server to the switch and configured user authentication on the
server. See “Example: Connecting a RADIUS Server for 802.1X to an EX Series Switch”
on page 2545.
•
Configured the VLANs. See “Example: Setting Up Bridging with Multiple VLANs for EX
Series Switches” on page 1312 for detailed information about configuring VLANs.
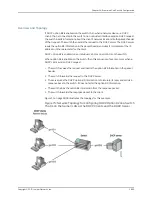
Overview and Topology
IP source guard checks the IP source address and MAC source address in a packet sent
from a host attached to an untrusted access interface on the switch. If IP source guard
determines that the packet header contains an invalid source IP address or source MAC
address, it ensures that the switch does not forward the packet—that is, the packet is
discarded.
When you configure IP source guard, you enable on it on one or more VLANs. IP source
guard applies its checking rules to untrusted access interfaces on those VLANs. By default,
on EX Series switches, access interfaces are untrusted and trunk interfaces are trusted.
IP source guard does not check packets that have been sent to the switch by devices
connected to either trunk interfaces or trusted access interfaces—that is, interfaces
configured with
dhcp-trusted
so that a DHCP server can be connected to that interface
to provide dynamic IP addresses.
IP source guard obtains information about IP-address/MAC-address/VLAN bindings
from the DHCP snooping database. It causes the switch to validate incoming IP packets
against the entries in that database.
2889
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 94: Examples: Port Security Configuration
Summary of Contents for JUNOS OS 10.3 - SOFTWARE
Page 325: ...CHAPTER 17 Operational Mode Commands for System Setup 229 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 1323: ...CHAPTER 56 Operational Mode Commands for Interfaces 1227 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 2841: ...CHAPTER 86 Operational Commands for 802 1X 2745 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3367: ...CHAPTER 113 Operational Mode Commands for CoS 3271 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3435: ...CHAPTER 120 Operational Mode Commands for PoE 3339 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3529: ...CHAPTER 126 Operational Mode Commands for MPLS 3433 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...