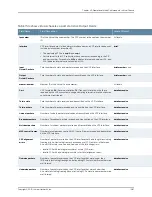
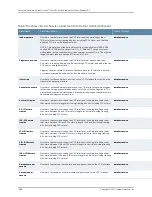
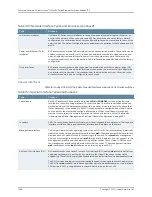
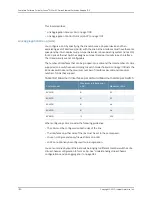
Logical Part of an Interface Name
The logical unit part of the interface name corresponds to the logical unit number, which
can be a number from 0 through 16384. In the virtual part of the name, a period (.)
separates the port and logical unit numbers:
type-fpc/pic/port.logical-unit-number
. For
example, if you issue the
show ethernet-switching interfaces
command on a system
with a default VLAN, the resulting display shows the logical interfaces associated with
the VLAN:
Interface State VLAN members Blocking
ge-0/0/0.0 down remote-analyzer unblocked
ge-0/0/1.0 down default unblocked
ge-0/0/10.0 down default unblocked
When you configure aggregated Ethernet interfaces, you configure a logical interface
that is called a
bundle
or a
LAG
. Each LAG can include up to 8 or 12 Ethernet interfaces,
depending on the switch model.
Wildcard Characters in Interface Names
In the
show interfaces
and
clear interfaces
commands, you can use wildcard characters
in the
interface-name
option to specify groups of interface names without having to type
each name individually. You must enclose all wildcard characters except the asterisk (*)
in quotation marks (" ").
Related
Documentation
EX Series Switches Interfaces Overview on page 1095
•
•
Front Panel of an EX2200 Switch
•
Front Panel of an EX3200 Switch
•
Front Panel of an EX4200 Switch
•
Front Panel of an EX4500 Switch
•
Slot Numbering for an EX8208 Switch
•
Slot Numbering for an EX8216 Switch
Understanding Aggregated Ethernet Interfaces and LACP
IEEE 802.3ad link aggregation enables you to group Ethernet interfaces to form a single
link layer interface, also known as a
link aggregation group (LAG)
or
bundle
.
Aggregating multiple links between physical interfaces creates a single logical
point-to-point trunk link or a LAG. The LAG balances traffic across the member links
within an aggregated Ethernet bundle and effectively increases the uplink bandwidth.
Another advantage of link aggregation is increased availability, because the LAG is
composed of multiple member links. If one member link fails, the LAG continues to carry
traffic over the remaining links.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), a component of IEEE 802.3ad, provides
additional functionality for LAGs.
1099
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 50: Interfaces—Overview
Summary of Contents for JUNOS OS 10.3 - SOFTWARE
Page 325: ...CHAPTER 17 Operational Mode Commands for System Setup 229 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 1323: ...CHAPTER 56 Operational Mode Commands for Interfaces 1227 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 2841: ...CHAPTER 86 Operational Commands for 802 1X 2745 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3367: ...CHAPTER 113 Operational Mode Commands for CoS 3271 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3435: ...CHAPTER 120 Operational Mode Commands for PoE 3339 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3529: ...CHAPTER 126 Operational Mode Commands for MPLS 3433 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...