•
One EX Series distribution switch
•
Junos OS Release 10.0 or later for EX Series switches
Overview and Topology
MVRP is used to manage dynamic VLAN registration in a LAN. It can also be used to
dynamically create VLANs.
This example uses MVRP to dynamically create VLANs on the switching network. You
can disable dynamic VLAN creation and create VLANs statically, if desired. Enabling
MVRP on the trunk interface of each switch in your switching network ensures that the
active VLAN information for the switches in the network is propagated to each switch
through the trunk interfaces, assuming dynamic VLAN creation is enabled for MVRP.
MVRP ensures that the VLAN membership information on the trunk interface is updated
as the switch’s access interfaces become active or inactive in the configured VLANs in a
static or dynamic VLAN creation setup.
You do not need to explicitly bind a VLAN to the trunk interface. When MVRP is enabled,
the trunk interface advertises all the VLANs that are active (bound to access interfaces)
on that switch. An MVRP-enabled trunk interface does not advertise VLANs that have
been configured on the switch but that are not currently bound to an access interface.
Thus, MVRP provides the benefit of reducing network overhead—by limiting the scope
of broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic to interested devices only.
When VLAN access interfaces become active or inactive, MVRP ensures that the updated
information is advertised on the trunk interface. Thus, in this example, distribution Switch
C does not forward traffic to inactive VLANs.
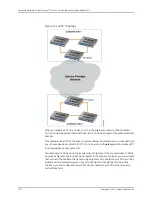
This example shows a network with three VLANs:
finance
,
sales
, and
lab
.
Access Switch A has been configured to support all three VLANS and all three VLANS
are active, bound to interfaces that are connected to personal computers:
•
ge-0/0/1
—Connects PC1 as a member of
finance
, VLAN ID 100
•
ge-0/0/2
—Connects PC2 as a member of
lab
, VLAN ID 200
•
ge-0/0/3
—Connects PC3 as a member of
sales
, VLAN ID 300
Access Switch B has also been configured to support three VLANS. However, currently
only two VLANs are active, bound to interfaces that are connected to personal computers:
•
ge-0/0/0
—Connects PC4 as a member of
finance
, VLAN ID 100
•
ge-0/0/1
—Connects PC5 as a member of
lab
, VLAN ID 200
Distribution Switch C learns the VLANs dynamically using MVRP through the connection
to the access switches. Distribution Switch C has two trunk interfaces:
•
xe-0/1/1
—Connects the switch to access Switch A.
•
xe-0/1/0
—Connects the switch to access Switch B.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
1358
Complete Software Guide for Junos
®
OS for EX Series Ethernet Switches, Release 10.3
Summary of Contents for JUNOS OS 10.3 - SOFTWARE
Page 325: ...CHAPTER 17 Operational Mode Commands for System Setup 229 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 1323: ...CHAPTER 56 Operational Mode Commands for Interfaces 1227 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 2841: ...CHAPTER 86 Operational Commands for 802 1X 2745 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3367: ...CHAPTER 113 Operational Mode Commands for CoS 3271 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3435: ...CHAPTER 120 Operational Mode Commands for PoE 3339 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...
Page 3529: ...CHAPTER 126 Operational Mode Commands for MPLS 3433 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc ...