Chapter 16 CHI Module
16-3
16.3 Detailed
Explanation
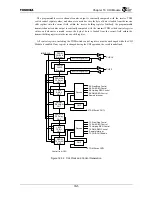
16.3.1 Transmitter
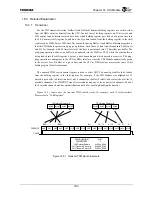
For the CHI transmit direction, Buffer-A and Buffer-B transmit holding registers are written either
from the DMA circuit or directly from the CPU. Each of these 2 holding registers are 32-bits wide, and
CHI control logic determines which byte from which holding register gets loaded at a given time into
the 8-bit transmit shift register. In addition, the byte data loaded from the holding register to the shift
register can be MSB-first or LSB-first. The reason for having Buffer-A and Buffer-B holding registers is
that the CHI Module operates in a ping-pong fashion. Each frame of data is partitioned into 2 buffers (A
and B); for example, with 64 timeslots total, the data is partitioned into 32 timeslots per buffer. The
ping-pong operation allows one buffer to be updated (via the DMA or CPU) while the other buffer is
being loaded into the shift register a byte at a time, depending on which timeslots are active. The ping-
pong operation is transparent to the CPU or DMA interface, since the CHI Module automatically points
to the correct A or B buffer at a given time and the CPU or DMA always accesses the same 32-bit
holding register for all transactions.
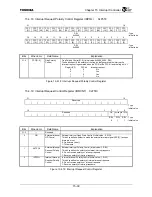
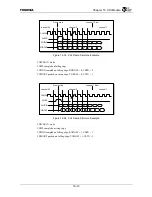
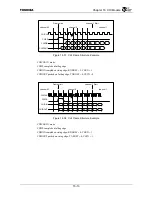
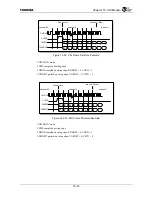
The transmit TDM switch control register is used to select ANY 4 channels per buffer to be loaded
from the holding register to the shift register. For example, if the CHI Module is configured for 32
timeslots per buffer (64 total timeslots), any 4 channels per buffer (8 total) can be selected out of the 32
available channels. The CHIDOUT signal is tri-stated during any of the non-selected channels. Each of
the 8 selected channels also has an individual control bit for enabling/disabling the timeslot.
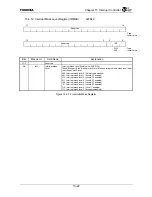
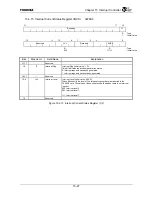
Figure 16.3.1 shows how the transmit TDM switch works, for example, with 16 total timeslots.
Please refer to “16.4 Registers”.
Figure 16.3.1 Transmit TDM Switch Example
byte3 byte2 byte1
byte0
TX Holding Register A
Bit31…………………….Bit0
byte3
byte2
byte1 byte0
TX Holding Register B
Bit31…………………….Bit0
ch0
ch1
ch2
ch3
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
ch9
Hi-Z
ch11 Hi-Z ch13 ch14 Hi-Z
Bit0……………….Bit31
Bit 16…13
8…15
24…31
0…7
CHINCHAN[4:0]
TXMSBFIRST
CHI Pointer Enable
CHI Transmit Pointer A
CHI Transmit Pointer B
0x07
0
0xFFxx_0000
0x0302_0100
0x0501_0306
CHIDOUT
CHIFS
Summary of Contents for TMPR4925
Page 1: ...64 Bit TX System RISC TX49 Family TMPR4925 Rev 3 0 ...
Page 4: ......
Page 15: ...Handling Precautions ...
Page 16: ......
Page 18: ...1 Using Toshiba Semiconductors Safely 1 2 ...
Page 40: ...3 General Safety Precautions and Usage Considerations 3 18 ...
Page 42: ...4 Precautions and Usage Considerations 4 2 ...
Page 43: ...TMPR4925 ...
Page 44: ......
Page 54: ...Chapter 1 Features 1 8 ...
Page 58: ...Chapter 2 Block Diagram 2 4 ...
Page 88: ...Chapter 4 Address Mapping 4 12 ...
Page 226: ...Chapter 8 DMA Controller 8 58 ...
Page 260: ...Chapter 9 SDRAM Controller 9 34 ...
Page 480: ...Chapter 15 Interrupt Controller 15 32 ...
Page 554: ...Chapter 19 Real Time Clock RTC 19 8 ...
Page 555: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 1 20 Removed ...
Page 556: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 2 ...
Page 564: ...Chapter 21 Extended EJTAG Interface 21 8 ...
Page 580: ...Chapter 22 Electrical Characteristics 22 16 ...
Page 588: ...Chapter 24 Usage Notes 24 2 ...