Chapter 15 Interrupt Controller
15-5
15.3.2 Interrupt
Request
Detection
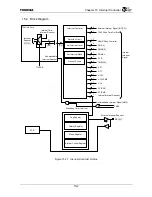
In order to perform interrupt detection, each register of the Interrupt Controller is initialized, then the
IDE bit of the Interrupt Detection Enable Register (IRDEN) is set to “1.” All interrupts detected by the
Interrupt Controller are masked when this bit is cleared.
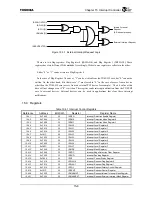
It is possible to set each interrupt factor detection mode using Interrupt Detection Mode Register 0
(IRDM0) and Interrupt Detection Mode Register 1 (IRDM1). There are four detection modes: Low
level, High level, falling edge, and rising edge.
The detected interrupt factors can be read out from the Interrupt Pending Register (IRPND).
15.3.3 Interrupt
Level
Assigning
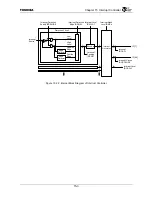
Interrupt levels from 0 to 7 are assigned to each detected interrupt using the Interrupt Level Register
(IRLVL0-7). Interrupt level 7 is the highest priority and interrupt level1 is the lowest priority. Level 0
interrupts will be masked. (Table 15.3.2).
The priorities set by these interrupt levels will be given higher priority than the priorities provided
for each interrupt source indicated in Table 15.3.1.
Table 15.3.2 Interrupt Levels
Priority
Interrupt Level
(IRLVLn.ILm)
High 111
110
101
100
011
010
Low 001
Mask 000
15.3.4 Interrupt
Priority
Assigning
When multiple interrupt requests exist, the Interrupt Controller selects the interrupt with the highest
priority according to the priority level and interrupt number. Interrupt factors with an interrupt level
lower than the interrupt level specified by the Interrupt Mask Level Register (IRMSK) will be excluded
(masked).
When the interrupt with the highest priority is selected, then the interrupt number of that interrupt is
set in the interrupt factor field (CAUSE) of the Interrupt Current Status Register (IRCS), the interrupt
level is set in the Interrupt Level field (LVL), and the Interrupt Flag bit (IF) is set.
Summary of Contents for TMPR4925
Page 1: ...64 Bit TX System RISC TX49 Family TMPR4925 Rev 3 0 ...
Page 4: ......
Page 15: ...Handling Precautions ...
Page 16: ......
Page 18: ...1 Using Toshiba Semiconductors Safely 1 2 ...
Page 40: ...3 General Safety Precautions and Usage Considerations 3 18 ...
Page 42: ...4 Precautions and Usage Considerations 4 2 ...
Page 43: ...TMPR4925 ...
Page 44: ......
Page 54: ...Chapter 1 Features 1 8 ...
Page 58: ...Chapter 2 Block Diagram 2 4 ...
Page 88: ...Chapter 4 Address Mapping 4 12 ...
Page 226: ...Chapter 8 DMA Controller 8 58 ...
Page 260: ...Chapter 9 SDRAM Controller 9 34 ...
Page 480: ...Chapter 15 Interrupt Controller 15 32 ...
Page 554: ...Chapter 19 Real Time Clock RTC 19 8 ...
Page 555: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 1 20 Removed ...
Page 556: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 2 ...
Page 564: ...Chapter 21 Extended EJTAG Interface 21 8 ...
Page 580: ...Chapter 22 Electrical Characteristics 22 16 ...
Page 588: ...Chapter 24 Usage Notes 24 2 ...