Chapter 16 CHI Module
16-1
16. CHI
Module
16.1 Characteristics
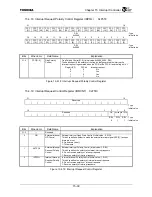
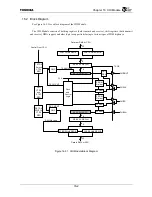
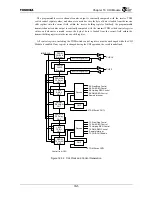
The CHI Module within the TX4925 contains holding registers, shift registers, DMA support, and other
logic to support interfacing to external full-duplex serial TDM communication peripherals, including ISDN
communication devices and PCM/TDM serial highways. The TX4925 implementation of the CHI Module is
based on the Concentration Highway Interface standard specified by Intel and AT&T, which is intended to
allow glueless interface to various TDM highways used by numerous commercial products. The TX4925
CHI Module can also be used to support an intra-system high-speed serial DMA channel within a PDA
system.
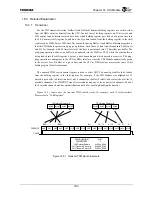
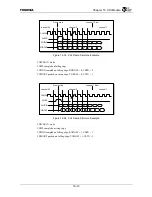
The TX4925 CHI Module utilizes a 4-signal interface consisting of clock, sync, transmit serial data, and
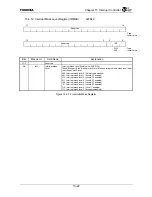
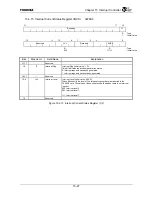
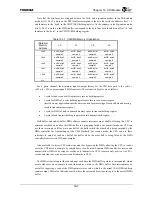
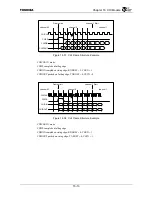
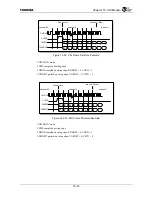
receive serial data. The data is organized as a TDM format, with up to 64 timeslots (nominally 8 bits each)
per frame, with a nominal frame rate of 8 kHz (8 bits
×
8 kHz
=
64 kbps nominal data rate per channel). Up
to four input timeslots and up to four output timeslots can be independently selected in each half-frame. The
CHI Module does not handle the timeslots which are not selected for input or output. The number of
timeslots and the data rate (up to 4.096 Mbps) and frame rate (up to 64 kHz, depending on the system
configuration) are programmable, providing flexibility for supporting various TDM communication
peripherals. These timeslots are commonly used to carry voice, data, or control and status information.
The CHI Module provides full-duplex DMA support for receive and transmit (two DMA channels). The
DMA buffers can be configured in a continuous (circular) buffer mode or a one-time (empty or fill, then
stop) buffer mode. Half-buffer and end-of-buffer DMA address counter interrupts are available, allowing the
CPU to minimize overhead and efficiently empty or fill half of the DMA buffer in a ping-pong fashion. The
DMA buffer size is programmable (from a minimum of 16 bytes up to a maximum of 16 Kbytes) and the
receive and transmit buffers can be configured to either reside in different memory spaces or share the same
memory space (overlapping buffers for loopback purposes or for optimum memory allocation). Also
available is a direct CPU read/write mode for bypassing the DMA, allowing the CPU to read or write the
CHI data on a sample by sample basis, if so desired.
Summary of Contents for TMPR4925
Page 1: ...64 Bit TX System RISC TX49 Family TMPR4925 Rev 3 0 ...
Page 4: ......
Page 15: ...Handling Precautions ...
Page 16: ......
Page 18: ...1 Using Toshiba Semiconductors Safely 1 2 ...
Page 40: ...3 General Safety Precautions and Usage Considerations 3 18 ...
Page 42: ...4 Precautions and Usage Considerations 4 2 ...
Page 43: ...TMPR4925 ...
Page 44: ......
Page 54: ...Chapter 1 Features 1 8 ...
Page 58: ...Chapter 2 Block Diagram 2 4 ...
Page 88: ...Chapter 4 Address Mapping 4 12 ...
Page 226: ...Chapter 8 DMA Controller 8 58 ...
Page 260: ...Chapter 9 SDRAM Controller 9 34 ...
Page 480: ...Chapter 15 Interrupt Controller 15 32 ...
Page 554: ...Chapter 19 Real Time Clock RTC 19 8 ...
Page 555: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 1 20 Removed ...
Page 556: ...Chapter 20 Removed 20 2 ...
Page 564: ...Chapter 21 Extended EJTAG Interface 21 8 ...
Page 580: ...Chapter 22 Electrical Characteristics 22 16 ...
Page 588: ...Chapter 24 Usage Notes 24 2 ...