13-64
Testing And Maintenance
BE1-CDS220
>400 ms
43
D2595-02.vsd
08-10-00
PU
DO
1
0
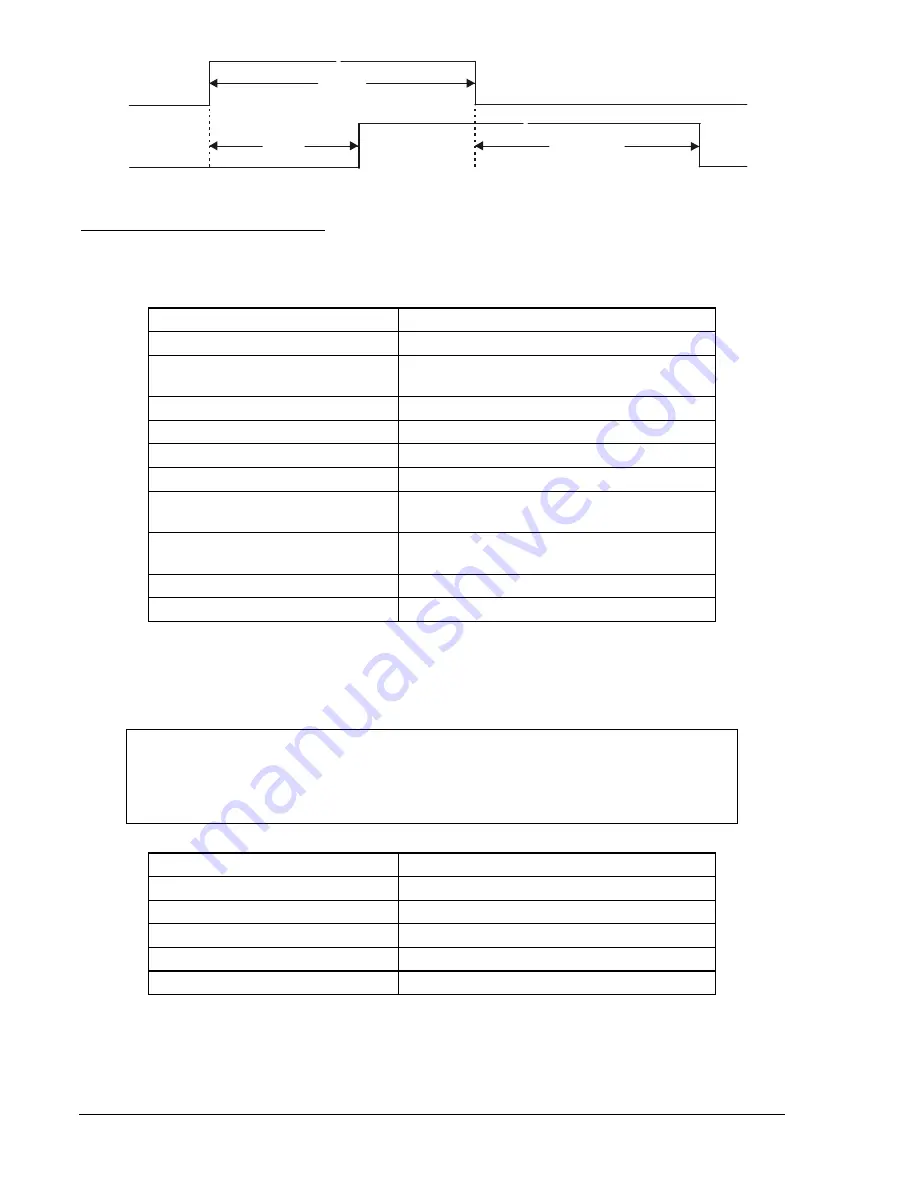
x62
400 ms
2,000 ms
~~
~~
Figure 13-17. x62 Mode 1 (Pickup/Dropout) Timing Example
Mode 2 – One Shot Nonretriggerable
Step 1.
Prepare for mode 2 logic timer verification testing by sending the commands in Table 13-72 to
the relay.
Table 13-72. x62 Mode 2 Test Commands
Command
Purpose
A=
Gain write access
SL-N=NONE
Zero out custom logic settings. Overwrite with
logic = none settings.
Y
Confirm overwrite
SL-N=T162
Sets T162 as custom logic name
SL-143=3
Enables 143 switch pulse mode
SN-143=162_INI,INI,NORMAL
Name switch to make SER easier to read
SL-162=2,143,0
Enables 162 1-shot, nonretriggerable mode,
143 initiate, no blocking
S0-162=400m,20s
Sets 162 delay at 400 milliseconds, 162
dropout at 20 seconds
EXIT
Exit
Y Save
settings
Step 2.
Send the commands in Table 13-73 to the relay. These commands supply the 162 timer with a
momentary initiate input by pulsing the 143 switch from a FALSE state to a TRUE state and
then back to a FALSE state. You may view the state changes of the 143 switch at front panel
interface \CTRL\43\143, screen 2.1.2.
NOTE
The 143 switch action is performed twice in this test. To illustrate the action of the timer
mode, the commands of Table 13-73 should be executed as quickly as possible. Ideally,
this test should be repeated within 20 seconds. If this is a problem, try extending the
dropout timer setting to 30 seconds.
Table 13-73. x62 Mode 2 Timer Initiate Commands
Command
Purpose
A=
Gain write access
CS-143=P
Selects 143 for pulse operation
CO-143=P
Executes 143 for pulse operation
CS-143=P
Selects 143 for pulse operation
CO-143=P
Executes 143 for pulse operation
Step 3.
Use the RS-LGC command to retrieve logic variable data from the SER. Verify that a 143 pulse
action (FALSE-TRUE-FALSE) was logged and that approximately 400 milliseconds after the
initial 143 FALSE-TRUE-FALSE initiate signal action, the 162 timer output went TRUE. Then,
approximately 20 seconds later, duration timer T2 expired and the timer output went FALSE
Summary of Contents for BE1-CDS220
Page 2: ......
Page 10: ...viii Introduction BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 36: ...ii Quick Start BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 48: ...ii Input And Output Functions BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 66: ...iv Protection and Control BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 112: ...ii Metering BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 116: ...5 4 Metering BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 166: ...ii BESTlogic Programmable Logic BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 176: ...7 10 BESTlogic Programmable Logic BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 234: ...8 56 Application BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 236: ...ii Security BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 240: ...9 4 Security BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 242: ...ii Human Machine Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 256: ...10 14 Human Machine Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 258: ...ii ASCII Command Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 422: ...14 32 BESTCOMS Software BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 424: ...ii Time Current Characteristics BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 452: ...ii Terminal Communication BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 456: ...C 4 Terminal Communication BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 458: ...ii Settings Calculations BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 475: ......
















































