13-56
Testing And Maintenance
BE1-CDS220
Using the basic information in Table 13-45, program the pickup of the elements for setting
group 1 and, optionally, proceed with the testing.
Timing Verification (51/151/251)
Purpose:
To verify the accuracy of the timing operation of the 51/151/251 elements.
Reference Commands:
SL-51/151/251, S<n>-51
Step 1.
Connect a current source to terminals B1 and B2 (A-phase input 1).
Step 2.
To initially prepare the 51/151/251 elements for testing, send the commands in Table 13-50 to
the relay.
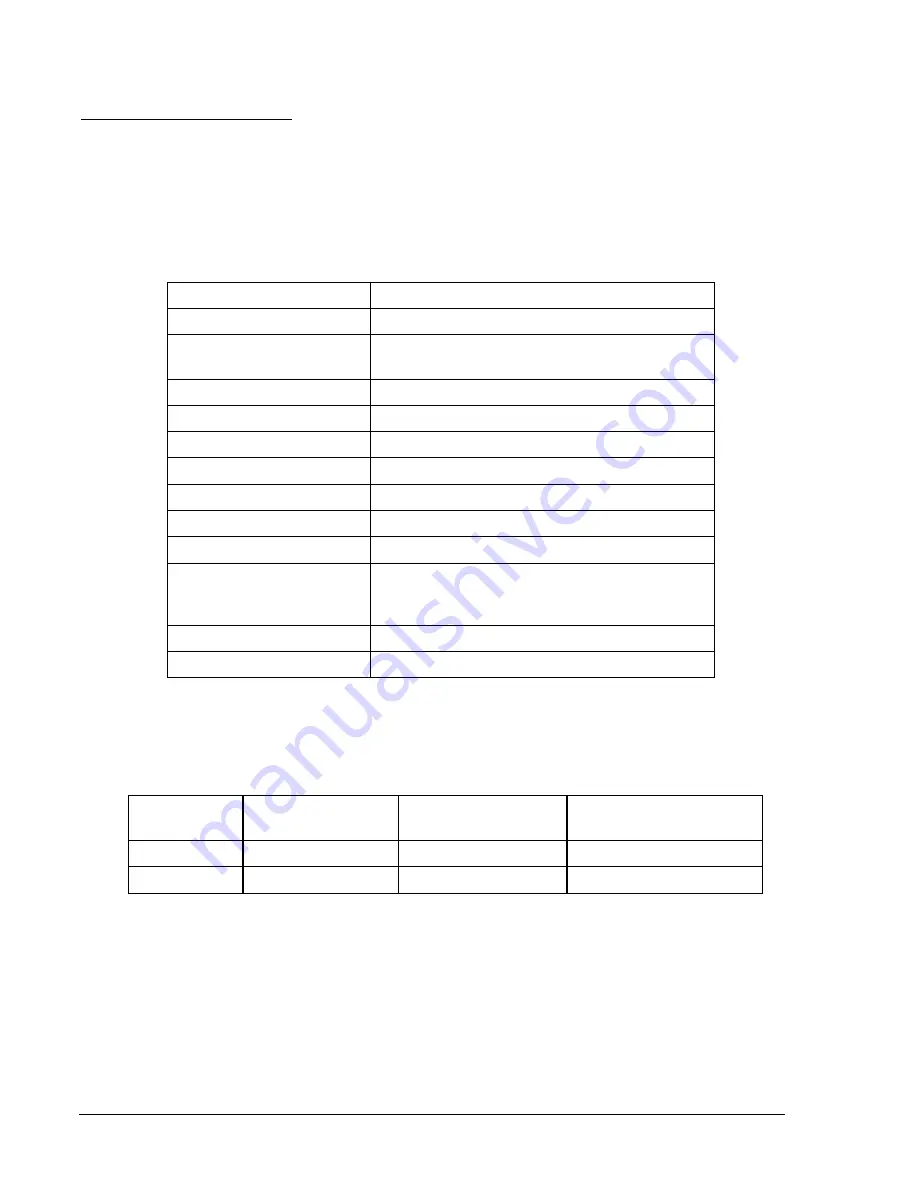
Table 13-50. 51/151/251 Overcurrent Timing Test Commands
Command Purpose
A= Gain
access
SL-N=NONE
Zero out custom logic settings/overwrite with
logic = none settings
Y Confirm
overwrite
SL-N= 51
Name custom logic for this test
SL-51=1,0
Enables 51P/51N/51Q, CT input 1
SL-VO1=51PT
Enables OUT1 to close for 50P trip
SL-VO2=51NT
Enables OUT2 to close for 51N trip
SL-VO3=51QT
Enables OUT3 to close for 51Q trip
SG-CT1=1,WYE,NA,0
Input 1 ctr=1, ct=wye, xfmr=na, no grd source
SG-TRIGGER=51PT+
51NT+51QT,51PPU+
51NPU+51QPU,0
Enable 51PT+51NT+51QT to log targets and
trigger fault recording
E Exit
Y Save
settings
Step 3.
Transmit to the relay the appropriate row of the setting commands S0-51P from Table 13-51. If
your relay is supplied with the HMI option, you may also go to the front panel interface screen
\PROT\SG0\50T\50T and edit the 51P, 51N, and 51Q settings.
Table 13-51. Time Overcurrent 51 Element Test Settings
Sensing
Input Type
Phase Neutral
Negative
Sequence
1 A
S0-51P=1.0,0.5,I2
S0-51N=1.0,0.5,I2 S0-51QN=0.33,0.5,I2
5 A
S0-51P=5.0,0.5,I2
S0-51N=5.0,0.5,I2 S0-51QN=1.67,0.5,I2
Notes for Table 13-51
1. See Sidebar 13-10 for more information on negative sequence pickup.
Step 4.
Using the values listed in Table 13-52, apply the current listed to the A phase current input and
measure the time between the application of current and the time it takes for the relay outputs
OUT1, OUT2, and OUT3 to close. Verify that the relay performs with the specified limits. An
ohm-meter or continuity tester may be used to monitor the output contacts status.
Step 5.
After each pickup occurs, slowly ramp current down until OUT1, OUT2, and OUT3 open.
Dropout should occur at 95%
±
2%.
Summary of Contents for BE1-CDS220
Page 2: ......
Page 10: ...viii Introduction BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 36: ...ii Quick Start BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 48: ...ii Input And Output Functions BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 66: ...iv Protection and Control BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 112: ...ii Metering BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 116: ...5 4 Metering BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 166: ...ii BESTlogic Programmable Logic BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 176: ...7 10 BESTlogic Programmable Logic BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 234: ...8 56 Application BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 236: ...ii Security BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 240: ...9 4 Security BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 242: ...ii Human Machine Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 256: ...10 14 Human Machine Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 258: ...ii ASCII Command Interface BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 422: ...14 32 BESTCOMS Software BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 424: ...ii Time Current Characteristics BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 452: ...ii Terminal Communication BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 456: ...C 4 Terminal Communication BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 458: ...ii Settings Calculations BE1 CDS220 This page intentionally left blank...
Page 475: ......






























