5-31
STANDARD AND PTS INTERRUPTS
Software starts a conversion on channel x. When the conversion is finished and the A/D conver-
sion complete interrupt is generated, the A/D scan mode routine begins. The PTS reads the com-
mand in location 3000H and stores it in a temporary location. Then it increments PTSPTR1 twice
and stores the value of the AD_RESULT register in location 3002H. The final step is to copy the
conversion command from the temporary location to the AD_COMMAND register. The CPU
could process or move the conversion results data from the table before the next conversion com-
pletes and a new PTS cycle begins. When the next cycle begins, PTSPTR1 again points to 3000H
and the repeats the events of the first cycle. The value of the AD_RESULT register is written to
location 3002H and the command at location 3000H is re-executed.
5.6.6
PWM Modes
The PWM toggle and PWM remap modes are designed for use with the event processor array
(EPA) to generate pulse-width modulated (PWM) output signals. These modes can also be used
with an interrupt signal from any other source. The PWM toggle mode uses a single EPA channel
to generate a PWM signal. The PWM remap mode uses two EPA channels, but it can generate
signals with duty cycles closer to 0% or 100% than are possible with the PWM toggle mode. Ta-
ble 5-12 compares the two PWM modes. For code examples, see AP-445, 8XC196KR Peripher-
als: A User’s Point of View, and “EPA PWM Output Program” on page 10-35.
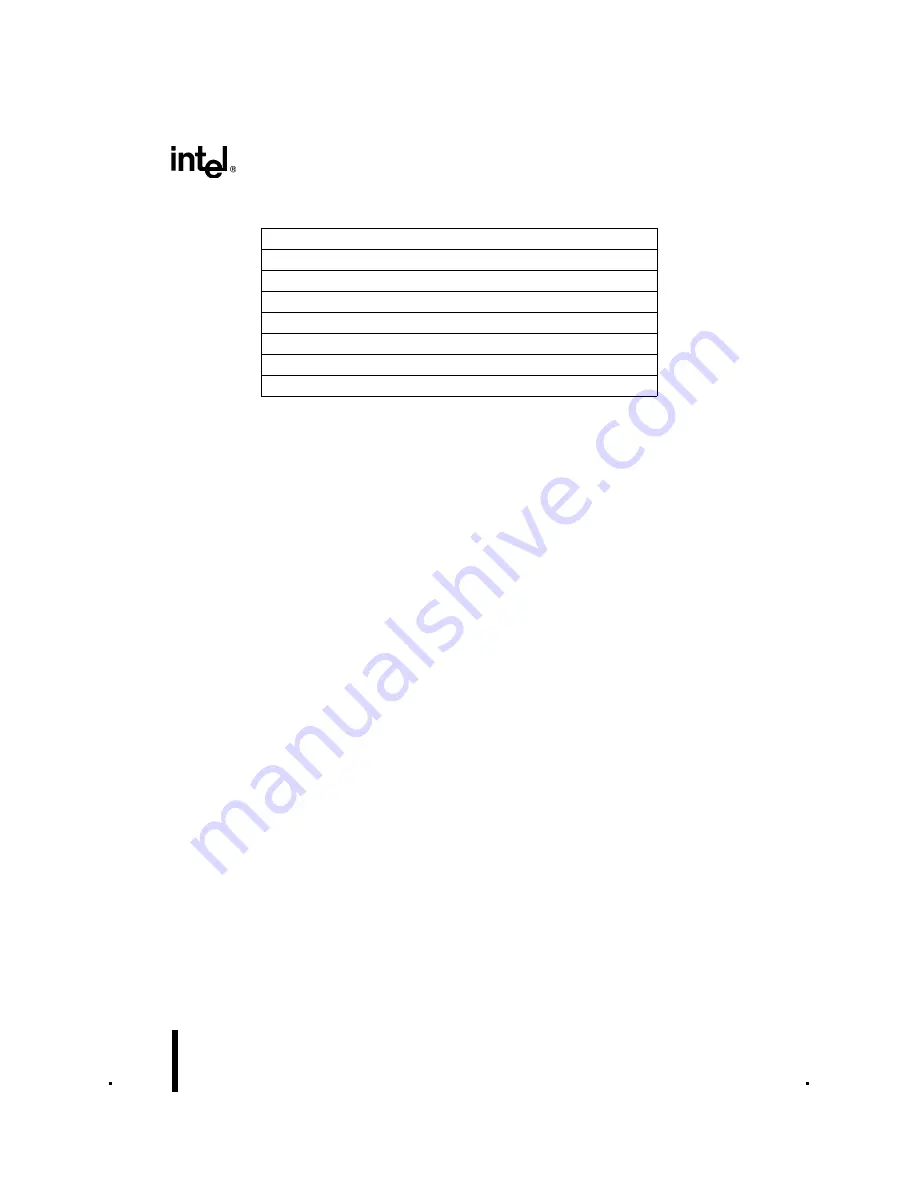
Table 5-11. A/D Scan Mode PTSCB (Example 2)
Unused
Unused
PTSPTR2 (HI) = 1FH
PTSPTR2 (LO) = AAH
PTSPTR1 (HI) = 30H
PTSPTR1 (LO) = 00H
PTSCON = C3H (Mode = 110, UPDT = 0)
PTSCOUNT = 0AH
Summary of Contents for 8XC196NT
Page 1: ...8XC196NT Microcontroller User s Manual...
Page 2: ...8XC196NT Microcontroller User s Manual June 1995 Order Number 272317 003...
Page 22: ...1 Guide to This Manual...
Page 23: ......
Page 35: ......
Page 36: ...2 Architectural Overview...
Page 37: ......
Page 49: ......
Page 50: ...3 Programming Considerations...
Page 51: ......
Page 66: ...4 Memory Partitions...
Page 67: ......
Page 104: ...5 Standard and PTS Interrupts...
Page 105: ......
Page 147: ......
Page 148: ...6 I O Ports...
Page 149: ......
Page 176: ...7 Serial I O SIO Port...
Page 177: ......
Page 194: ...8 Synchronous Serial I O SSIO Port...
Page 195: ......
Page 211: ......
Page 212: ...9 Slave Port...
Page 213: ......
Page 231: ......
Page 232: ...10 Event Processor Array EPA...
Page 233: ......
Page 270: ...11 Analog to digital Converter...
Page 271: ......
Page 291: ......
Page 292: ...12 Minimum Hardware Considerations...
Page 293: ......
Page 306: ...13 Special Operating Modes...
Page 307: ......
Page 317: ......
Page 318: ...14 Interfacing with External Memory...
Page 319: ......
Page 362: ...15 Programming the Nonvolatile Memory...
Page 363: ......
Page 408: ...A Instruction Set Reference...
Page 409: ......
Page 476: ...B Signal Descriptions...
Page 477: ......
Page 493: ......
Page 494: ...C Registers...
Page 495: ......
Page 565: ......
Page 566: ...Glossary...
Page 567: ......
Page 580: ...Index...
Page 581: ......
Page 597: ......






























