• An RX differential pair from another bank can be used as an input reference clock pin on the
same side of the device.
• refclk switching cannot be performed when dual-purpose RX differential pins are used refclk
pins.
Note:
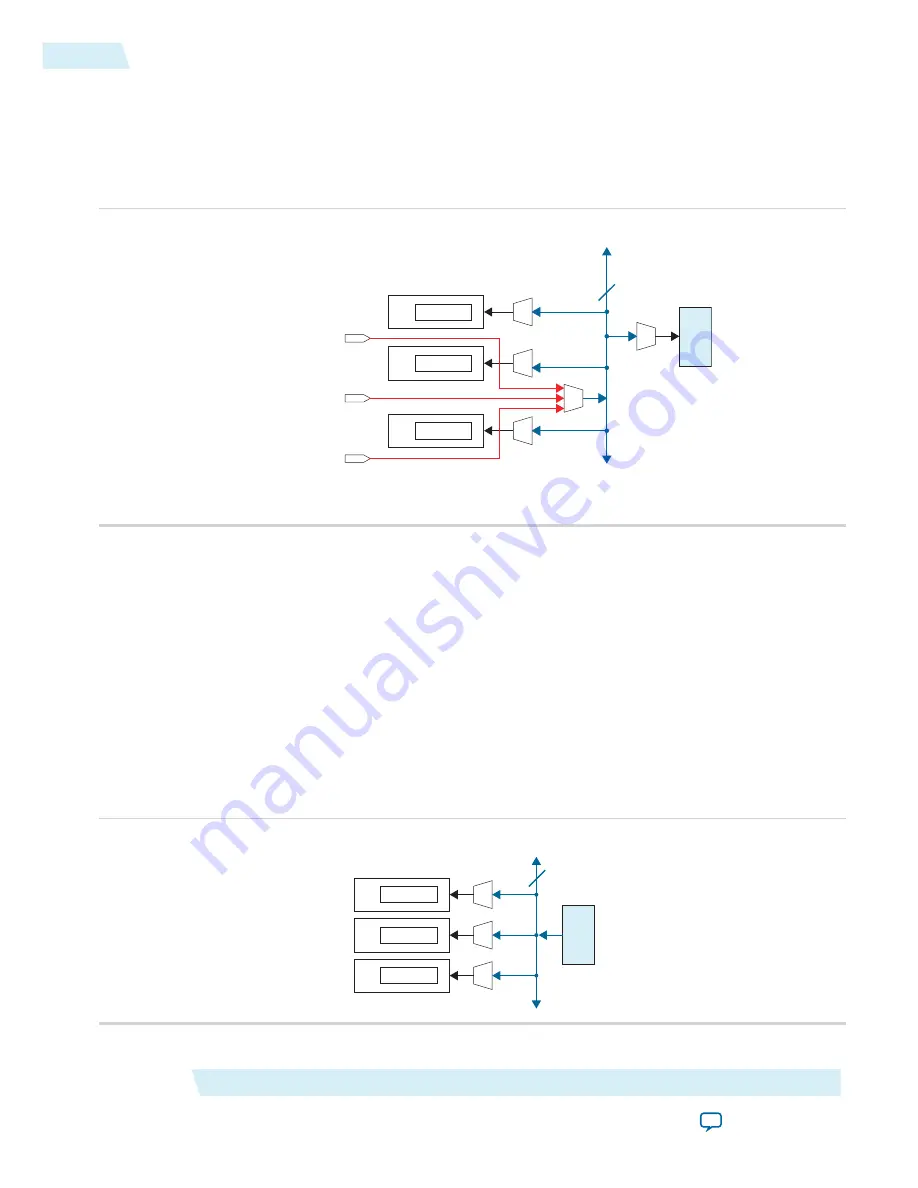
Figure 2-3: Dual-Purpose RX/refclk Pin as an Input Reference Clock
Channel PLL
CH2
Channel PLL
CH1
Channel PLL
CH0
Dual-Purpose RX/refclk Pin
fPLL
0
RX Clock
Network
N (1)
Dual-Purpose RX/refclk Pin
Dual-Purpose RX/refclk Pin
Note (1): N is the number of transceiver channels on a side divided by 3.
Fractional PLL (fPLL)
The fPLL clock output can be used as input reference clock source to transmitter PLL or CDR.
Cascading the fPLL to transmitter PLL or CDR enables you to use an input reference clock that is not
supported by the transmitter PLL or CDR. The fPLL synthesizes a supported input reference clock for the
transmitter PLL or CDR.
A fPLL is available for each bank of three transceiver channels. Each fPLL drives one of two fPLL cascade
clock network lines that can provide an input reference clock to any transmitter PLL or CDR on the same
side of a device. fPLLs support fractional and integer modes. The fractional mode allows you to synthesize
a clock of any supported frequency, and the integer mode allows you to synthesize an output clock that is
an integer multiple or factor of the input clock. For example, fPLLs allow you to take a 100 MHz clock and
synthesize a clock of 50 or 200 MHz in integer mode, or 614.4 MHz in fractional mode.
Figure 2-4: fPLL Clock Output as Input Reference Clock
Channel PLL
CH2
Channel PLL
CH1
Channel PLL
CH0
fPLL Cascade
Clock Network
fPLL
0
2
Transceiver Clocking in Cyclone V Devices
Altera Corporation
CV-53002
Fractional PLL (fPLL)
2-4
2013.05.06















































