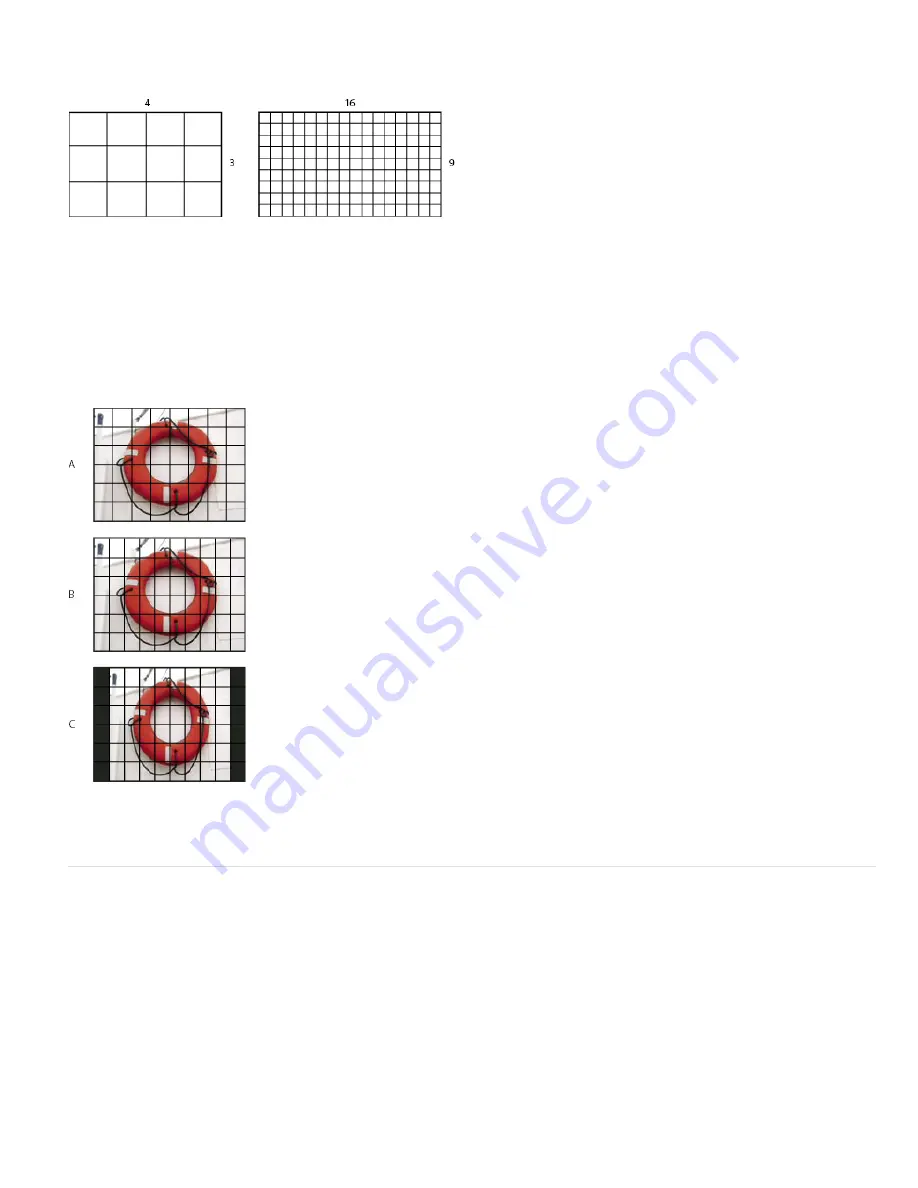
Frame aspect ratio describes the ratio of width to height in the dimensions of an image. For example, DV NTSC has a frame aspect ratio of 4:3 (or
4 width by 3 height) and a typical widescreen frame has a frame aspect ratio of 16:9. Some video cameras can record various frame aspect ratios.
Many cameras that have a widescreen mode use the 16:9 aspect ratio. Many professional films have been shot using even wider aspect ratios.
4:3 frame aspect ratio (left), and wider 16:9 frame aspect ratio (right)
Pixel aspect ratio describes the ratio of width to height of a single pixel in a frame. Different video standards use different pixel aspect ratios. For
example, many computer video standards define a 4:3 aspect ratio frame as 640 pixels wide by 480 pixels high, which results in square pixels.
The computer video pixels in this example have a pixel aspect ratio of 1:1 (square), whereas the DV NTSC pixels have a pixel aspect ratio of 0.91
(nonsquare). DV pixels, which are always rectangular, are vertically oriented in systems producing NTSC video and horizontally oriented in
systems producing PAL video.
If you display rectangular pixels on a square-pixel monitor without alteration, images appear distorted; for example, circles distort into ovals.
However, when displayed on a broadcast monitor, the images appear correctly proportioned because broadcast monitors use rectangular pixels.
Note: When copying or importing images into a nonsquare pixel document, Photoshop automatically converts and scales the image to the pixel
aspect ratio of the document. Images imported from Adobe Illustrator are also properly scaled.
Pixel and frame aspect ratios
A. 4:3 square-pixel image displayed on 4:3 square-pixel (computer) monitor B. 4:3 square-pixel image interpreted correctly for display on 4:3 non-
square pixel (TV) monitor C. 4:3 square-pixel image interpreted incorrectly for display on 4:3 non-square pixel (TV) monitor
Create an image for use in video
1. Create a new document.
2. From the Preset menu in the New dialog box, choose the Film & Video preset.
3. Choose the size that’s appropriate for the video system on which the image will be shown.
4. Click Advanced to specify a color profile and specific pixel aspect ratio.
Important: By default, nonsquare pixel documents open with Pixel Aspect Ratio Correction enabled. This setting scales the image so it
appears as it would on the nonsquare-pixel output device (usually a video monitor).
5. To view the image as it would appear on a computer monitor (square pixel), choose View > Pixel Aspect Ratio Correction.
Summary of Contents for Photoshop CS6
Page 1: ...ADOBE PHOTOSHOP Help and tutorials...
Page 65: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 100: ...Image and color basics...
Page 108: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 176: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 182: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 193: ...applied to the original Smart Object More Help topics Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 236: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 286: ...More Help topics Adjusting image color and tone in CS6 Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 376: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 457: ...Text...
Page 461: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 548: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 570: ...Saving and exporting...
Page 598: ...Printing...
Page 627: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 646: ...Web graphics...
Page 662: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 722: ...Legal Notices Online Privacy Policy...
Page 730: ...Color Management...
Page 739: ......
Page 748: ......






























