TC1796
System Units (Vol. 1 of 2)
Introduction
User’s Manual
1-15
V2.0, 2007-07
Intro, V2.0
1.3.1.1
Asynchronous/Synchronous Serial Interfaces
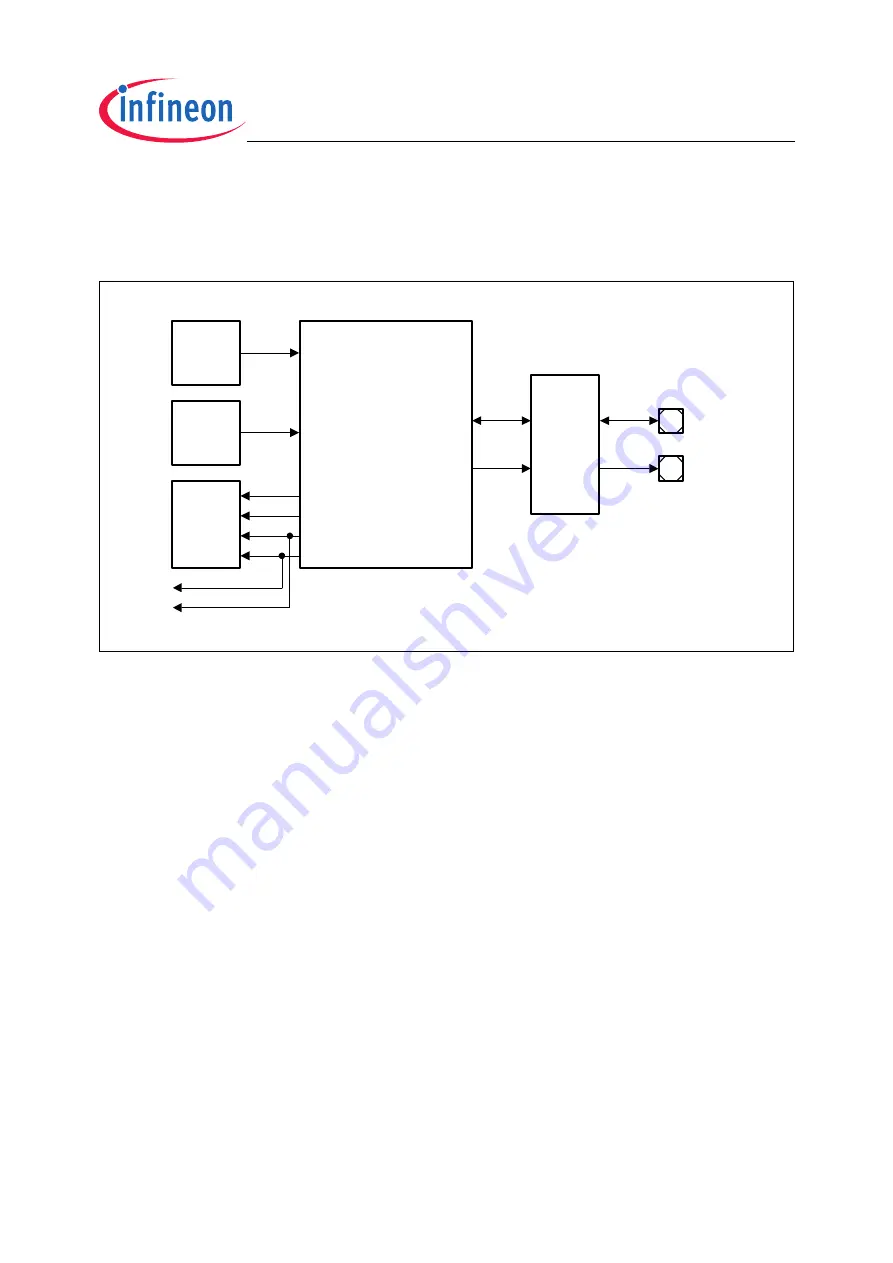
shows a global view of the Asynchronous/Synchronous Serial Interface
(ASC)
Figure 1-2
General Block Diagram of the ASC Interface
The ASC provides serial communication between the TC1796 and other
microcontrollers, microprocessors, or external peripherals.
The ASC supports full-duplex asynchronous communication and half-duplex
synchronous communication. In Synchronous Mode, data is transmitted or received
synchronous to a shift clock that is generated by the ASC internally. In Asynchronous
Mode, 8-bit or 9-bit data transfer, parity generation, and the number of stop bits can be
selected. Parity, framing, and overrun error detection are provided to increase the
reliability of data transfers. Transmission and reception of data is double-buffered. For
multiprocessor communication, a mechanism is included to distinguish address bytes
from data bytes. Testing is supported by a loop-back option. A 13-bit baud rate generator
provides the ASC with a separate serial clock signal which can be very accurately
adjusted by a prescaler implemented as a fractional divider.
Each ASC module, ASC0 and ASC1, communicates with the external world via two I/O
lines. The RXD line is the receive data input signal (in Synchronous Mode also output).
TXD is the transmit output signal. Clock control, address decoding, and interrupt service
request control are managed outside the ASC module kernel.
MCB05574
Clock
Control
Address
Decoder
Interrupt
Control
f
ASC
ASC
Module
(Kernel)
Port
Control
RXD
TXD
RXD
TXD
To DMA
EIR
TBIR
TIR
RIR






























