TC1796
Peripheral Units (Vol. 2 of 2)
Micro Link Interface (MLI)
User’s Manual
23-19
V2.0, 2007-07
MLI, V2.0
23.1.3
Handshake Description
The description of the transmitter/receiver signal handshaking refers to an MLI
connection between an MLI transmitter and an MLI receiver. MLI module transmitter I/O
signals are indicated with prefix “T” and MLI receiver I/O signals are indicated with the
prefix “R”. The 4-line MLI bus between a transmitter and a receiver outside the
controllers uses signal names without any prefix.
In order to lay emphasis where a signal is generated or sampled, actions taken by the
transmitter are described referring to signals with the prefix “T”, whereas receiver actions
are referring to signals with the prefix “R”.
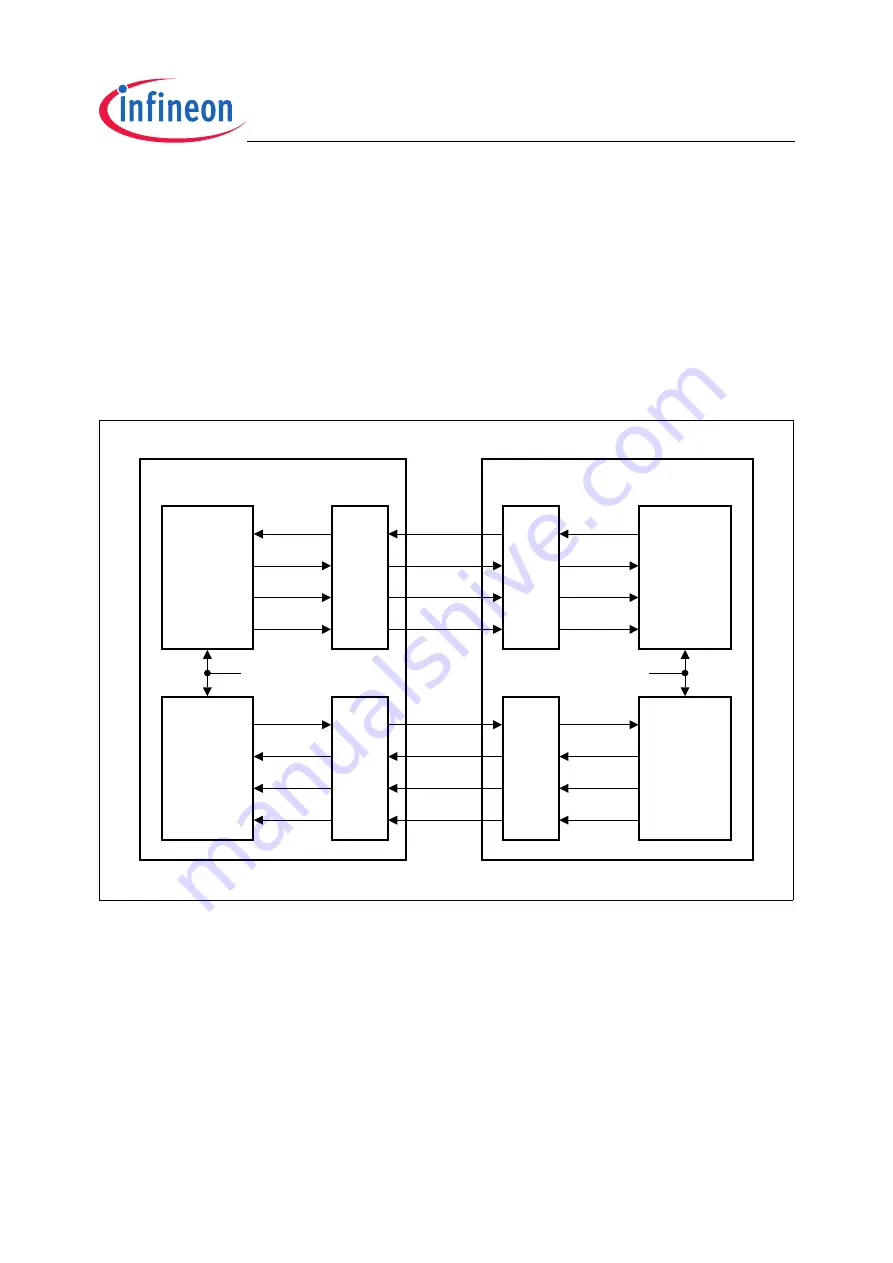
Figure 23-16 Transmitter/Receiver Signal Definitions
The MLI connection allows high data rates and, at the same time, supports significant
signal propagation delays between the transmitter and the receiver. As shown in
, each output signal passes through the port stage, reaches the physical
interface line between the MLI modules, enters via an input stage and can be finally
evaluated. All these steps introduce an accumulating propagation delay. In standard
synchronous serial connections (such as SPI), this delay limits the reachable baud rate
to a few Mbit/s (closed-loop delay problem). In order to support higher baud rates than
a standard SPI, the MLI protocol is based on a full handshake (READY-VALID) to deal
Controller 2
MCA05873_mod
Port
Control
Controller 1
MLI
Receiver
Port
Control
READY
VALID
DATA
CLK
TREADY
TVALID
TDATA
TCLK
RREADY
RVALID
RDATA
RCLK
f
SYS
Controller 1
MLI
Transmitter
Port
Control
MLI
Transmitter
Port
Control
READY
VALID
DATA
CLK
RREADY
RVALID
RDATA
RCLK
TREADY
TVALID
TDATA
TCLK
MLI
Receiver
f
SYS
Controller 2






























