Section 15
Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
Rev. 1.00 Apr. 28, 2008 Page 451 of 994
REJ09B0452-0100
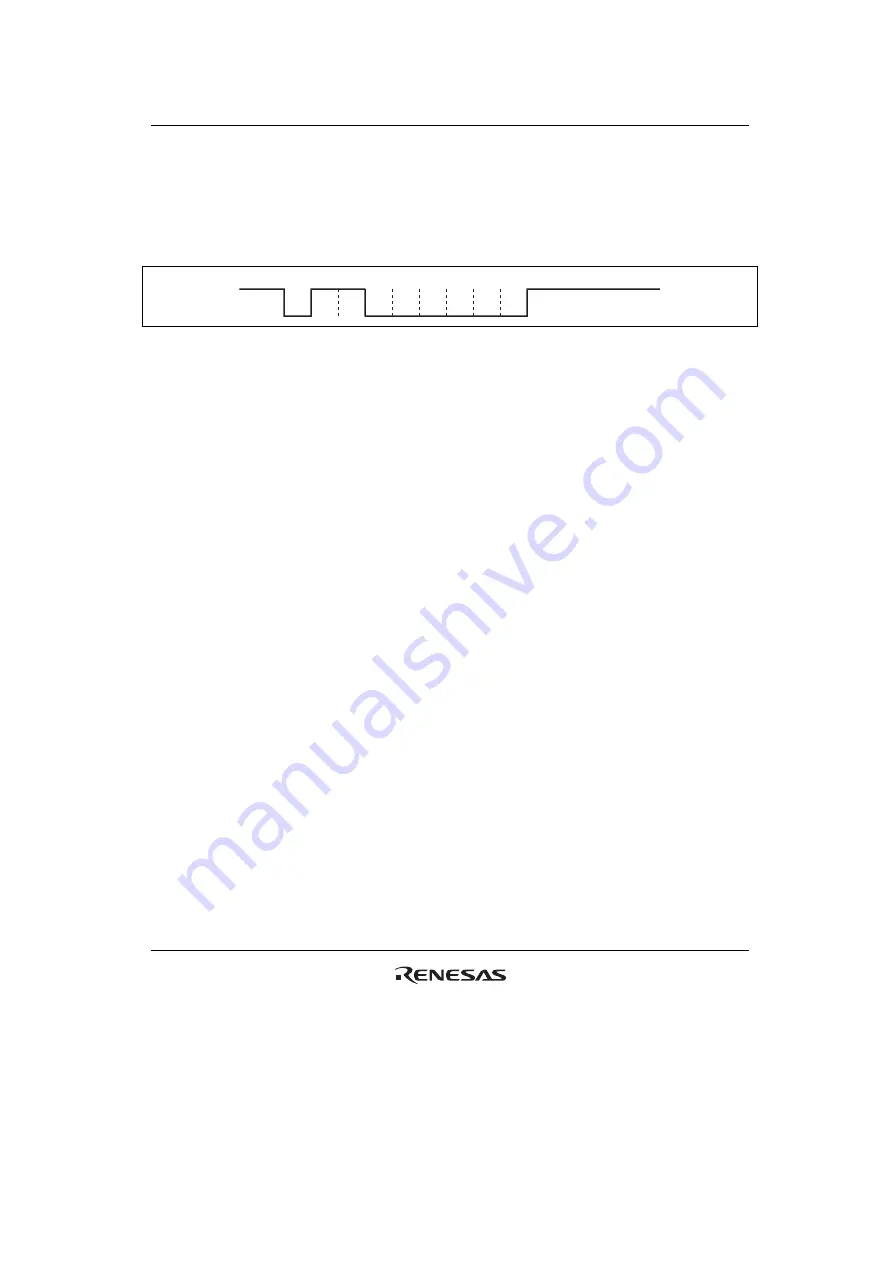
For the direct convention type, logic levels 1 and 0 correspond to states Z and A, respectively, and
data is transferred with LSB-first as the start character, as shown in figure 15.23. Therefore, data
in the start character in the figure is H'3B. When using the direct convention type, write 0 to both
the SDIR and SINV bits in SCMR. Write 0 to the O/
E
bit in SMR in order to use even parity,
which is prescribed by the smart card standard.
Ds
A
Z
Z
A
A
A
Z
A
A
A
(Z)
(Z) state
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Dp
Figure 15.24 Inverse Convention (SDIR = SINV = O/
E
= 1)
For the inverse convention type, logic levels 1 and 0 correspond to states A and Z, respectively
and data is transferred with MSB-first as the start character, as shown in figure 15.24. Therefore,
data in the start character in the figure is H'3F. When using the inverse convention type, write 1 to
both the SDIR and SINV bits in SCMR. The parity bit is logic level 0 to produce even parity,
which is prescribed by the smart card standard, and corresponds to state Z. Since the SINV bit of
this LSI only inverts data bits D7 to D0, write 1 to the O/
E
bit in SMR to invert the parity bit in
both transmission and reception.
15.7.3
Block Transfer Mode
Block transfer mode is different from normal smart card interface mode in the following respects.
•
If a parity error is detected during reception, no error signal is output. Since the PER bit in
SSR is set by error detection, clear the bit before receiving the parity bit of the next frame.
•
During transmission, at least 1 etu is secured as a guard time after the end of the parity bit
before the start of the next frame.
•
Since the same data is not re-transmitted during transmission, the TEND flag in SSR is set
11.5 etu after transmission start.
•
Although the ERS flag in block transfer mode displays the error signal status as in normal
smart card interface mode, the flag is always read as 0 because no error signal is transferred.
Summary of Contents for H8S/2100 Series
Page 2: ...Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page ii of xxvi...
Page 54: ...Section 1 Overview Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 28 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 92: ...Section 2 CPU Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 66 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 158: ...Section 5 Interrupt Controller Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 132 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 244: ...Section 8 8 Bit PWM Timer PWMU Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 218 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 330: ...Section 10 16 Bit Timer Pulse Unit TPU Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 304 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 416: ...Section 13 8 Bit Timer TMR Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 390 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 612: ...Section 18 I 2 C Bus Interface IIC Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 586 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 706: ...Section 20 LPC Interface LPC Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 680 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 752: ...Section 21 FSI Interface Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 726 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 774: ...Section 23 RAM Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 748 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 1008: ...Section 28 Electrical Characteristics Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 982 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 1020: ...Rev 1 00 Apr 28 2008 Page 994 of 994 REJ09B0452 0100...
Page 1023: ......
Page 1024: ...H8S 2117R Group Hardware Manual...
















































