MOTOROLA
Chapter 14. Serial Interface with Time-Slot Assigner
14-13
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
When MCC = 1, the SI
x
RAM entry Þelds function as described in Table 14-2.
14.4.4 SI
x
RAM Programming Example
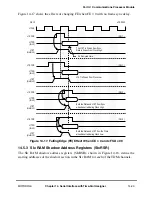
This example shows how to program the RAM to support the 10-bit IDL bus. Figure 14-23
shows the 10-bit IDL bus format. In this example, the TSA supports the B1 channel with
SCC2, the D channel with SCC1, the Þrst 4 bits of the B2 channel with an external device
(using a strobe to enable the external device), and the last 4 bits of B2 with SMC1.
Additionally, the TSA marks the D channel with another strobe signal.
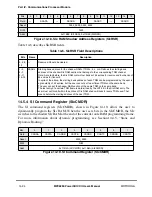
Table 14-2. SI
x
RAM Entry (MCC = 1)
Bits
Name Description
0
MCC
If MCC =1, the other SI
x
RAM entries in this table are valid:
1
LOOP/
ECHO
Channel loopback or echo.
0 Normal mode of operation.
1 Operation depends on the following conÞgurations:
In the receive SI
x
RAM, this bit selects loopback mode for this MCC channel. The channelÕs
transmit data is sent to both the receiverÕs input and to the data output line.
In the transmit SI
x
RAM, this bit selects echo mode for this MCC channel. The channelÕs receive
data is sent both to the transmitterÕs line and to the receiverÕs input.
To use the loop/echo modes, program the receive and transmit SI
x
RAMs identically, except that
the LOOP/ECHO bit should be set in only one of the entry pairs; that is, select only one of the
modes (echo or loopback, not both) per MCC slot. Also, the receive and transmit clocks must be
identical.
2
SUPER MCC super channel enable. See Section 27.5, ÒSuper-Channel Table.Ó
0 The current entry refers to a regular channel.
1 The current entry refers to a super channel.
3Ð10
MCSEL MCC channel select. Indicates the MCC channel the bit/byte group is routed to. 0000_0000 selects
channel 0; 1111_1111, selects channel 255.
For SI1 use values 0Ð127 and for SI2 use values 128Ð255. Note that the channel programming
must be coherent with the MCCF; see Section 27.8, ÒMCC ConÞguration Registers (MCCFx).Ó
11Ð13
CNT
Count.
If SUPER = 0 (normal mode), CNT indicates the number of bits/bytes (according to the BYT bit)
that the routing select of this entry controls. 000 = 1 bit/byte; 111 = 8 bits/bytes.
If SUPER = 1 (MCC super channel), CNT and BYT together indicate whether the current entry is
the Þrst byte of the MCC super channel.
CNT= 000 and BYT = 1ÑThe current entry is the Þrst byte of this MCC super channel.
CNT= 111 and BYT = 0ÑThe current entry is not the Þrst byte of this MCC super channel.
Note that because all SI
x
RAM entries relating to super channels must be 1-byte in resolution, only
the above two combinations of CNT and BYT are allowed when SUPER = 1.
14
BYT
Byte resolution
0 Bit resolution. The CNT value indicates the number of bits in this group.
1 Byte resolution. The CNT value indicates the number of bytes in this group.
15
LST
Last entry in the RAM. Whenever the SI
x
RAM is used, LST must be set in one of the Tx or Rx
entries of each group. Even if all entries of a group are used, LST must still be set in the last entry.
0 Not the last entry in this section of the route RAM.
1 Last entry in this RAM. After this entry, the SI waits for the sync signal to start the next frame.
Note that there must be only an even number of entries in an SI
x
RAM frame, because LST is
active only in odd-numbered entries (assuming the entry count starts with 0). Therefore, to obtain
an even number of entries, an entry may need to be split into two entries.
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......