MOTOROLA
Chapter 2. PowerPC Processor Core
2-25
Part I. Overview
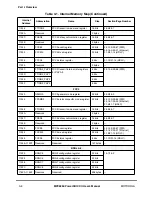
ISI
00400
An ISI exception is caused when an instruction fetch cannot be performed for any of
the following reasons:
¥
The effective (logical) address cannot be translated. That is, there is a page fault
for this portion of the translation, so an ISI exception must be taken to load the
PTE (and possibly the page) into memory.
¥
The fetch access is to a direct-store segment (indicated by SRR1[3] set).
¥
The fetch access violates memory protection (indicated by SRR1[4] set). If the
key bits (Ks and Kp) in the segment register and the PP bits in the PTE are set to
prohibit read access, instructions cannot be fetched from this location.
External
interrupt
00500
An external interrupt is caused when MSR[EE] = 1 and the INT signal is asserted.
Alignment
00600
An alignment exception is caused when the processor core cannot perform a
memory access for any of the reasons described below:
¥
The operand of a ßoating-point load or store is to a direct-store segment.
¥
The operand of a ßoating-point load or store is not word-aligned.
¥
The operand of a
lmw
,
stmw
,
lwarx
, or
stwcx.
is not word-aligned.
¥
The operand of an elementary, multiple or string load or store crosses a segment
boundary with a change to the direct store T bit.
¥
The operand of
dcbz
instruction is in memory that is write-through required
or caching inhibited, or
dcbz
is executed in an implementation that has either no
data cache or a write-through data cache.
¥
A misaligned
eciwx
or
ecowx
instruction
¥
A multiple or string access with MSR[LE] set
The processor core differs from
MPC603e UserÕs Manual
in that it initiates an
alignment exception when it detects a misaligned
eciwx
or
ecowx
instruction and
does not initiate an alignment exception when a little-endian access is misaligned.
Program
00700
A program exception is caused by one of the following exception conditions, which
correspond to bit settings in SRR1 and arise during execution of an instruction:
¥
Illegal instructionÑAn illegal instruction program exception is generated when
execution of an instruction is attempted with an illegal opcode or illegal
combination of opcode and extended opcode Þelds (including PowerPC
instructions not implemented in the processor core), or when execution of an
optional instruction not provided in the processor core is attempted (these do not
include those optional instructions that are treated as no-ops).
¥
Privileged instructionÑA privileged instruction type program exception is
generated when the execution of a privileged instruction is attempted and the
MSR register user privilege bit, MSR[PR], is set. In the processor core, this
exception is generated for
mtspr
or
mfspr
with an invalid SPR Þeld if SPR[0] = 1
and MSR[PR] = 1. This may not be true for all PowerPC processors.
¥
TrapÑA trap type program exception is generated when any of the conditions
speciÞed in a trap instruction is met.
Floating-point
unavailable
00800
If MSR[FP] = 0, the FPRs are disabled and attempting to execute any ßoating-point
instruction causes a ßoating-point unavailable exception. A ßoating-point
unavailable exception cannot occur if MSR[FP] = 1.
Decrementer
00900
The decrementer exception occurs when the most signiÞcant bit of the decrementer
(DEC) register transitions from 0 to 1. Must also be enabled with the MSR[EE] bit.
Reserved
00A00Ð00BFF Ñ
System call
00C00
A system call exception occurs when a System Call (
sc
) instruction is executed.
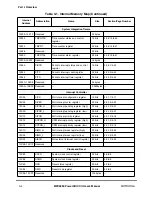
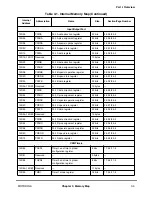
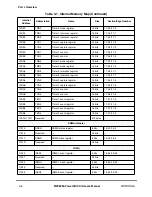
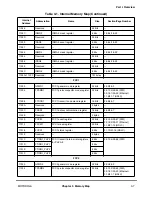
Table 2-5. Exceptions and Conditions (Continued)
Exception
Type
Vector Offset
(hex)
Causing Conditions
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......