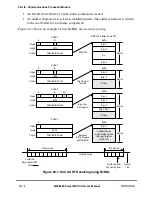
21-6
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
Receive commands are described in Table 21-3.
21.7 Handling Errors in the SCC HDLC Controller
The SCC HDLC controller reports frame reception and transmission errors using BDs,
error counters, and the SCCE. Transmission errors are described in Table 21-4.
Reception errors are described in Table 21-5.
Table 21-3. Receive Commands
Command
Description
ENTER
HUNT
MODE
After a hardware or software reset, once an SCC is enabled in the GSMR, the receiver is
automatically enabled and uses the Þrst BD in the RxBD table. While the SCC is looking for the
beginning of a frame, that SCC is in hunt mode. The
ENTER
HUNT
MODE
command is used to force the
HDLC receiver to stop receiving the current frame and enter hunt mode, in which the HDLC
continually scans the input data stream for a ßag sequence. After receiving the command, the buffer is
closed and the CRC is reset. Further frame reception uses the next BD.
CLOSE
RXBD
Should not be used in the HDLC protocol.
INIT
RX
PARAMETERS
Resets the Rx parameters in the parameter RAM.; issue only when the receiver is disabled. Note that
INIT
TX
AND
RX
PARAMETERS
resets both Tx and Rx parameters.
Table 21-4. Transmit Errors
Error
Description
Transmitter
Underrun
The channel stops transmitting, closes the buffer, sets TxBD[UN], and generates a TXE interrupt if not
masked. Transmission resumes when a
RESTART
TRANSMIT
command is issued. The SCC send and
receive FIFOs are 32 bytes each.
CTS Lost
during Frame
Transmission
The channel stops transmitting, closes the buffer, sets TxBD[CT], and generates the TXE interrupt if
not masked. Transmission resumes after a
RESTART
TRANSMIT
command. If this error occurs on the Þrst
or second buffer of the frame and PSMR[RTE] = 1, the channel resends the frame when CTS is
reasserted and no error is reported. If collisions are possible, to ensure proper retransmission of multi-
buffer frames, the Þrst two buffers of each frame should in total contain more than 36 bytes for SCC or
20 bytes for SCC. The channel also increments the retransmission counter RETRC in the parameter
RAM.
Table 21-5. Receive Errors
Error
Description
Overrun
Each SCC maintains an internal FIFO for receiving data. The CP begins programming the SDMA
channel (if the buffer is in external memory) and updating the CRC when a full or partial FIFOÕs worth
of data (according to GSMR_H[RFW]) is received in the Rx FIFO. When an Rx FIFO overrun occurs,
the previous byte is overwritten by the next byte. The previous data byte and the frame status are lost.
The channel closes the buffer with RxBD[OV] set and generates an RXF interrupt if not masked. The
receiver then enters hunt mode. Even if an overrun occurs during a frame whose address is not
recognized, an RxBD with data length two is opened to report the overrun and the interrupt is
generated.
CD Lost
during Frame
Reception
Highest priority error. The channel stops frame reception, closes the buffer, sets RxBD[CD], and
generates the RXF interrupt if not masked. The rest of the frame is lost and other errors are not
checked in that frame. At this point, the receiver enters hunt mode.
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......