25-2
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
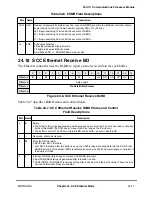
The control byte within the LocalTalk frame indicates the type of frame. Control byte
values from 0x01Ð0x7F are data frames; control byte values from 0x80Ð0xFF are control
frames. Four control frames are deÞned:
¥
ENQÑEnquiry
¥
ACKÑEnquiry acknowledgment
¥
RTSÑRequest to send a data frame
¥
CTSÑClear to send a data frame
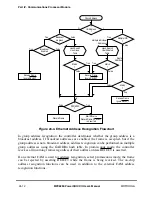
Frames are sent in groups known as dialogs, which are handled by the software. For
instance, to transfer a data frame, three frames are sent over the network. An RTS frame
(not to be confused with the RS-232 RTS pin) is sent to request the network, a CTS frame
is sent by the destination node, and the data frame is sent by the requesting node. These
three frames comprise one possible type of dialog. After a dialog begins, other nodes cannot
start sending until the dialog is complete. Frames within a dialog are sent with a maximum
interframe gap (IFG) of 200 µs. Although the LocalTalk speciÞcation does not state it, there
is also a minimum recommended IFG of 50 µs. Dialogs must be separated by a minimum
interdialog gap (IDG) of 400 µs. In general, these gaps are implemented by the software.
Depending on the protocol, collisions should be encountered only during RTS and ENQ
frames. Once frame transmission begins, it is fully sent, regardless of whether it collides
with another frame. ENQ frames are infrequent and are sent only when a node powers up
and enters the network. A higher-level protocol controls the uniqueness and transmission
of ENQ frames.
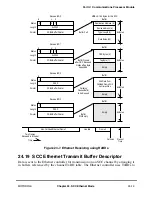
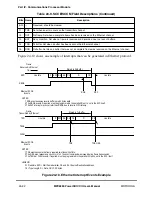
In addition to the frame Þelds, LocalTalk requires that the frame be FM0 (differential
Manchester space) encoded, which requires one level transition on every bit boundary. If
the value to be encoded is a logical zero, FM0 requires a second transition in the middle of
the bit time. The purpose of FM0 encoding is to avoid having to transmit clocking
information on a separate wire. With FM0, the clocking information is present whenever
valid data is present.
25.2 Features
The following list summarizes the features of the SCC in AppleTalk mode:
¥
Superset of the HDLC controller features
¥
FM0 encoding/decoding
¥
Programmable transmission of sync sequence
¥
Automatic postamble transmission
¥
Reception of sync sequence does not cause extra SCCE[DCC] interrupts
¥
Reception is automatically disabled while sending a frame
¥
Transmit-on-demand feature expedites frames
¥
Connects directly to an RS-422 transceiver
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......