19-8
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
24Ð25 DIAG
Diagnostic mode.
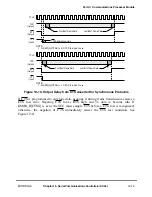
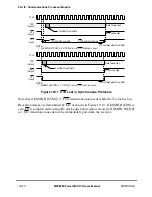
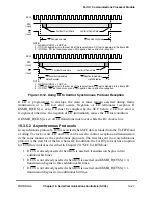
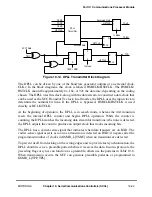
00 Normal operation, CTS and CD are under automatic control. Data is received through RXD and
transmitted through TXD. The SCC uses modem signals to enable or disable transmission and
reception. These timings are shown in Section 19.3.5, ÒControlling SCC Timing with RTS, CTS,
and CD.Ó
01 Local loopback mode. Transmitter output is connected internally to the receiver input, while the
receiver and the transmitter operate normally. The value on RXD is ignored. If enabled, data
appears on TXD, or the parallel I/O registers can be programmed to make TXD high. RTS can also
be programmed to be disabled in the appropriate parallel I/O register. The transmitter and receiver
must share the same clock source, but separate CLK
x
pins can be used if connected to the same
external clock source.
If external loopback is preferred, program DIAG for normal operation and externally connect TXD
and RXD. Then, physically connect the control signals (RTS connected to CD, and CTS grounded)
or set the parallel I/O registers so CD and CTS are permanently asserted to the SCC by
conÞguring the associated CTS and CD pins as general-purpose I/O.
10 Automatic echo mode. The transmitter automatically resends received data bit-by-bit using the Rx
clock provided. The receiver operates normally and receives data if CD is asserted. CTS is
ignored.
11 Loopback and echo mode. Loopback and echo operation occur simultaneously. CD and CTS are
ignored. See the loopback bit description above for clocking requirements.
For TDM operation, the diagnostic mode is selected by SI
x
MR[SDM
x
]; see Section 14.5.2, ÒSI Mode
Registers (SIxMR).Ó
26
ENR
Enable receive. Enables the receiver hardware state machine for this SCC.
0 The receiver is disabled and data in the Rx FIFO is lost. If ENR is cleared during reception, the
receiver aborts the current character.
1 The receiver is enabled.
ENR can be set or cleared, regardless of whether serial clocks are present. Section 19.3.8,
ÒReconÞguring the SCCs,Ó describes how to disable/enable an SCC. Note that other tools, including
the
ENTER
HUNT
MODE
and
CLOSE
RXBD
commands and the E bit of the Rx BD, data provide the
capability to control the receiver.
27
ENT
Enable transmit. Enables the transmitter hardware state machine for this SCC.
0 The transmitter is disabled. If ENT is cleared during transmission, the current character is aborted
and TXD returns to the idle state. Data already in the Tx shift register is not sent.
1 The transmitter is enabled.
ENT can be set or cleared, regardless of whether serial clocks are present. Section 19.3.8,
ÒReconÞguring the SCCs,Ó describes how to disable/enable an SCC. Note that other tools, such as
the
STOP
TRANSMIT
,
GRACEFUL
STOP
TRANSMIT
, and
RESTART
TRANSMIT
commands, the freeze option
and CTS ßow control option in UART mode, and the R bit of the TxBD, also provide the capability to
control the transmitter.
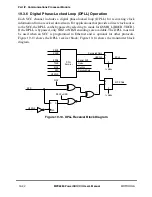
28Ð31 MODE Channel protocol mode. See also GSMR_H[TTX, TRX].
0000 HDLC
0001 Reserved
0010 AppleTalk/LocalTalk
0011 SS7Ñreserved for RAM microcode
0100 UART
0101 ProÞbusÑreserved for RAM microcode
0110 Reserved
0111 Reserved
1000 BISYNC
1001 Reserved
101x Reserved
1100 Ethernet
11xx Reserved
Table 19-2. GSMR_L Field Descriptions (Continued)
Bit
Name
Description
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......