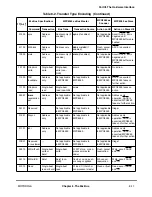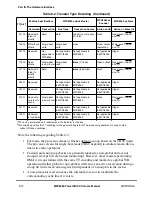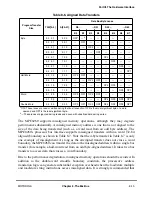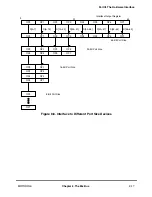
MOTOROLA
Chapter 8. The 60x Bus
8-25
Part III. The Hardware Interface
also detect this event and abort any transfer in progress. If this TA/ARTRY relationship is
not met, the master may enter an undeÞned state. Users may use PPC_ACR[DBGD] to
ensure correct operation of the system.
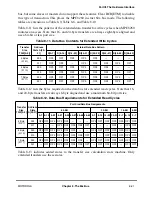
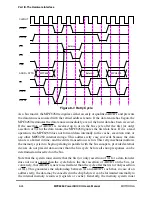
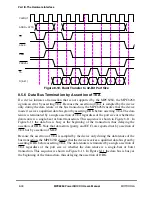
During the clock of a qualiÞed ARTRY, each device master determines whether it should
negate BR and ignore BG on the following cycle. The following cycle is referred to as the
window-of-opportunity for the snooping master. During this window, only the snooping
master that asserted ARTRY and requires a snoop copyback operation is allowed to assert
BR. This guarantees the snooping master a window of opportunity to request and be granted
the bus before the just-retried master can restart its transaction. BG is also blocked in the
window-of-opportunity, so the arbiter has a chance to negate BG to an already granted
potential bus master to perform a new arbitration.
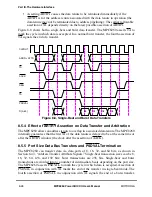
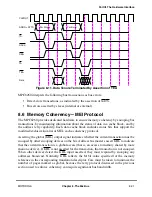
Note that in some systems, an external processor may be unable to perform a pending snoop
copyback when a new snoop operation is performed. In this case, the MPC8260 requests
the window of opportunity if it hits on the new snooped address. To clear its internal snoop
queue, it performs the snoop copyback operation for the earlier snooped address instead of
the current snooped address.
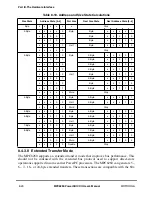
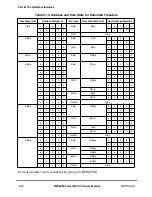
8.4.4.2 Address Tenure Timing ConÞguration
During address tenures initiated by 60x-bus devices, the timing of the assertion of AACK
by the MPC8260 is determined by the BCR[APD] and the pipeline status of the 60x bus.
Because the MPC8260 can support one level of pipelining, it uses AACK to control the
60x-bus pipeline condition. To maintain the one-level pipeline, AACK is not asserted for a
pipelined address tenure until the current data tenure ends. The MPC8260 also delays
asserting AACK until no more address retry conditions can occur. Note that the earliest the
MPC8260 can assert AACK is the clock cycle when the wait-state values set by BCR[APD]
have expired.
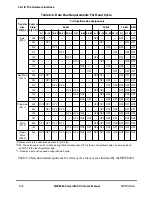
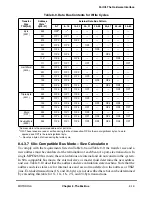
BCR[APD] speciÞes the minimum number of address tenure wait states for address
operations initiated by 60x-bus devices. APD indicates how many cycles the MPC8260
should wait for ARTRY, but because it is assumed that ARTRY can be asserted (by other
masters) only on cacheable address spaces, APD is considered only on transactions that hit
a 60x-assigned memory controller bank and that have GBL asserted during the address
phase.
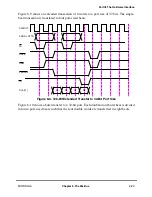
Extra wait states may occur because of other MPC8260 conÞguration parameters. Note that
in a system with an L2 cache, the number of wait states conÞgured by BCR[APD] should
be at least as large as the value needed by the L2 controller to assert hit response. In systems
with multiple potential masters, the number of wait states conÞgured by BCR[APD] should
be at least as large as the value the slowest master would need by to assert a snoop response.
For example, additional wait states are required when the internal processor is in 1:1 clock
mode; this case requires at least one wait state to generate the ARTRY response.
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......