MOTOROLA
Chapter 28. Fast Communications Controllers (FCCs)
28-5
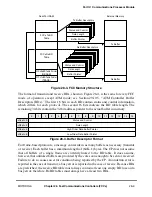
Part IV. Communications Processor Module
5
CDP
CD pulse (transparent mode only)
0 Normal operation (envelope mode). CD should envelope the frame; to negate CD while receiving
causes a CD lost error.
1 Pulse mode. Once CD is asserted (high to low transition), synchronization has been achieved,
and further transitions of CD do not affect reception.
This bit must be set if this FCC is used in the TSA.
6
CTSP
CTS pulse
0 Normal operation (envelope mode). CTS should envelope the frame; to negate CTS while
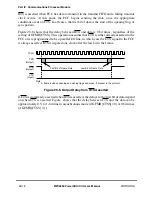
transmitting causes a CTS lost error. See Section 28.11, ÒFCC Timing Control.Ó
1 Pulse mode. CTS is asserted when synchronization is achieved; further transitions of CTS do not
affect transmission.
7
CDS
CD sampling
0 The CD input is assumed to be asynchronous with the data. The FCC synchronizes it internally
before data is received. (This mode is illegal in transparent mode when SYNL = 0b00.)
1 The CD input is assumed to be synchronous with the data, giving faster operation. In this mode,
CD must transition while the receive clock is in the low state. When CD goes low, data is
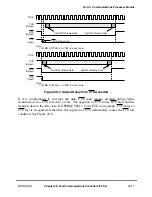
received. This is useful when connecting MPC8260s in transparent mode since it allows the RTS
signal of one MPC8260 to be connected directly to the CD signal of another MPC8260.
8
CTSS
CTS sampling
0 The CTS input is assumed to be asynchronous with the data. When it is internally synchronized
by the FCC, data is sent after a delay of no more than two serial clocks.
1 The CTS input is assumed to be synchronous with the data, giving faster operation. In this mode,
CTS must transition while the transmit clock is in the low state. As soon as CTS is low, data
transmission begins. This mode is useful when connecting MPC8260 in transparent mode
because it allows the RTS signal of one MPC8260 to be connected directly to the CTS signal of
another MPC8260.
9--15
Ñ
Reserved, should be 0.
16Ð17 SYNL
Sync length (transparent mode only). Determines the operation of an FCC receiver conÞgured for
totally transparent operation only. See Section 32.3.1, ÒIn-Line Synchronization Pattern.Ó
00 The sync pattern in the FDSR is not used. An external sync signal is used instead (CD signal
asserted: high to low transition).
01 Automatic sync (assumes always synchronized, ignores CD signal).
10 8-bit sync. The receiver synchronizes on an 8-bit sync pattern stored in the FDSR. Negation of
CD causes CD lost error.
11 16-bit sync. The receiver synchronizes on a 16-bit sync pattern stored in the FDSR. Negation of
CD causes CD lost error.
18
RTSM
RTS mode
0 Send idles between frames as deÞned by the protocol. RTS is negated between frames (default).
1 Send ßags/syncs between frames according to the protocol. RTS is asserted whenever the FCC
is enabled.
19Ð20 RENC
Receiver decoding method. The user should set RENC = TENC in most applications.
00 NRZ
01 NRZI (one bit mode HDLC or transparent only)
1x Reserved
21
REVD
Reverse data (valid for a totally transparent channel only)
0 Normal operation
1 The totally transparent channels on this FCC (either the receiver, transmitter, or both, as deÞned
by TTX and TRX) reverse bit order, transmitting the MSB of each octet Þrst.
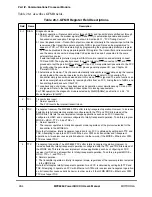
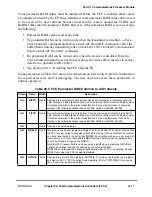
Table 28-1. GFMR Register Field Descriptions (Continued)
Field
Name Description
Summary of Contents for MPC8260 PowerQUICC II
Page 1: ...MPC8260UM D 4 1999 Rev 0 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual ª ª ...
Page 66: ...lxvi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 88: ...1 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 120: ...2 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 138: ...Part II iv MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II Configuration and Reset ...
Page 184: ...4 46 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II ConÞguration and Reset ...
Page 202: ...Part III vi MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 266: ...8 34 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 382: ...10 106 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 392: ...11 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III The Hardware Interface ...
Page 430: ...Part IV viii MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 490: ...14 36 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 524: ...17 10 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 556: ...18 32 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 584: ...19 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 632: ...21 24 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 652: ...22 20 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 668: ...23 16 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 758: ...27 28 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 780: ...28 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 874: ...29 94 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 920: ...31 18 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Communications Processor Module ...
Page 980: ...A 4 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1002: ...Index 22 MPC8260 PowerQUICC II UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA INDEX ...
Page 1006: ......