Exporting
16
242
Lightscape
Note:
Depending on the type of format that you
select, Lightscape displays the appropriate exten-
sion in the Filename box.
6.
If you selected Generic Image in the Panoramic
Format list, choose a format from the Image Format
list.
7.
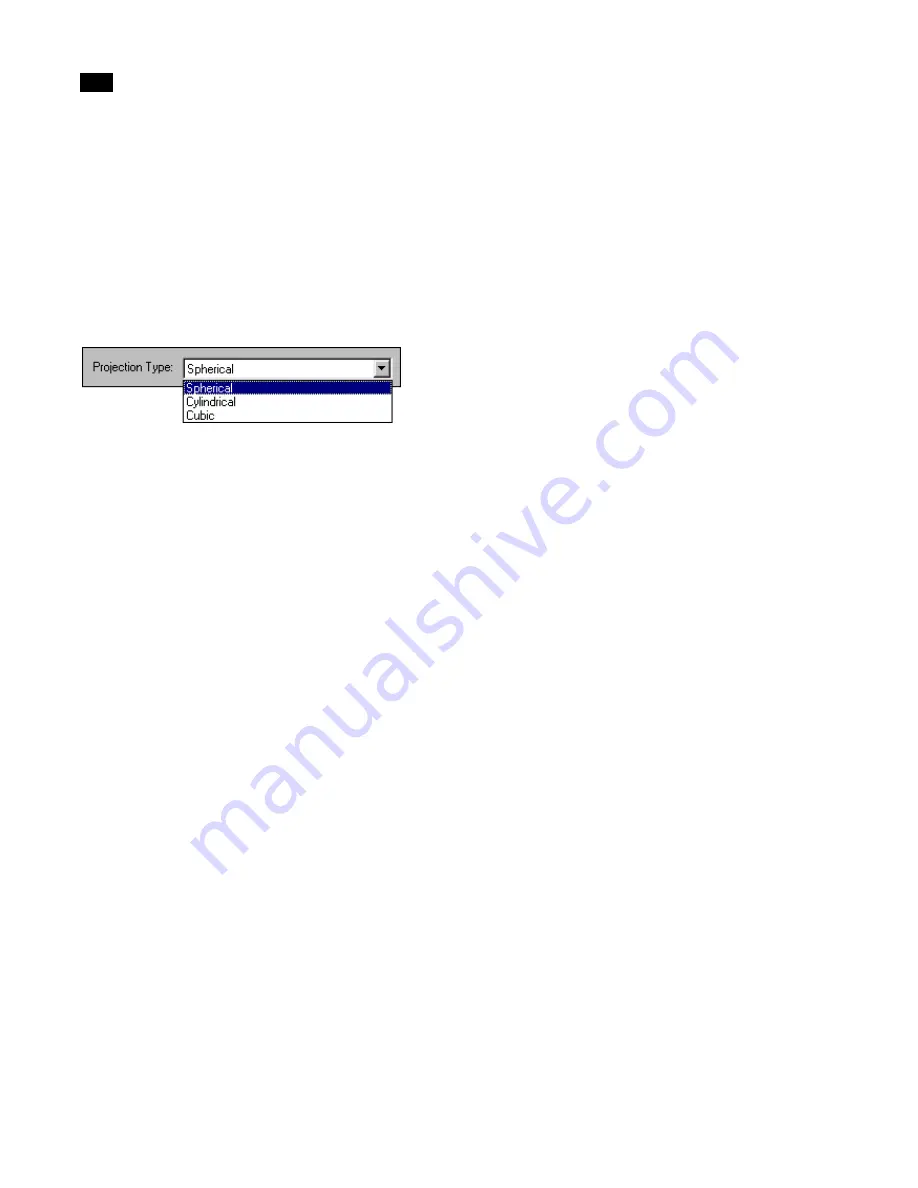
Select the type of projection from the Projection
Type list.
8.
Choose the image size from the Image Size list,
or enter the width and height values (in pixels) in the
corresponding boxes.
9.
Click OK.
A panoramic image file is created from the Solution
file.
To stop exporting the image:
Press Esc while Lightscape is creating the panoramic
image.
Choosing a Panoramic Image Format
You can choose the panoramic image format to
which you want to export your Solution file. You can
generate panoramic images for use in a supported
panoramic viewer or create a generic image.
Generic Image
Use this option to export an image for use in an
authoring kit that you can use to create panoramics
in unsupported formats. This is the default format.
RealSpace (IVR)
Use this option to export a RealVR™ Traveler (.ivr)
panoramic file. This file format supports spherical,
cylindrical, and cubic projections.
VRML 2.0 (Background)
Use this option to export a VRML (.wrl) panoramic
file. This file format supports cubic projections only.
IBM PanoramIX
Use this option to export an IBM PanoramIX (.pan)
file. This file format supports cylindrical and cubic
projections.
Selecting a Projection Type
The projection type (and your panoramic viewer)
determines the way you look around in the image.
For example, some projections provide a full view of
the image and other projection types only provide
left and right viewing in the image.
Spherical
Choose a spherical projection to look anywhere in
the image (including left, right, up, and down).
Cylindrical
Choose a cylindrical projection to look left and right
in the image but not up or down. This option creates
an image that is half the size of a spherical
projection.
Cubic
Choose a cubic projection to look up and down in
addition to left and right. This option creates an
image that has a slower viewing speed than spherical
or cylindrical projections, but better image quality
for the size of the image.
If you choose this option, the system ignores your
current focus point and generates an axis-aligned
projection. This means that the direction of the
initial view may not be the same as the direction of
the view in Lightscape.
Summary of Contents for LIGHTSCAPE
Page 1: ...SULO 4 31 93 36034333308355 LJKWVFDSH...
Page 18: ...NOTES 10...
Page 110: ...NOTES 102...
Page 136: ...NOTES 128...
Page 166: ...NOTES 158...
Page 176: ...NOTES 168...
Page 202: ...NOTES 194...
Page 210: ...NOTES 202...
Page 248: ...NOTES 240...
Page 294: ...NOTES 286...
Page 308: ...NOTES 300...
Page 316: ...NOTES 308...
Page 324: ...NOTES 316...
Page 342: ...Glossary 334 Lightscape...
Page 360: ...Index ix 352 Lightscape...
Page 362: ......






























