Modeling Guidelines
193
❚❘❘
Model Efficiently
Model surfaces in the most efficient way possible.
For example, when creating a revolved surface, set
the tessellation complexity of the object to a coarse
value, and use smoothing within Lightscape to get
the curved effect.
Model Surfaces as Regular Polygons
Many shadow artifacts are the product of meshing
strangely shaped surfaces (such as adjacent, long,
thin, triangular surfaces). Rectangular polygons and
equilateral triangles produce the best effects.
Avoid Overlapping Coplanar Surfaces
Overlapping coplanar surfaces may display artifacts
or noise when processed. In the Preparation file,
coplanar surfaces appear to blink or sparkle when
you orbit around the model. Delete one of the
surfaces, and verify the orientation of the remaining
surface. For more information, see “Working with
Surfaces” on page 95.
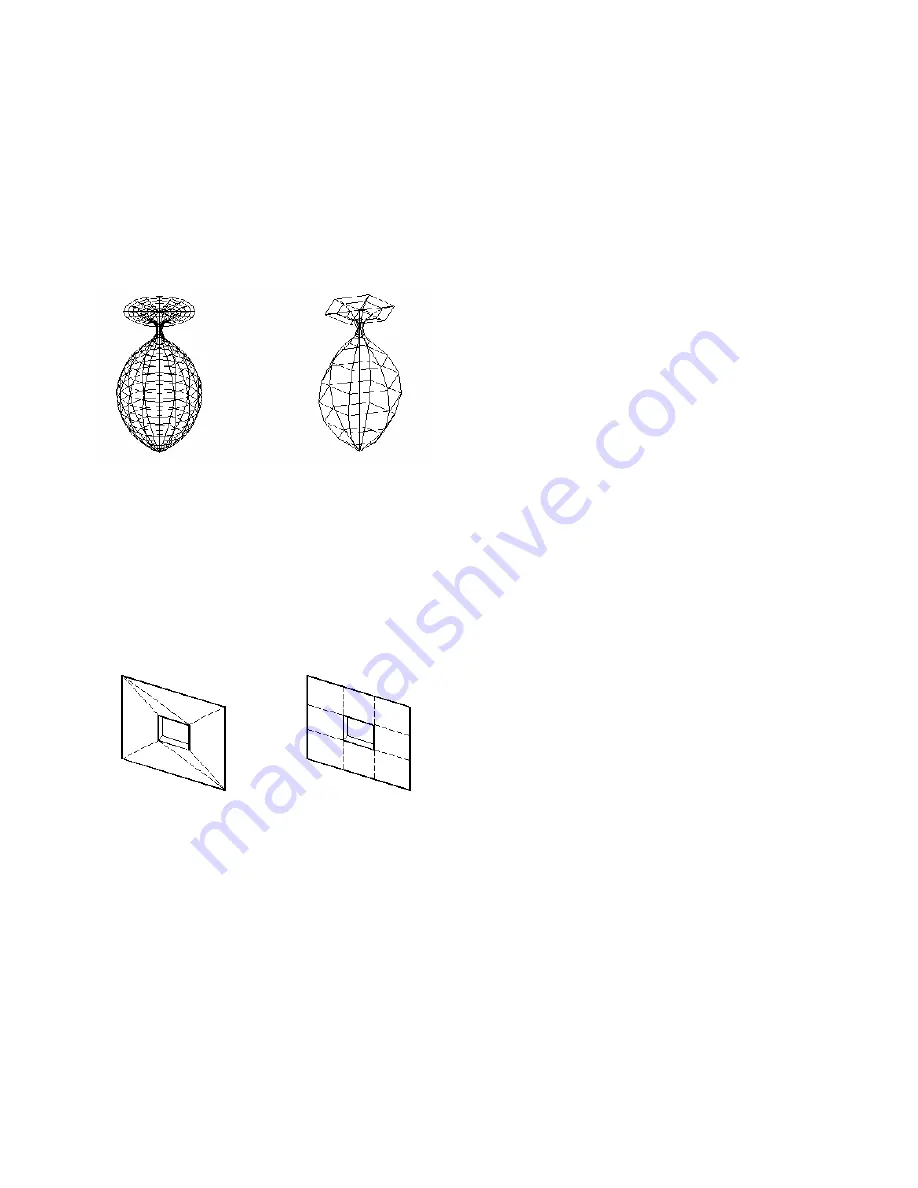
Complex geometry processes faster when
modeled efficiently, as shown on the right
Surfaces with openings are best modeled as
shown on the right
Summary of Contents for LIGHTSCAPE
Page 1: ...SULO 4 31 93 36034333308355 LJKWVFDSH...
Page 18: ...NOTES 10...
Page 110: ...NOTES 102...
Page 136: ...NOTES 128...
Page 166: ...NOTES 158...
Page 176: ...NOTES 168...
Page 202: ...NOTES 194...
Page 210: ...NOTES 202...
Page 248: ...NOTES 240...
Page 294: ...NOTES 286...
Page 308: ...NOTES 300...
Page 316: ...NOTES 308...
Page 324: ...NOTES 316...
Page 342: ...Glossary 334 Lightscape...
Page 360: ...Index ix 352 Lightscape...
Page 362: ......
















































