Chapter 16: Diagnostic Console
310
Option
Description
No DNS Resolution
Does not resolve addresses to host
names.
Use ICMP (vs. normal
UDP)
Use ICMP ECHO instead of UDP
datagrams.
4. Type values for how many hops the traceroute command will use in
outgoing probe packets (default is 30), the UDP destination port to
use in probes (default is 33434), and the size for the traceroute
packets. If left blank, defaults will be used.
Optional.
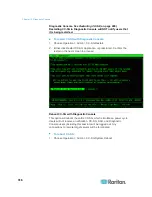
5. Click Traceroute in the bottom right-hand corner of the window.
6. Press Ctrl+C or Ctrl+Q to terminate the traceroute session. A
Return? prompt appears; press Enter to return to the Traceroute
menu. The Return? prompt also appears when Traceroute
terminates d
ue to “destination reached” or “hop count exceeded”
events occur.
Edit Static Routes
In Static Routes, you can view the current IP routing table and modify,
add, or delete routes. Careful use and placement of static routes may
actually improve the performance of your network, allowing you to
conserve bandwidth for important business applications. Click with the
mouse or use the Tab and arrow keys to navigate and press the Enter
key to select a value.
To view or change static routes:
1. Choose Operation > Network Interfaces > Static Routes.
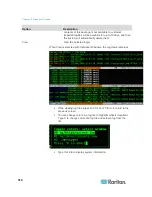
2. The current IP routing table page opens. You can add associated IP
route to the routing table by selecting Add Host Route or Add
Network Route. The items in the routing table are selectable, and
you can delete a route from the table by selecting Delete Route.The
Refresh button updates the routing information in the table.
Add Host Route takes a Destination Host IP Address, and either
a Gateway IP Address or interface name as shown in Status
Console, or both.
Add Network Route is similar but takes a Destination Network
and Netmask.
With every item selected or highlighted in the table, you can
select Delete Route to remove the route. The only exception is
the route associated with current host and interface, which
CC-SG does not allow you to delete.