Chapter 16: Diagnostic Console
309
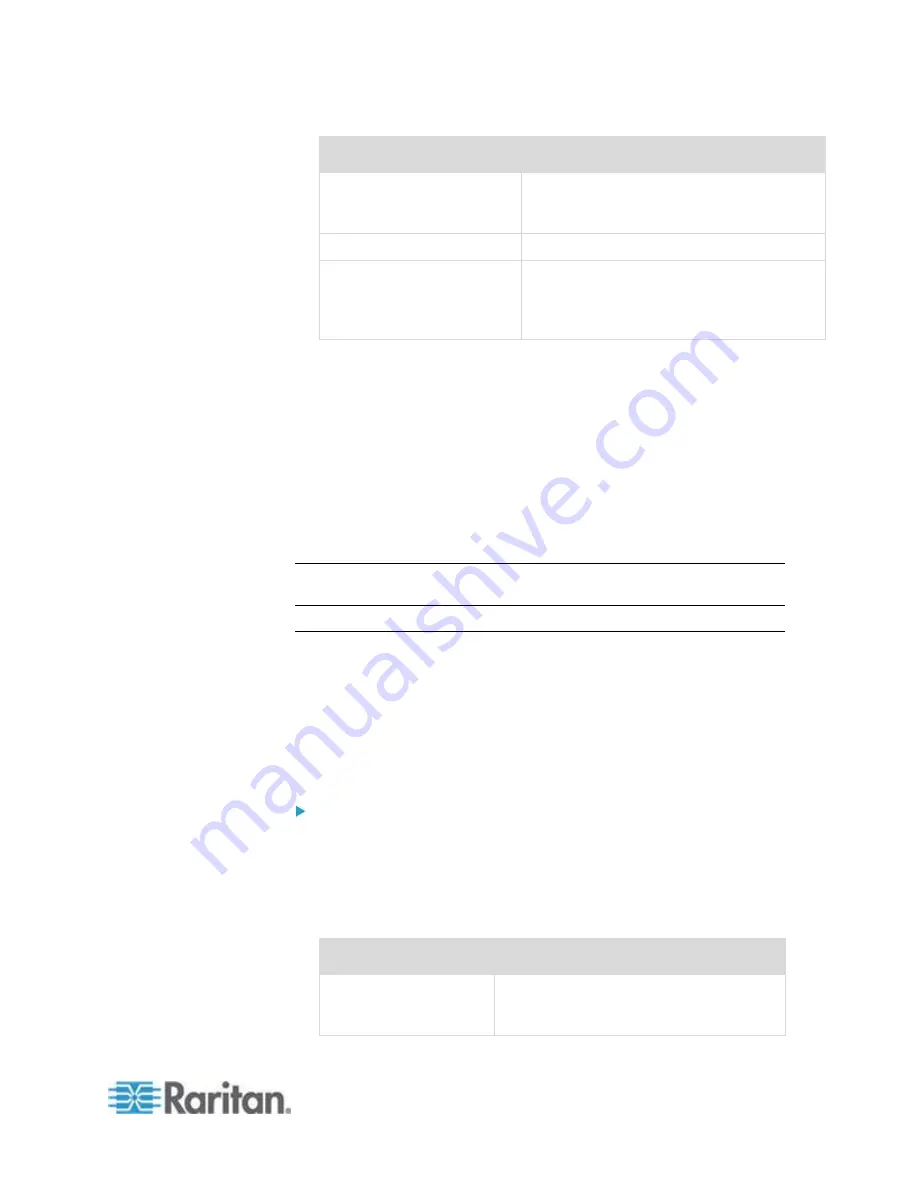
Option
Description
Record Route
Records route. Turns on the IP record route
option, which will store the route of the
packet inside the IP header.
Use Broadcast Address
Allows pinging a broadcast message.
Adaptive Timing
Adaptive ping. Interpacket interval adapts to
round-trip time, so that effectively not more
than one unanswered probes present in the
network. Minimal interval is 200 msec.
4. Type values for how many seconds the ping command will execute,
how many ping requests are sent, and the size for the ping packets.
Default is 56, which translates into 64 ICMP data bytes when
combined with 8 bytes of ICMP header data. If left blank, defaults are
used.
Optional.
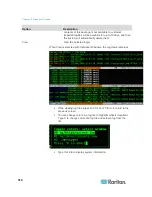
5. Click Ping. If the results show a series of replies, the connection is
working. The time shows you how fast the connection is. If you see a
"timed out" error instead of a reply, the connection between your
computer and the domain is not working. See
Edit Static Routes
(on page 310).
6. Press Ctrl+C to terminate the session.
Note: Press CTRL+Q to display a statistics summary for the session so
far and continue to ping the destination.
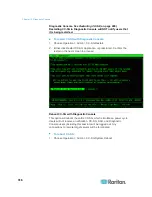
Use Traceroute
Traceroute is often used for network troubleshooting. By showing a list of
routers traversed, it allows you to identify the path taken from your
computer to reach a particular destination on the network. It will list all
the routers it passes through until it reaches its destination, or fails to and
is discarded. In addition to this, it will tell you how long each 'hop' from
router to router takes. This can help identify routing problems or firewalls
that may be blocking access to a site.
To perform a traceroute on an IP address or hostname:
1. Choose Operation > Network Interfaces > Traceroute.
2. Enter the IP address or hostname of the target you wish to check in
the Traceroute Target field.
3. Select:
Optional.
Option
Description
Verbose
Verbose output, which lists received ICMP
packets other than TIME_EXCEEDED
and UNREACHABLEs.