16.3
Current reversal and Weak-end infeed logic for
distance protection 3-phase ZCRWPSCH (85)
IP15751-1 v4
16.3.1
Identification
M15073-1 v5
Function description
IEC 61850
identification
IEC 60617
identification
ANSI/IEEE C37.2
device number
Current reversal and weak-end infeed
logic for distance protection 3-phase
ZCRWPSCH
-
85
16.3.2
Application
IP15023-1 v1
16.3.2.1
Current reversal logic
M13895-4 v6
To avoid this kind of disturbances, a fault current reversal logic (transient blocking
logic) can be used.
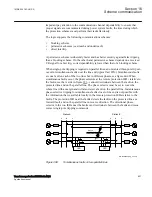
The unwanted operations that might occur can be explained by looking into Figure
. Initially the protection A2 at A side will detect a fault in forward
direction and send a communication signal to the protection B2 at remote end, which is
measuring a fault in reverse direction.
en99000043_ansi.vsd
Strong
source
LINE 1
LINE 2
A:1
A:2
B:1
B:2
A
B
Weak
source
FAULT
CLOSED
CLOSED
CLOSED
CLOSED
ANSI99000043 V1 EN-US
Figure 387:
Current distribution for a fault close to B side when all breakers are
closed
When the breaker B1 opens for clearing the fault, the fault current through B2 bay will
invert. If the communication signal has not reset at the same time as the distance
protection function used in the teleprotection scheme has switched on to forward
direction, we will have an unwanted operation of breaker B2 at B side.
Section 16
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Scheme communication
826
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RET670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 64: ...58 ...
Page 74: ...68 ...
Page 104: ...98 ...
Page 194: ...188 ...
Page 518: ...512 ...
Page 618: ...612 ...
Page 648: ...642 ...
Page 666: ...660 ...
Page 672: ...666 ...
Page 682: ...676 ...
Page 844: ...838 ...
Page 868: ...862 ...
Page 956: ...950 ...
Page 964: ...958 ...
Page 1004: ...998 ...
Page 1014: ...1008 ...
Page 1015: ...1009 ...