may cause cavitations. The risk for damages to hydro turbines can justify reverse
power protection in unattended plants.
A hydro turbine that rotates in water with closed wicket gates will draw electric power
from the rest of the power system. This power will be about 10% of the rated power. If
there is only air in the hydro turbine, the power demand will fall to about 3%.
Diesel engines should have reverse power protection. The generator will take about
15% of its rated power or more from the system. A stiff engine may require perhaps
25% of the rated power to motor it. An engine that is well run in might need no more
than 5%. It is necessary to obtain information from the engine manufacturer and to
measure the reverse power during commissioning.
Gas turbines usually do not require reverse power protection.
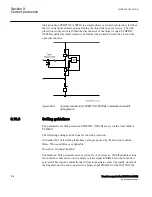
Figure
illustrates the reverse power protection with underpower IED and with
overpower IED. The underpower IED gives a higher margin and should provide better
dependability. On the other hand, the risk for unwanted operation immediately after
synchronization may be higher. One should set the underpower IED to trip if the active
power from the generator is less than about 2%. One should set the overpower IED to
trip if the power flow from the network to the generator is higher than 1%.
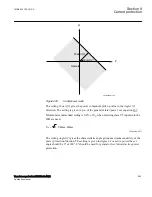
Underpower IED
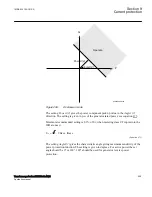
Overpower IED
Q
Q
P
P
Operating point
without
turbine torque
Margin
Margin
Operate
Line
Operate
Line
Operating point
without
turbine torque
IEC06000315-2-en.vsd
IEC06000315 V2 EN-US
Figure 287:
Reverse power protection with underpower IED and overpower IED
9.13.3
Setting guidelines
SEMOD172150-4 v7
GlobalBaseSel
: Selects the global base value group used by the function to define
IBase
,
VBase
and
SBase
as applicable.
Operation
: With the parameter
Operation
the function can be set
Enabled
/
Disabled
.
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Section 9
Current protection
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
587
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RET670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 64: ...58 ...
Page 74: ...68 ...
Page 104: ...98 ...
Page 194: ...188 ...
Page 518: ...512 ...
Page 618: ...612 ...
Page 648: ...642 ...
Page 666: ...660 ...
Page 672: ...666 ...
Page 682: ...676 ...
Page 844: ...838 ...
Page 868: ...862 ...
Page 956: ...950 ...
Page 964: ...958 ...
Page 1004: ...998 ...
Page 1014: ...1008 ...
Page 1015: ...1009 ...