Hotline: +49 5251 688865-99
Hotline: +49 5251 688865-99
Hotline: +49 5251 688865-99
Hotline: +49 5251 688865-99
Hotline: +49 5251 688865-99
. Operating Manual grandMA Version 5.4
125
125
125
125
125
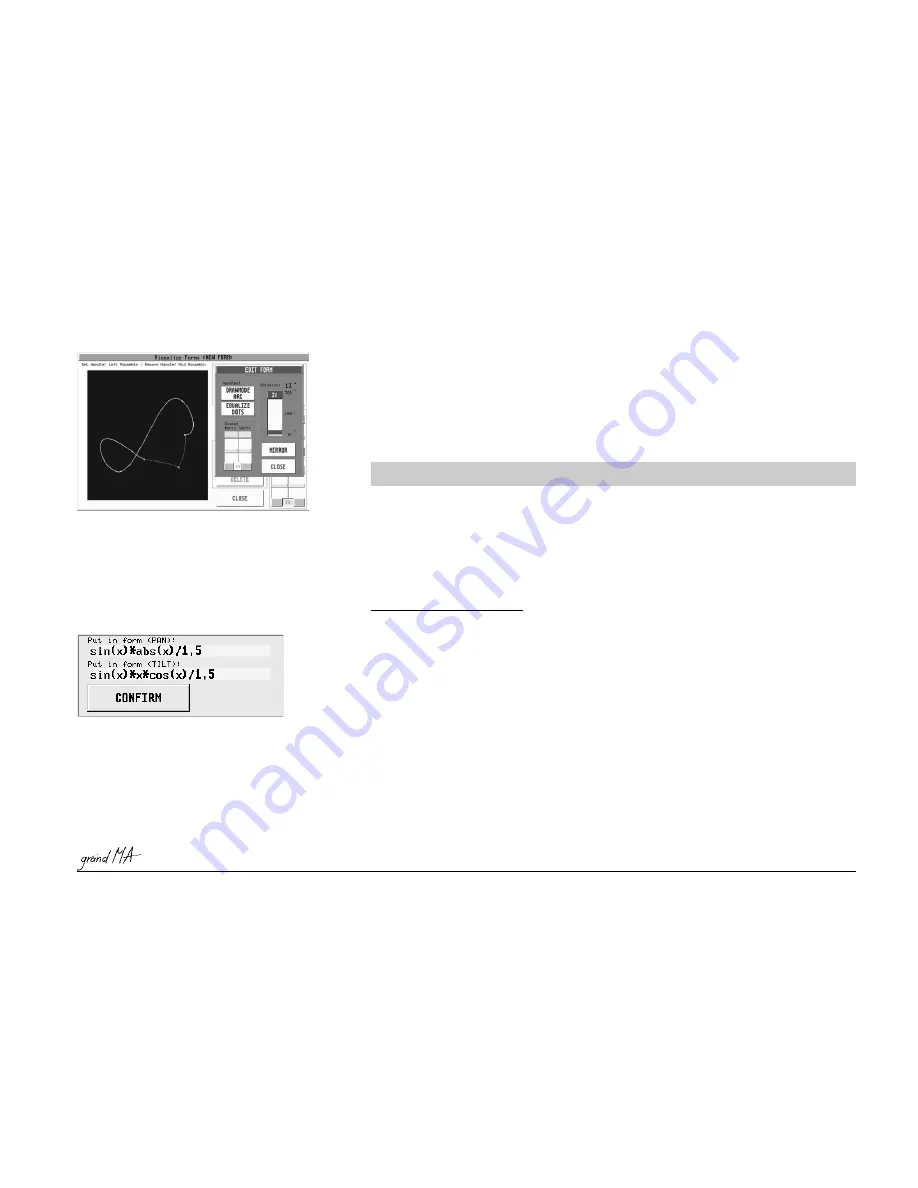
Make a left mouse click on the respective fields –
now enter the formula via keyboard.
The form will be confirmed by pressing CONFIRM.
6.7.2
6.7.2
6.7.2
6.7.2
6.7.2Modifying Forms
Modifying Forms
Modifying Forms
Modifying Forms
Modifying Forms
The EDIT FORMS window will open by pressing the EDIT key.
Make a left click with the mouse on at least three positions of the marked form. With each click on the form, a
new red dot will be displayed on that position. In order to delete one of the dots, middle click with the mouse on
this dot.
To reshape the form, click and drag with the mouse on one of the red dots. If you click the right mouse key during
the reshaping (while holding the left mouse key), you can define the reshaping each time.
By pressing the key, you can program in which way the lines shall be drawn when reshaping the form:
- ANGLE: straight line
- ARC: outer arc
- ARROW: inner arc
By reshaping the form, the lines will be expanded and, respectively, the extended positions of the form will be
reported to the Fixture faster.
If the extended lines and, consequently, the longer ways for the Fixture are to be transmitted with the same
speed, you have to press the EQUALIZE DOTS key once.
The form can be modified in its horizontal or vertical size using the Hori: and Vert: sliders. By pressing the dark-
grey key below the modified sliders shortly, both values can be set simultaneously. By pressing the “< >“ key,
both sliders can be coupled, so that the size can be modified simultaneously.
Using the ROTATION slider, the form can be turned from 0° to 360°.
By pressing the MIRROR key, the form can be mirrored.
You can leave the EDIT menu with the CLOSE key.
With good knowledge in maths, you can also use formulas for PAN and TILT.
Syntax to enter a formula manually:
The standard display of mathematic formulas will be executed. The following is allowed:
Mathematic Basic Operators: +, –, *, /
Numerical constants: integers, floatingpoint numbers or exponential figures
Example for valid numerical constants: 2.71818
1.2e – 2
0,4
Other constants:
pi
corresponds to the circle figure
π
Variables:
x
Mathematical functions:
–
sin(x)
or
sinus(x)
–
cos(x)
or
cosinus(x)
–
abs(x)
corresponds to the absolute amount
–
sqrt(x)
corresponds to the square root
–
pow(x; y)
corresponds to the y Power of x
Arguments errors with x = 0 und y < = 0 or with x < 0 and y are no integers
Examples: sin(3 * x)
sqrt(abs(x)) * sin(x)
sin(x) * cos(3 * x) * pi/2
(cos(x) * abs(x) + 1) / pow(x;2)
(cos(0.5 * x) * abs(x) + 0.5) / 2






























