IO-390-D Series Engine Maintenance Manual
© 2020 Avco Corporation. All Rights Reserved
72-30
March 2020
Page 199
IO-390-D Series Engine Maintenance Manual
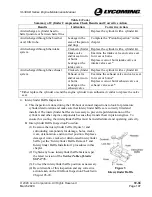
Table 3
Borescope Inspection Steps, Results and Corrective Action
Inspection Step
If these are the results…
Take this corrective action…
Examine valve seat inserts for
scoring, pitting, erosion,
burning or damage
Eroded, scored, burnt, pitted
or damaged valve seats
Replace the cylinder or send the
engine cylinder to an authorized
vendor to replace the valve guide.
Examine spark plug Heli-
Coils
®
for protrusion into the
combustion chamber
Spark plug Heli-Coil
®
protrudes into combustion
chamber
Replace the Heli-Coil
®
per the
“Heli-Coil
®
Replacement”
procedure in this chapter.
Look for discoloration on the
circumference of the exhaust
valve face
Discoloration on the
circumference of the exhaust
valve face
Remove and examine the exhaust
valve.
Look for cracks and erosion
on the exhaust valve face
Cracks or erosion on the
exhaust valve face
Remove and examine the exhaust
valve.
Look for discoloration on the
circumference of the intake
valve face
Discoloration on the
circumference of the intake
valve face
Remove and examine the intake
valve.
Look for cracks and erosion
on the intake valve face
Cracks or erosion on the
intake valve face
Replace the intake valve.
Examine the cylinder bore for
scoring, rubbing, or corrosion
Scoring or piston rub or
corrosion on cylinder bore
Remove and examine the engine
cylinder.
Look for excessive oil in the
cylinder
Excessive oil in the cylinder
Remove and examine the engine
cylinder.
Remove and examine the suction
screen and oil filter/pressure
screen per Chapter 12-10.
Examine the piston crown for
erosion or damage
Erosion or damage on piston
crown
Remove the engine cylinder and
examine the piston.
6.
Exhaust Valve and Guide Inspection
On IO-390-D engines, this inspection is to be done after every 1000 hours of engine operation or
earlier if valve sticking is suspected.
NOTICE:
If valve sticking is a problem, this inspection must be done every 400 hours. Refer
to “Corrective Action for Valve Sticking” in this chapter.
Sticking between the valve stem and guide (on intake and exhaust valves) can
substantially change valve opening and closing. If the valve cannot open or close
correctly, incomplete combustion will occur, which can cause formation of more
deposits and increased valve sticking. Because a correctly-timed sequence of valve
opening and closing is essential to efficient and reliable engine operation, the cause
of valve sticking must be identified and corrected.
WARNING
A STUCK VALVE CAN CAUSE ENGINE DAMAGE.