CHAPTER 7: PROTECTION
GROUPED PROTECTION ELEMENTS
D90
PLUS
LINE DISTANCE PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
207
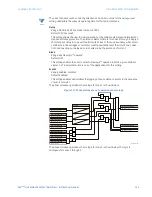
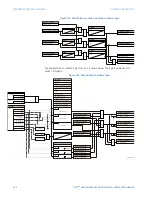
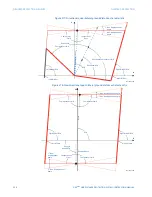
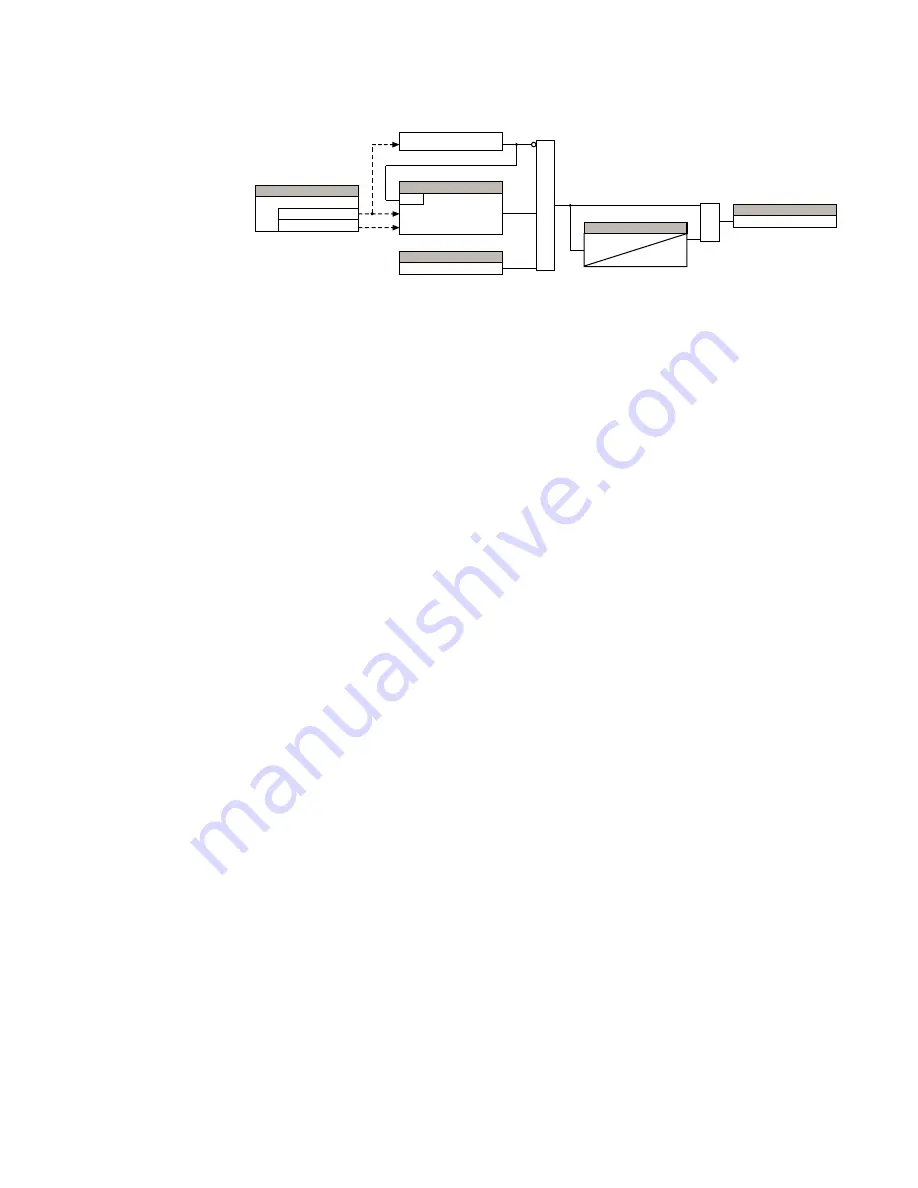
Figure 183: Ground directional supervision scheme logic
Power swing detect settings
The power swing detect element provides both power swing blocking and out-of-step
tripping functions. The element measures the positive-sequence apparent impedance and
traces its locus with respect to either two or three user-selectable operating characteristic
boundaries. Upon detecting appropriate timing relations, the blocking and/or tripping
indication is given through FlexLogic™ operands. The element incorporates an adaptive
disturbance detector. This function does not trigger on power swings, but is capable of
detecting faster disturbances – faults in particular – that may occur during power swings.
Operation of this dedicated disturbance detector is signaled via the
POWER SWING 50DD
operand.
The power swing detect element asserts two operands intended for blocking selected
protection elements on power swings:
POWER SWING BLOCK
is a traditional signal that is
safely asserted for the entire duration of the power swing, and
POWER SWING UN/BLOCK
is
established in the same way, but resets when an extra disturbance is detected during the
power swing. The
POWER SWING UN/BLOCK
operand may be used for blocking selected
protection elements if the intent is to respond to faults during power swing conditions.
Different protection elements respond differently to power swings. If tripping is required for
faults during power swing conditions, some elements may be blocked permanently (using
the
POWER SWING BLOCK
operand), and others may be blocked and dynamically unblocked
upon fault detection (using the
POWER SWING UN/BLOCK
operand).
The operating characteristic and logic figures should be viewed along with the following
discussion to develop an understanding of the operation of the element.
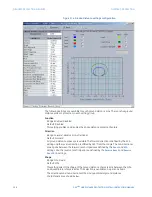
The power swing detect element has a three-step or two-step mode operation sequence.
•
In three-step operation, the power swing blocking sequence essentially times the
passage of the locus of the positive-sequence impedance between the outer and the
middle characteristic boundaries. If the locus enters the outer characteristic
(indicated by the
POWER SWING OUTER
FlexLogic™ operand) but stays outside the
middle characteristic (indicated by the
POWER SWING MIDDLE
FlexLogic™ operand) for
an interval longer than the
Pickup Delay 1
setting, the power swing blocking signal
(
POWER SWING BLOCK
FlexLogic™ operand) is established and sealed-in. The blocking
signal resets when the locus leaves the outer characteristic, but not sooner than the
time specified by the
Reset Delay 1
setting.
•
The two-step operation sequence is identical to the three-step sequence, except that
the outer and inner characteristics that are used to time the power swing locus.
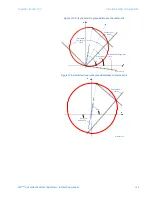
The out-of-step tripping feature operates as follows for three-step and two-step power
swing detection modes.
For three-step operation, the out-of-step trip sequence identifies unstable power swings
by determining if the impedance locus spends a finite time between the outer and middle
characteristics and then a finite time between the middle and inner characteristics. The
9B!YROWV
581
=HURVHTXHQFHGLUHFWLRQDO
$&'5
$1'
25
&RRUGLQDWLQJWLPH
3LFNXSF\FOH5HVHWF\FOH
6RXUFH
6(77,1*
9B
,B
23(132/(23
)/(;/2*,&23(5$1'
7SNS
7UVW
*1'',67=6831
)/(;/2*,&23(5$1'
7,0(5
&+$5$&7(5,67,&