D90
PLUS
LINE DISTANCE PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
167
D90
Plus
Line Distance Protection System
Chapter 7: Protection
Protection
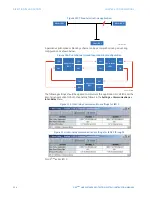
This section describes how to program the D90
Plus
protection features.
Protection overview
The D90
Plus
is intended for use on transmission lines of any voltage level, without, with, and
in the vicinity of series compensation, in three-pole and single-pole tripping applications.
The distance elements are optimized to provide good measurement accuracy with a sub-
cycle operating time, even when used with capacitive voltage transformers, and can be
supervised by detection of power swings. The primary function of the relay consists of five
phase and ground distance zones of protection, either mho or quadrilateral as per user
selection, with built-in logic for the six common pilot aided schemes. The relay also
provides directional ground overcurrent elements, which are commonly used as part of an
overall line protection system.
The phase distance zones can be configured to work with voltages and currents fed from
VTs and CTs located independently from one another on either side of a three-phase
power transformer. The relay compensates accordingly to preserve reach and correct
target information regardless of the location and type of fault. This feature allows backup
protection applications for generators and power transformers.
A close-into-fault, or switch-on-to-fault, function is performed by the line pickup element.
Out-of-step tripping, three-pole and single-pole dual-breaker autoreclosing, load
encroachment, and many other functions are also available. In addition, overcurrent and
undervoltage protection, fault diagnostics, power metering, and RTU functions are
provided. The D90
Plus
provides phase, neutral, and ground time overcurrent protection. The
time overcurrent functions can be programmed with multiple curve shapes or
FlexCurves™ for optimum coordination.
Introduction to protection elements
In the design of the UR
Plus
-series protection system, the term
element
is used to describe a
feature based around a comparator. The comparator is provided with an input (or set of
inputs) that is tested against a programmed setting (or group of settings) to determine if
the input is within the defined range that will set the output to logic 1, also referred to as
setting the flag
. A single comparator may make multiple tests and provide multiple outputs.
For example, the time overcurrent comparator sets a pickup flag when the current input is