CHAPTER 7: PROTECTION
GROUPED PROTECTION ELEMENTS
D90
PLUS
LINE DISTANCE PROTECTION SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
245
The positive-sequence restraint is removed for low currents. If the positive-sequence
current is less than 0.8 pu, the restraint is removed by changing the constant
K
to zero. This
facilitates better response to high-resistance faults when the unbalance is very small and
there is no danger of excessive CT errors as the current is low.
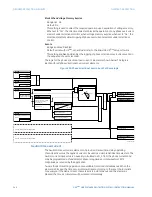
The directional unit uses the zero-sequence current (I_0) or ground current (IG) for fault
direction discrimination and may be programmed to use either zero-sequence voltage
(“Calculated V0” or “Measured VX”), ground current (IG), or both for polarizing. The phasors
for the neutral directional overcurrent element directional unit are described below, where
V_0 is the zero-sequence voltage, I_0 is the zero-sequence current, ECA is the element
characteristic angle, and IG is the ground current, and:
Eq. 28
Eq. 29
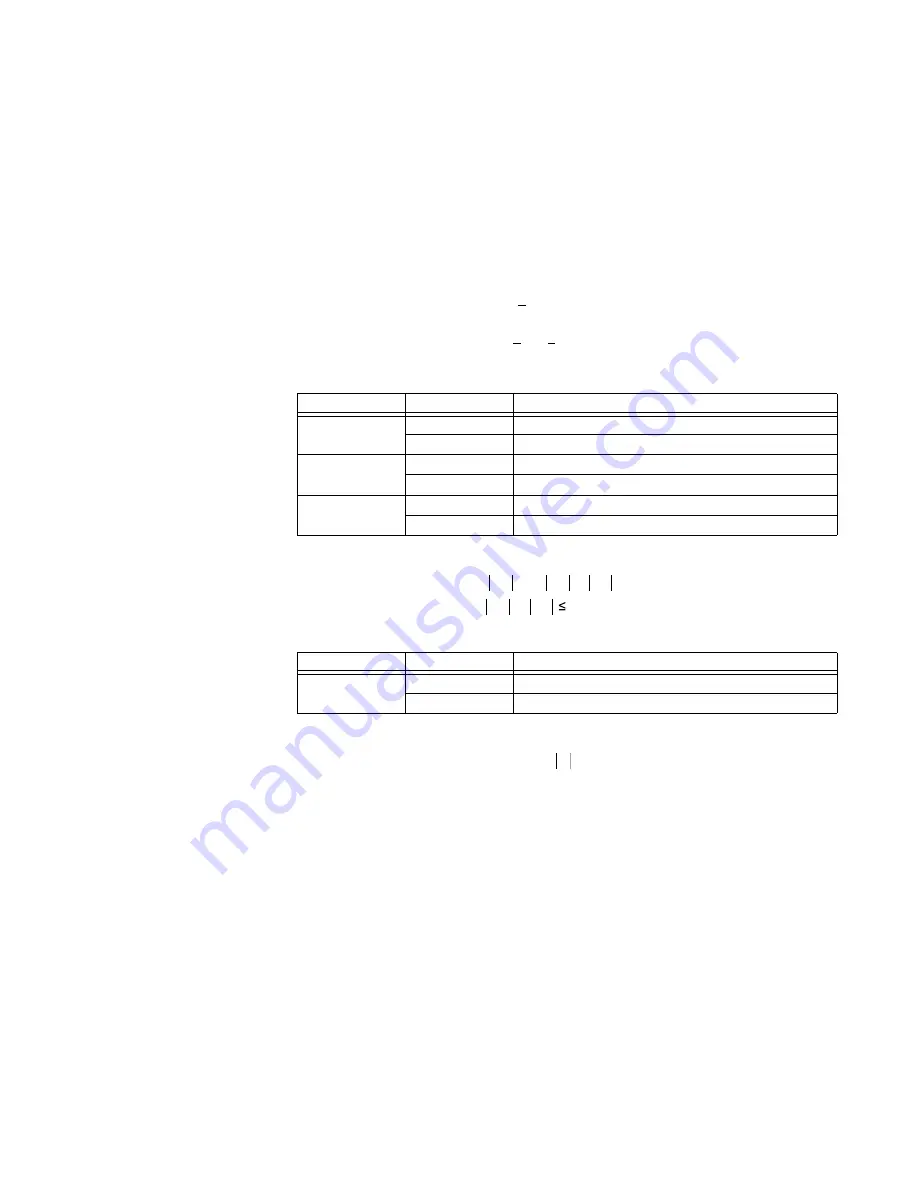
Table 14: Phasors for “Calculated 3I_0” configuration
The operating current for overcurrent unit for the “Calculated 3I_0” configuration is:
Eq. 30
Table 15: Phasors for “Measured IG” configuration
The operating current for overcurrent unit for the “Measured IG” configuration is:
Eq. 31
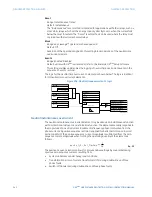
When the
Polarizing Voltage
setting is programmed as “Measured VX”, one-third of this
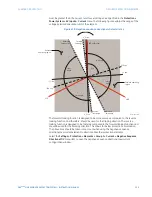
voltage is used in place of V_0. The following figure explains the voltage polarized
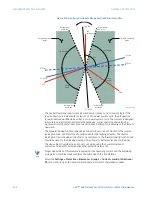
directional unit of the element and illustrates the phase angle comparator characteristics
for a phase A to ground fault, with the element characteristic angle equal to 90° (center
line of operating characteristic), forward limit angle equal to 80° (the ± angular limit with
the ECA for operation), and reverse limit angle equal to 80° (the ± angular limit with the ECA
for operation).
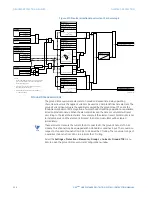
Polarizing mode
Direction
Compared phasors
Voltage
Forward
–V_0 + Z_offset × I_0 and I_0 × 1
∠
ECA
Reverse
–V_0 + Z_offset × –I_0 and I_0 × 1
∠
ECA
Current
Forward
IG and I_0
Reverse
IG and –I_0
Dual
Forward
–V_0 + Z_offset × I_0 and I_0 × 1
∠
ECA or IG and I_0
Reverse
–V_0 + Z_offset × I_0 and I_0 × 1
∠
ECA or IG and –I_0
Polarizing mode
Direction
Compared phasors
Voltage
Forward
–V_0 + Z_offset × IG/3 and IG × 1
∠
ECA
Reverse
–V_0 + Z_offset × –IG/3 and –IG × 1
∠
ECA
&*
%*
$*
9
9
9
9
B
&
%
$
1
,
,
,
,
,
B
SX
B
LI
B
SX
B
LI
B
B
î
!
î
²
î
,
,
,
,
,
.
,
,
RS
RS
,*
,
RS