February 2013
8-38
ColorQube® 9303 Family
Principles of Operation
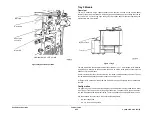
Feeder
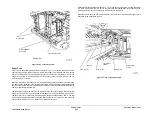
The feed mechanism is a top friction feeder with semi-active retard. The feeder consists of an
input gate, nudger roll, feed roll, and a retard roll. The nudger, feed and retard rolls are Cus-
tomer Replaceable Units, (CRUs).
The nudger and feed rolls are driven by the DADH feed motor, MOT005-074, through an elec-
tromechanical friction feed clutch, CL005-062. A DADH nudger motor, MOT005-098, is oper-
ated to lower the nudger roll to contact the top sheet of the stack while simultaneously
disengaging the input gates until the first sheet is acquired from the stack. The input gates are
prevented from returning to their reset position until after the last sheet is fed off the stack.
The clutch de-energizes and the DADH nudger motor returns to the nudger roll up position,
when the lead edge of the document arrives at the DADH feed sensor, Q005-204, except in the
case of the first sheet, when both the clutch remains energized and the DADH nudger motor
remains at its current position, until the LE of the sheet arrives at the DADH TAR sensor, Q005-
096. When the document is called for, this event being triggered by the TE departure of the
previous sheet from the takeaway sensor, the clutch is re-energized and the (DADH nudger
motor returns to the nudger roll down position), until the LE reaches the take away sensor.
The semi-active retard roll consists of an elastomer-covered outer member and a stationary
inner member, with a wrap spring slip clutch between them. Spring loaded against the feed roll
to provide the required force, the retard rotates during feed and the wrap spring winds until it’s
slip torque is developed, at which point it overruns in the feed direction. The device maintains
this condition when a single sheet is in the pinch. When two sheets are fed into the nip, the tor-
sion spring unwinds, thus turning the retard roll in the reverse direction and driving the multi-fed
sheet backwards out of the feed/retard nip and towards the stack. In the case of singly fed
sheets, the semi-active retard roll is driven in the direction of feed by the motion of the drive
roll.
De-skew - Takeaway Rolls (TAR)
Document de-skew and lead edge registration for both simplex and duplex paths are accom-
plished by a combination of the following methods:
•
Document lead edge buckle at TAR - By driving the document with the feed roll assembly
at a higher speed than the TAR rolls, a buckle is formed. This allows the document lead
edge to help correct any skew that exists during this first stage of feeding.
•
Width Guides - The position of the width guides relative to the edges of the stack is the
most important factor in the control of skew within the DADH. Easy movement of the
guides is a requirement to ensure customers can easily obtain a “tight” stack.
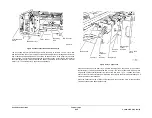
Constant Velocity Transport (CVT)
The document is scanned as it passes over the CVT glass with the scan carriage parked
beneath. During this time the document is driven by one large diameter CVT roll and is in con-
tact with a minimum of 2 double nip rolls. The DADH CVT sensor, Q005-097, positioned before
the scan zone, detects the document’s arrival to begin the scan. This sensor also detects the
document’s departure for end of scan or jam detection. Image registration correction occurs at
the image processing PWB.
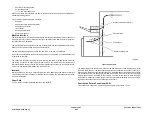
Duplex Inverter
The inverter function is provided by a reversing roll nip. The elements include the nip, a duplex
gate, the feed motor, MOT005-074, and the DADH duplex solenoid, SOL005-100. The docu-
ment is inverted after the trail edge is sensed by the DADH exit sensor, Q005-209. By control-
ling the time beyond the DADH exit sensor, the document is stopped by the DADH feed motor,
Q005-074, after the trail edge passes the duplex gate, but prior to leaving the nip. At this time,
the DADH feed motor is reversed. The DADH feed motor continues to drive the document
along the duplex path, so that it re-enters the original input path. The document lead edge
arriving at the DADH CVT sensor causes the DADH duplex solenoid, SOL005-100, to open.
The DADH CVT Motor continues to feed the document past the scanning position, as in sim-
plex mode. After side 2 is scanned, the document is re-inverted, prior to being re-stacked for
correct document orientation. This is accomplished by sending the document through the
duplex path at maximum speed, without scanning, to the exit.
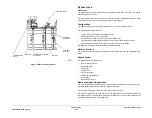
Re-stack
The document re-stack function is provided by passing the documents through the inverter nip
into a catch tray above the manual platen cover. The profile of the exit tray together with a re-
stack arm ensures an orderly document re-stack.
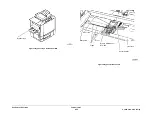
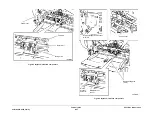
Drives
Refer to
Figure 2
. The DADH is driven by two 24V DC stepper motors. The DADH CVT motor,
MOT005-099, drives the CVT roll by means of a synchronous belt. The DADH feed motor,
Q005-074, provides drive to the feed assembly rolls, TAR assembly and exit roll. The feed
shaft is isolated from the motor by the DADH feed clutch, CL005-062. The DADH feed motor,
Q005-074, drives the exit roll assembly in both forward (exit) and reverse (duplex) directions.
In addition, the DADH duplex solenoid SOL005-100, is required to open the exit / duplex nip
during document inversion in duplex mode. This is necessary because the document is
wrapped around the CVT roll and both the leading and trailing edges are passing through the
exit / duplex nip.
Summary of Contents for ColorQube 9303 Series
Page 1: ...Xerox ColorQube 9303 Family Service Manual 708P90290 February 2013...
Page 4: ...February 2013 ii ColorQube 9303 Family Introduction...
Page 18: ...February 2013 1 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Service Call Procedures...
Page 92: ...February 2013 2 68 ColorQube 9303 Family 05F Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 104: ...February 2013 2 80 ColorQube 9303 Family 12 701 00 65 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 200: ...February 2013 2 176 ColorQube 9303 Family 12N 171 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 292: ...February 2013 2 268 ColorQube 9303 Family 16D Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 320: ...February 2013 2 296 ColorQube 9303 Family 42 504 00 42 505 00 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 500: ...February 2013 2 476 ColorQube 9303 Family 94B Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 648: ...February 2013 3 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Image Quality...
Page 653: ...February 2013 3 7 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 1 IQ defects 1...
Page 654: ...February 2013 3 8 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 2 IQ defects 2...
Page 655: ...February 2013 3 9 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 3 IQ defects 3...
Page 656: ...February 2013 3 10 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 4 IQ defects 4...
Page 657: ...February 2013 3 11 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 5 IQ defects 5...
Page 658: ...February 2013 3 12 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 6 IQ defects 6...
Page 660: ...February 2013 3 14 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 9 IQ defects 9...
Page 661: ...February 2013 3 15 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 10 IQ defects 10...
Page 662: ...February 2013 3 16 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 11 IQ defects 11...
Page 663: ...February 2013 3 17 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 12 IQ defects 12...
Page 664: ...February 2013 3 18 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 13 IQ defects 13...
Page 728: ...February 2013 3 82 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 29 IQ 30 Image Quality...
Page 736: ...February 2013 3 90 ColorQube 9303 Family TP 15 Image Quality Figure 2 Media path test pages...
Page 758: ...February 2013 3 112 ColorQube 9303 Family IQS 7 IQS 8 Image Quality...
Page 778: ...February 2013 4 20 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 1 9 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 794: ...February 2013 4 36 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 3 10 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1144: ...February 2013 4 386 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 94 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1176: ...February 2013 4 418 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 62 3 ADJ 62 4 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1182: ...February 2013 4 424 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 75 3 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1184: ...February 2013 4 426 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 82 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1186: ...February 2013 4 428 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 91 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1552: ...February 2013 6 260 ColorQube 9303 Family dC140 General Procedures Information...
Page 1576: ...February 2013 6 284 ColorQube 9303 Family dC640 General Procedures Information...
Page 1578: ...February 2013 6 286 ColorQube 9303 Family dC708 dC715 General Procedures Information...
Page 1600: ...February 2013 7 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Wiring Data...
Page 1696: ...February 2013 8 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Principles of Operation...
Page 1808: ...February 2013 8 114 ColorQube 9303 Family Principles of Operation...
Page 1809: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1810: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1811: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1812: ...XEROX EUROPE...