February 2013
8-54
ColorQube® 9303 Family
Principles of Operation
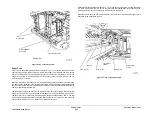
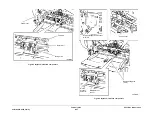
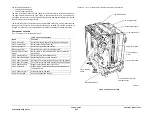
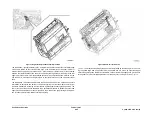
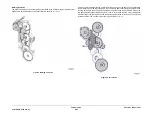
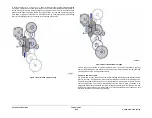
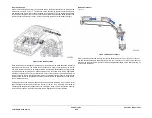
Figure 3 SAR Feeders
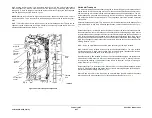
A separation nip is formed by the nudger roll and a retard roll which is not shown. The nudger
roll is sprung and rests on the stack to feed the top sheet. If the stack is not within the feeding
position, the stack height sensor triggers the elevator to rise to the feeding position.
The SAR mechanism substantially reduces the incidence of multi-sheet feeding.
Because the speed of the sheet is slightly reduced by the effect of the retard roll, when the
leading edge reaches the paper feed sensor, the feeding speed is controlled to ensure the
sheet reaches the hand-over point in the IME within the allowable time window.
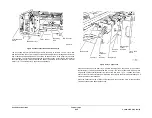
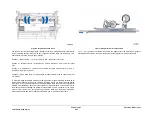
Paper Feed and Retard Rolls
Tray 5 feed roll / retard rolls are accessible from tray door access and by sliding the tray away
from the IME. The host controller monitors their usage, recording the sheet feed count in the
NVM, along with their life expectancy, to inform the customer service engineer (CSE) when
their end of life occurs.
Paper Present Detection
When the tray is less than 10% full, and the tray is in the up position, the software checks after
each sheet feed for an ‘out of paper’ condition. The tray 5 empty sensor is a reflective type and
is situated directly over a hole in the paper tray, normally covered by paper. There will be no
reflection when the last sheet has been fed, and an ‘out of paper’ condition will be declared.
The GUI instructs the operator to refill the tray and further paper feeds will be inhibited. In a
normal tray 5 module, with A4 or 8.5 x 11 inch LEF stock and a door present, the tray is auto-
matically lowered. If there is no door, and a paper kit is installed, the tray is lowered when the
manual push button is pressed and released. The out of paper status is raised to the host con-
troller. The tray will elevate again when the door is closed after refilling the tray.
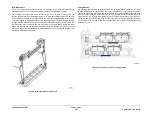
Tray Height Sensor
The machine keeps track of the tray height, based on the distance travelled from the start of lift.
A software height counter is zeroed when the tray starts to rise and the stack down sensor
goes low. As the tray rises, the elevator motor encoder sensor increments the height counter
for each pulse sensed from the vertical encoder track. When the tray reaches its upper posi-
tion, and the stack height sensor is actuated by the nudger roll, the value of the height counter
is passed to the IME, as a percentage of the tray 5 paper stock left on the tray. The IME holds
the stack height value as 0%, 5%, 10% and at 10% intervals up to 100% full, and this is avail-
able for display to the remote web UI. The counter value is updated whenever the elevator
motor encoder sensor, changes state, and is saved to the NVM each time. If an expected
change in state of the height encoder does not occur, when the elevator motor is operating, a
fault condition is declared.
Stack Height when Feeding
The stack height sensor maintains the stack height by triggering activity of the elevator motor.
When a change in the condition of this sensor is detected, there is a de-bounce delay of 33
milli-seconds to allow the condition to settle, and if the change in the state of the sensor is con-
firmed, the elevator motor raises the tray, after the paper leading edge has passed the trans-
port rolls. The amount of movement is determined by the current position of the tray. This
position is used to read the ‘motor-on time’ from a look-up table, held within the machine.
Tray Overload
If the stack height sensor indicates the tray is at the feeding position, and at the same time the
stack down sensor detects the tray in the fully lowered position, the ‘overloaded tray’ status is
raised. The elevator motor movement is inhibited and an error is raised. This error condition is
maintained until the conditions producing it no longer apply.
Elevator Motor Stop
The elevator motor is never stopped by simply removing the power and allowing it to coast to a
stop. Whenever the motor is stopped, it is dynamically, actively braked to a stand still.
Elevator Upper and Lower Positions
The commonly used tray control sensors are:
•
The stack height sensor
•
The stack down sensor
•
The paper empty sensor
•
The elevator motor encoder sensor.
Tray elevated in the up and
ready to feed position
Nudger roll
Stack height
sensor
Nudger roll
Note: Retard roll and other parts of
SAR assembly not shown
Stack height
sensor
Summary of Contents for ColorQube 9303 Series
Page 1: ...Xerox ColorQube 9303 Family Service Manual 708P90290 February 2013...
Page 4: ...February 2013 ii ColorQube 9303 Family Introduction...
Page 18: ...February 2013 1 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Service Call Procedures...
Page 92: ...February 2013 2 68 ColorQube 9303 Family 05F Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 104: ...February 2013 2 80 ColorQube 9303 Family 12 701 00 65 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 200: ...February 2013 2 176 ColorQube 9303 Family 12N 171 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 292: ...February 2013 2 268 ColorQube 9303 Family 16D Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 320: ...February 2013 2 296 ColorQube 9303 Family 42 504 00 42 505 00 Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 500: ...February 2013 2 476 ColorQube 9303 Family 94B Status Indicator RAPs...
Page 648: ...February 2013 3 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Image Quality...
Page 653: ...February 2013 3 7 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 1 IQ defects 1...
Page 654: ...February 2013 3 8 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 2 IQ defects 2...
Page 655: ...February 2013 3 9 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 3 IQ defects 3...
Page 656: ...February 2013 3 10 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 4 IQ defects 4...
Page 657: ...February 2013 3 11 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 5 IQ defects 5...
Page 658: ...February 2013 3 12 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 6 IQ defects 6...
Page 660: ...February 2013 3 14 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 9 IQ defects 9...
Page 661: ...February 2013 3 15 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 10 IQ defects 10...
Page 662: ...February 2013 3 16 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 11 IQ defects 11...
Page 663: ...February 2013 3 17 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 12 IQ defects 12...
Page 664: ...February 2013 3 18 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 1 Image Quality Figure 13 IQ defects 13...
Page 728: ...February 2013 3 82 ColorQube 9303 Family IQ 29 IQ 30 Image Quality...
Page 736: ...February 2013 3 90 ColorQube 9303 Family TP 15 Image Quality Figure 2 Media path test pages...
Page 758: ...February 2013 3 112 ColorQube 9303 Family IQS 7 IQS 8 Image Quality...
Page 778: ...February 2013 4 20 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 1 9 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 794: ...February 2013 4 36 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 3 10 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1144: ...February 2013 4 386 ColorQube 9303 Family REP 94 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1176: ...February 2013 4 418 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 62 3 ADJ 62 4 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1182: ...February 2013 4 424 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 75 3 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1184: ...February 2013 4 426 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 82 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1186: ...February 2013 4 428 ColorQube 9303 Family ADJ 91 1 Repairs Adjustments...
Page 1552: ...February 2013 6 260 ColorQube 9303 Family dC140 General Procedures Information...
Page 1576: ...February 2013 6 284 ColorQube 9303 Family dC640 General Procedures Information...
Page 1578: ...February 2013 6 286 ColorQube 9303 Family dC708 dC715 General Procedures Information...
Page 1600: ...February 2013 7 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Wiring Data...
Page 1696: ...February 2013 8 2 ColorQube 9303 Family Principles of Operation...
Page 1808: ...February 2013 8 114 ColorQube 9303 Family Principles of Operation...
Page 1809: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1810: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1811: ...XEROX EUROPE...
Page 1812: ...XEROX EUROPE...