16-12
MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Hardware Interface
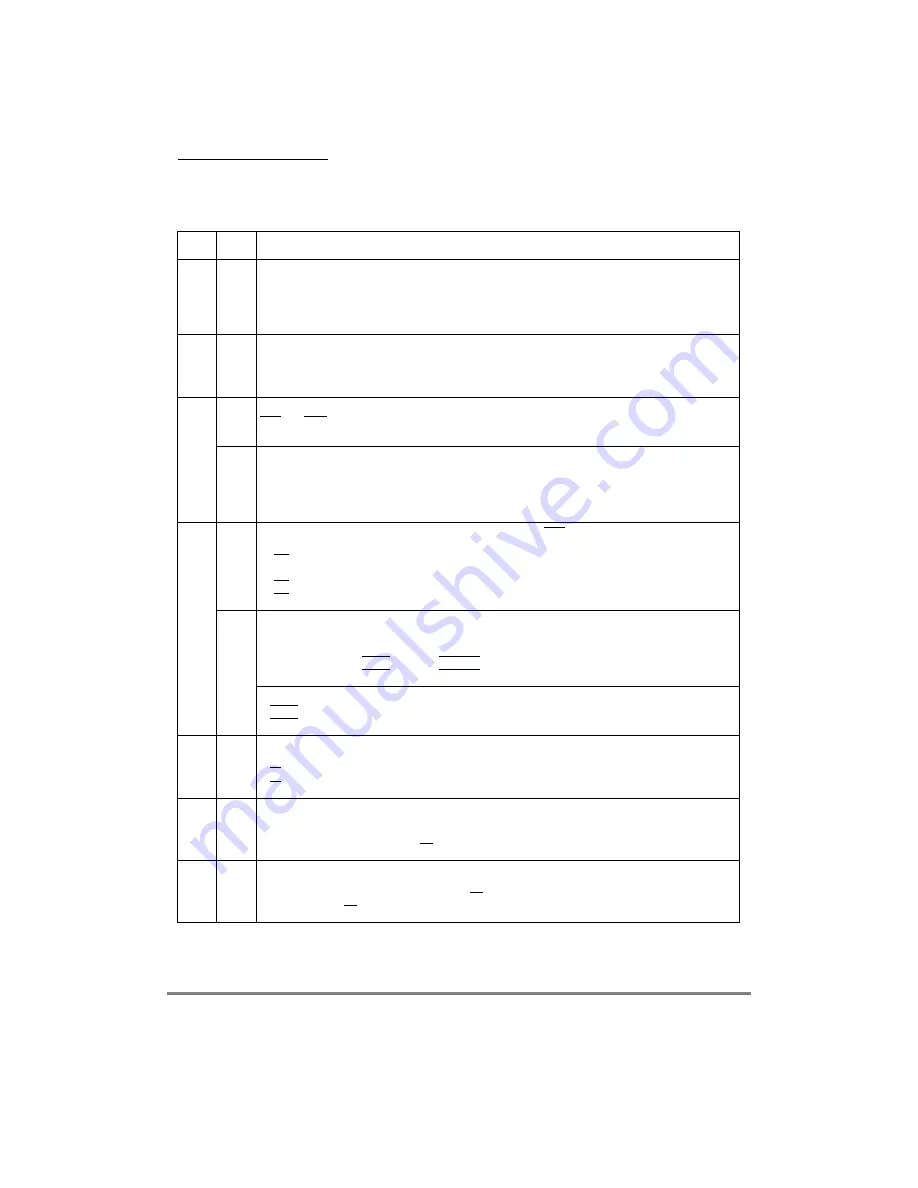
Table 16-4 describes ORx Þelds.
Table 16-4. ORx Field Descriptions
Bits
Name
Description
0Ð16
AM
Address mask. This read/write Þeld independently masks bits A[0Ð16] on the address bus so
external devices of different size address ranges can be used. AM bits can be set or cleared in any
order, allowing a resource to reside in more than one area of the address map.
0 The corresponding address bit is masked.
1 The corresponding address bit is used in address pin comparison.
17Ð19 ATM
Address type mask. Masks certain bits in address type, AT[0Ð2], allowing more than one address
space type to be assigned to a chip-select. Any set bit causes the corresponding address type code
bits to be used as part of the address comparison. Any cleared bit masks the corresponding address
type code bit. If address-type protection is not desired, then ATM should be cleared.
20
CSNT
CSNT (chip-select negation time). Used for the GPCM with ACS and TRLX to control negation of
CSx and WEx during an external memory write access. Provides extended address/data hold time
for slower memories and peripherals. See Table 16-11.
SAM
Start address multiplex. Used for a UPM to determine the address output on the Þrst cycle of an
external memory access. Should be set only if address multiplexing is to be performed internally.
0 Address pins are not multiplexed internally.
1 Address pins reßect the address requested by the internal master multiplexed according to the
setting of MAMR[AMA] (UPMA) or MBMR[AMB] (UPMB).
21Ð22 ACS
ACS (address to chip-select setup). Lets the GPCM control CSx assertion relative to address lines
valid.
00 CS is output at the same time as the address lines.
01 Reserved.
10 CS is output a quarter of a clock after the address lines.
11 CS is output half a clock after the address lines.
G5LA,
G5LS
G5LA and G5LS (general-purpose line 5 A/line 5 start) are used for the UPM to determine how the
internal controls and timing generator signal outputs GPL5 when a UPM handles a memory access.
G5LA (valid only for UPMB):
0 Output the internal GPL5 signal on GPL_B5.
1 Output the internal GPL5 signal on GPL_A5.
G5LS (valid for UPMA or UPMB)
0 GPL5 is driven low on the falling edge of GCLK1_50 in the Þrst clock cycle of a memory access.
1 GPL5 is driven high on the falling edge of GCLK1_50 in the Þrst clock cycle of a memory access.
23
BIH
Burst inhibit. Determines whether this memory bank supports burst accesses. If the machine
selected to handle this access is the GPCM, BIH must be set.
0 BI is negated. The bank supports burst accesses.
1 BI is asserted. The bank does not support burst accesses.
24Ð27 SCY
Select cycle length (GPCM only). Binary representation of the number of wait states inserted in the
cycle when the GPCM handles an external memory access (0000 = 0 clock cycle, 0001 = 1 clock
cycle, É, 1111 = 15 clock cycle). Total cycle length is also affected by TRLX. See Table 16-11 for the
total number of cycles. If external TA response is selected (SETA = 1), SCY is not used.
28
SETA
Select external transfer acknowledge (GPCM only).
0 Internal or external transfer acknowledge can acknowledge this access, whichever comes Þrst.
1 The memory controller does not generate TA for this bank; instead the peripheral must generate it
on the external TA signal.
Summary of Contents for MPC860 PowerQUICC
Page 3: ...MPC860UM AD 07 98 REV 1 MPC860 PowerQUICC ª UserÕs Manual ...
Page 36: ...xxxvi MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA CONTENTS Paragraph Number Title Page Number ...
Page 78: ...I iv MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 88: ...1 10 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 114: ...3 16 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 226: ...8 32 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II PowerPC Microprocessor Module ...
Page 262: ...9 36 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II PowerPC Microprocessor Module ...
Page 274: ...III iv MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III Configuration ...
Page 320: ...12 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III Configuration ...
Page 325: ...MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface IV v Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 326: ...IV vi MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 352: ...13 26 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 394: ...14 42 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 426: ...15 32 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 530: ...17 26 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 632: ...21 44 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 660: ...22 28 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 708: ...24 24 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 748: ...27 20 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 846: ...31 20 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 914: ...35 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 948: ...36 34 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 998: ...37 48 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part VI Debug and Test ...
Page 1016: ...A 10 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1024: ...B 8 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1030: ...C 6 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1086: ...Glossary 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 1106: ......
















































